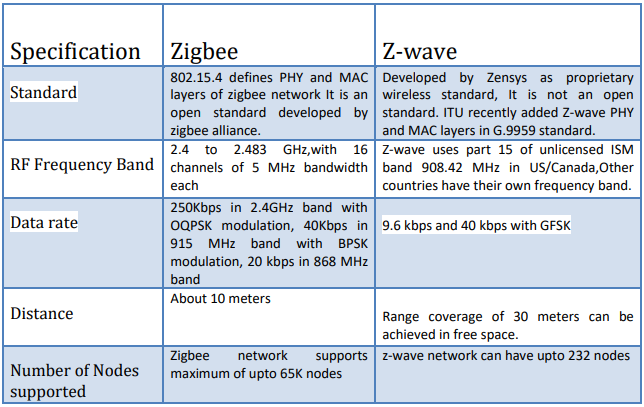
When it comes to making your home smarter, choosing the right technology can feel overwhelming. You’ve probably heard about Zigbee and Z-Wave, but what exactly sets them apart?
Understanding these differences is key to creating a seamless, reliable smart home system that fits your needs. You’ll discover how Zigbee and Z-Wave work, which one suits your devices better, and how to avoid common pitfalls. Keep reading to make confident choices that bring convenience and security right to your doorstep.
Smart Home Protocols
Smart homes use special protocols to connect devices. These protocols help devices talk to each other.
Zigbee and Z-Wave are two popular protocols. They help control lights, locks, and sensors in your home.
What Is Zigbee?
Zigbee is a wireless protocol for smart devices. It works on low power and uses a mesh network.
This protocol connects many devices quickly. It uses the 2.4 GHz frequency band worldwide.
- Supports thousands of devices in one network
- Works well in busy Wi-Fi areas
- Good for smart lights and sensors
- Open standard used by many brands
What Is Z-wave?
Z-Wave is a wireless protocol for home automation. It also uses a mesh network to connect devices.
Z-Wave works on a lower frequency than Zigbee. This helps it avoid Wi-Fi interference.
- Supports up to 232 devices per network
- Uses 800-900 MHz frequency bands
- Good range and reliability for smart locks
- Proprietary but widely supported
Frequency Bands
Zigbee and Z-Wave use different radio frequencies to connect smart devices. These frequency bands affect range and interference.
Choosing the right frequency helps devices work better in your home or office.
Zigbee Frequency Range
Zigbee mainly uses the 2.4 GHz frequency band worldwide. This is the same band used by Wi-Fi and Bluetooth.
The 2.4 GHz band allows Zigbee devices to send data quickly but may face interference from other devices.
- Frequency: 2.4 GHz globally
- Data speed: Up to 250 kbps
- Range: About 10-20 meters indoors
- Common interference: Wi-Fi, Bluetooth
Z-wave Frequency Range
Z-Wave uses lower frequency bands between 800 MHz and 900 MHz. The exact band varies by country.
Lower frequencies help Z-Wave devices have better range and less interference from Wi-Fi signals.
- Frequency: 800-900 MHz (varies by region)
- Data speed: Up to 100 kbps
- Range: About 30-50 meters indoors
- Common interference: Less from Wi-Fi
Network Range And Coverage
Network range and coverage are key factors in choosing smart home devices. These features affect how well devices communicate over distance.
Zigbee and Z-Wave use different technologies that impact their network range. Understanding these differences helps pick the right option.
Zigbee Range Capabilities
Zigbee devices usually have a range of about 10 to 20 meters indoors. The signal can travel further outdoors, up to 100 meters.
Zigbee creates a mesh network. This means devices pass signals to each other to increase coverage.
- Indoor range: 10-20 meters
- Outdoor range: Up to 100 meters
- Mesh network extends coverage
Z-wave Range Capabilities
Z-Wave devices have a longer range, about 30 meters indoors. Outdoors, the signal can reach up to 150 meters.
Z-Wave also uses a mesh network. Each device can relay signals to others, boosting overall coverage.
- Indoor range: Around 30 meters
- Outdoor range: Up to 150 meters
- Mesh network improves signal reach
Device Compatibility
Zigbee and Z-Wave are popular smart home technologies. They help devices talk to each other.
Device compatibility means if devices work together well. This depends on the technology they use.
Zigbee Device Ecosystem
Zigbee supports many devices from many brands. It uses an open standard anyone can join.
