Are you worried about keeping your data safe in the cloud? You’re not alone.
As more businesses and individuals store important information online, understanding cloud security storage becomes crucial. Imagine your files protected from hackers, data loss, and unauthorized access—all while being easy to access whenever you need them. You’ll discover simple but powerful ways to secure your cloud storage.
Keep reading, and take control of your digital safety today.
Cloud Storage Basics
Cloud storage lets you save data on the internet instead of your computer. It helps you access files anytime and anywhere.
Many businesses and people use cloud storage to keep their information safe and easy to reach.
Types Of Cloud Storage
There are different types of cloud storage to fit various needs. Each type works best for certain tasks.
- File Storage:Stores files like photos and documents. It is like a virtual hard drive.
- Block Storage:Divides data into blocks. Used by databases and servers for fast access.
- Object Storage:Stores data as objects with metadata. Good for large amounts of data like videos.
How Cloud Storage Works
Cloud storage saves your data on remote servers managed by providers. You send and get data through the internet.
Your data is stored in data centers. These centers use many servers to keep data safe and available.
- You upload files from your device to the cloud.
- The cloud provider stores data in secure data centers.
- You can download or share files anytime using the internet.
Benefits Of Cloud Storage
Cloud storage offers many advantages over traditional storage. It is flexible and easy to use.
- Accessibility:Access files from any device with internet.
- Cost-Effective:Pay only for the storage you use.
- Scalability:Increase or decrease storage space easily.
- Backup and Recovery:Your data is backed up and safe from loss.
- Collaboration:Share files and work with others in real time.
Common Cloud Security Threats
Cloud security storage faces many risks that can harm data safety. Understanding these threats helps protect your information.
Many cloud users do not realize the dangers that come with storing data online. Knowing common threats is the first step to prevention.
Data Breaches
Data breaches happen when unauthorized people access sensitive data. These breaches can cause loss of trust and legal problems.
Weak passwords, poor security settings, and software bugs often lead to data breaches. Attackers can steal personal and business information.
- Unencrypted data transfers
- Misconfigured cloud storage
- Vulnerable application interfaces
Insider Threats
Insider threats come from people within the organization. They may misuse access to steal or damage cloud data.
These threats can be intentional or accidental. Employees may share passwords or expose data without knowing the risk.
- Disgruntled employees leaking data
- Careless handling of access permissions
- Lack of employee security training
Account Hijacking
Account hijacking means attackers take control of cloud user accounts. They use stolen credentials to access data and services.
Phishing, weak passwords, and malware help criminals hijack accounts. This threat can lead to data loss and service disruption.
- Phishing emails to steal login info
- Using weak or reused passwords
- Malware capturing keystrokes
Encryption Techniques
Cloud security storage uses encryption to keep data safe. Encryption changes data into a secret code.
This helps protect information from unauthorized access. Different encryption methods secure data at various stages.
At-rest Encryption
At-rest encryption protects data stored on disks or drives. It stops thieves from reading data if they steal the storage device.
Data is encrypted before it is saved and decrypted when accessed. This keeps files safe even if physical security fails.
- Encrypts files on hard drives or servers
- Uses algorithms like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
- Protects against unauthorized physical access
- Works silently without affecting user tasks
In-transit Encryption
In-transit encryption secures data while it moves over the internet or networks. It stops hackers from spying during transfer.
Data is encrypted before sending and decrypted after receiving. This ensures privacy and integrity in communication.
- Uses protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security)
- Protects emails, files, and messages during transfer
- Prevents data tampering and eavesdropping
- Common in web browsers and cloud services
Key Management
Key management controls the encryption keys used to lock and unlock data. Strong key management keeps data secure.
Keys must be stored safely and rotated often to avoid theft. Proper key management reduces risks from lost or stolen keys.
- Generates strong, random encryption keys
- Stores keys in secure hardware or software vaults
- Rotates keys regularly to limit exposure
- Controls who can access and use keys

Credit: moldstud.com
Access Control Methods
Access control is key to keeping cloud storage safe. It decides who can see or change data.
Good access control stops unwanted users from entering and protects sensitive information.
Multi-factor Authentication
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) needs users to give two or more proofs. This makes access harder for hackers.
MFA often uses a password plus a code sent to a phone or a fingerprint scan.
- Something you know, like a password
- Something you have, like a phone or token
- Something you are, like a fingerprint
Role-based Access Control
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) gives access based on user roles. Each role has specific permissions.
This limits users to only what they need for their work. It reduces the risk of data leaks.
- Admins have full control
- Editors can change content
- Viewers can only see files
Identity And Access Management
Identity and Access Management (IAM) manages user identities and their access rights. It tracks who logs in and what they do.
IAM helps enforce rules like strong passwords and session limits. It supports security policies across cloud storage.
Data Backup And Recovery
Cloud security storage helps keep data safe. It stores copies of your data in secure places.
Data backup and recovery protect information from loss or damage. They ensure you can get data back fast.
Backup Strategies
Backup strategies decide how and when data is copied. Good plans keep data safe and easy to find.
Common strategies include full, incremental, and differential backups. Each type saves data differently.
- Full backups copy all data at once
- Incremental backups save changes since last backup
- Differential backups save changes since last full backup
Disaster Recovery Plans
Disaster recovery plans prepare you for data loss events. They show how to restore data quickly.
These plans include backup locations, recovery steps, and team roles. Clear plans reduce downtime and data loss.
- Identify critical data to protect
- Set recovery time goals
- Choose backup storage sites
- Assign team tasks for recovery
Testing Recovery Procedures
Testing recovery procedures checks if backups work well. It ensures data can be restored without problems.
Regular tests find issues early. They help improve backup and recovery steps.
- Run scheduled recovery drills
- Verify data integrity after recovery
- Update plans based on test results
Compliance And Regulations
Cloud security storage must meet legal rules to protect data. Companies follow these rules to avoid fines and build trust.
Different laws apply based on location and type of data. Compliance helps keep sensitive information safe and private.
Gdpr
The General Data Protection Regulation protects personal data in the European Union. It requires clear consent for data use.
Cloud storage must encrypt data and allow users to access or delete their information. Companies must report data breaches fast.
- Get user permission before storing data
- Keep data secure with strong encryption
- Allow users to view and delete their data
- Report breaches within 72 hours
Hipaa
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act protects health data in the United States. It sets strict rules for cloud storage.
Cloud providers must secure health records