Many lights, sensors, and switches use Zigbee. Devices from different makers can usually work together.
- Works with brands like Philips Hue, Samsung SmartThings, and IKEA
- Supports thousands of devices
- Uses IEEE 802.15.4 radio standard
- Allows multiple vendors to create compatible devices
Z-wave Device Ecosystem
Z-Wave devices focus on home automation. It is a closed standard controlled by one company.
Z-Wave devices from different brands often work well together. There is strong focus on interoperability.
- Includes brands like Aeotec, Fibaro, and Schlage
- Supports over 3,000 certified devices
- Uses a proprietary radio frequency
- Ensures device compatibility through certification
Power Consumption
Power consumption is important for smart home devices. It affects battery life and device performance.
Zigbee and Z-Wave use low energy to communicate. Their power use differs based on technology and design.
Zigbee Battery Life
Zigbee devices use very little power. They can run for months or years on small batteries.
Zigbee uses sleep modes to save battery. It wakes only to send or receive signals.
- Low power usage during sleep
- Short bursts of activity
- Ideal for battery-powered sensors
Z-wave Battery Life
Z-Wave devices also use low power. They focus on efficient communication to extend battery life.
Z-Wave often uses less power per message. This helps devices last longer without charging.
- Efficient message sending
- Long battery life for sensors
- Good for devices needing long operation

Credit: marcusyatim.medium.com
Security Features
Zigbee and Z-Wave are popular smart home protocols. Both focus on keeping your devices safe.
We will look at their security features and how they protect your network.
Zigbee Security Measures
Zigbee uses strong encryption to protect data. It applies AES-128 encryption for all communication.
Zigbee devices join the network using a trust center. The trust center controls device access and keys.
- Uses AES-128 bit encryption for security
- Trust center manages device authentication
- Supports network key updates to reduce risks
- Encrypts data between devices and the hub
Z-wave Security Measures
Z-Wave uses AES-128 encryption as well. It secures messages between devices in the network.
Z-Wave introduced S2 security framework for better protection. It improves device authentication and privacy.
- Employs AES-128 encryption for all data
- S2 security framework for enhanced safety
- Uses unique keys for each device
- Protects against eavesdropping and replay attacks
Network Topology
Network topology is how devices connect and communicate in a smart home system. It shapes the system’s speed, range, and reliability.
Zigbee and Z-Wave use mesh networks but differ in their setup and device roles. Understanding these differences helps choose the right system.
Zigbee Mesh Networking
Zigbee creates a mesh where many devices connect directly or through others. Each device can send and receive data.
This setup lets signals hop between devices. It extends range and improves network strength by adding more devices.
- Devices act as routers and end nodes
- Supports thousands of devices in one network
- Self-healing: routes change if a device fails
- Works on 2.4 GHz frequency worldwide
Z-wave Mesh Networking
Z-Wave also uses a mesh network but limits how many devices act as repeaters. Only certain devices forward signals.
The network supports up to 232 devices. It uses low-frequency bands, which helps reduce interference.
- Repeater role limited to mains-powered devices
- Supports fewer devices than Zigbee
- Self-healing network with automatic routing
- Operates around 900 MHz frequency

Credit: www.vesternet.com
Interoperability
Interoperability means devices from different brands work well together. It is important for smart home systems.
Zigbee and Z-Wave both offer cross-brand support. This lets users mix devices from many makers.
Zigbee Cross-brand Support
Zigbee is an open standard. Many brands use it in their smart home products.
Zigbee devices can communicate with each other if they follow the same profile. This profile sets rules for device behavior.
- Zigbee devices use a common application profile.
- Brands like Philips, Samsung, and IKEA support Zigbee.
- Users can mix bulbs, sensors, and switches from different brands.
- Some devices may need a Zigbee hub to connect.
Z-wave Cross-brand Support
Z-Wave is a closed standard managed by the Z-Wave Alliance. Only licensed brands can make Z-Wave products.
All Z-Wave devices follow strict rules to ensure they work together. This creates strong cross-brand support.
- Z-Wave devices use a common protocol for communication.
- Brands like Aeotec, Fibaro, and GE make Z-Wave products.
- Devices from different brands connect easily in one network.
- Z-Wave hubs control all devices without compatibility issues.
Setup And Ease Of Use
Zigbee and Z-Wave are popular smart home systems. They connect devices like lights and locks.
Both systems need a hub to control devices. This guide explains their setup and ease of use.
Zigbee Installation
Zigbee devices connect through a hub or gateway. Many hubs support Zigbee and are easy to find.
To install, plug in your Zigbee hub and connect it to Wi-Fi. Use the app to add devices by following simple steps.
- Plug in Zigbee hub and connect to Wi-Fi
- Open the app and create an account
- Put devices into pairing mode
- Add devices through the app
- Control devices from your phone
Z-wave Installation
Z-Wave also uses a hub to connect devices. It works on a different wireless frequency than Zigbee.
Setup involves plugging in the Z-Wave hub and linking it to your network. Use the app to include devices one by one.
- Connect the Z-Wave hub to power and internet
- Download and open the hub’s app
- Put devices into inclusion mode
- Add each device in the app
- Manage devices remotely

Credit: marcusyatim.medium.com
Cost Comparison
Zigbee and Z-Wave are popular smart home technologies. Their device prices affect your budget.
Knowing the price differences helps you choose the right system for your home.
Zigbee Device Pricing
Zigbee devices usually cost less than Z-Wave ones. This is because many brands make Zigbee products.
You can find Zigbee sensors, lights, and switches at affordable prices. This lowers your total setup cost.
- Basic Zigbee sensors start around $10 to $20
- Zigbee smart bulbs cost about $15 to $40
- Switches and plugs range from $20 to $50
Z-wave Device Pricing
Z-Wave devices tend to be pricier than Zigbee. The Z-Wave market has fewer manufacturers.
Prices reflect the higher cost of certification and technology used in Z-Wave devices.
- Basic Z-Wave sensors cost $20 to $40
- Z-Wave smart bulbs are usually $30 to $60
- Switches and plugs range from $30 to $70
Best Use Cases
Zigbee and Z-Wave are popular wireless technologies for smart home devices. They both help connect devices like lights, sensors, and locks. Choosing the right one depends on your needs.
This guide explains the best use cases for Zigbee and Z-Wave. It helps you decide which technology suits your smart home setup.
When To Choose Zigbee
Zigbee is great for homes with many devices from different brands. It supports many devices and works well in dense networks.
It uses the 2.4 GHz frequency, which offers fast communication but may face interference from Wi-Fi. Zigbee is good for smart bulbs, sensors, and switches.
- Large number of devices in one network
- Devices from multiple manufacturers
- Fast data transmission needed
- Smart lighting and sensors
- Integration with voice assistants
When To Choose Z-wave
Z-Wave works well in homes with fewer devices that need strong, reliable connections. It uses a lower frequency, which reduces interference.
Z-Wave is best for security devices like locks and alarms. Its mesh network extends range by passing signals through devices.
- Strong, reliable connections required
- Devices focused on security and safety
- Homes with moderate device numbers
- Lower risk of wireless interference
- Longer battery life for devices
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Main Difference Between Zigbee And Z-wave?
Zigbee uses the IEEE 802. 15. 4 standard, while Z-Wave operates on a proprietary protocol. Zigbee supports more devices and higher data rates, but Z-Wave offers better range and interoperability among smart home products.
Which Protocol Is Better For Smart Home Security?
Z-Wave is often preferred for smart home security due to its reliable mesh network and lower interference. Zigbee is also secure but can face interference from Wi-Fi devices operating on the same frequency.
How Do Zigbee And Z-wave Differ In Range And Coverage?
Z-Wave generally offers a longer range, up to 100 meters per hop, with a robust mesh network. Zigbee covers shorter distances per device but supports more nodes, enhancing overall network coverage.
Are Zigbee And Z-wave Compatible With Each Other?
No, Zigbee and Z-Wave are not natively compatible because they use different frequencies and protocols. However, some smart hubs support both, allowing integration of devices from both networks.
Conclusion
Choosing between Zigbee and Z-Wave depends on your smart home needs. Zigbee offers more device compatibility. Great for larger networks. Z-Wave provides excellent range and reliability. Ideal for smaller setups. Both have strengths that suit different preferences. Consider your existing devices.
Think about network size and your budget. Zigbee might fit better if you value flexibility. Z-Wave could be perfect for a robust connection. Assess your priorities. Make an informed choice for your home.
20 min read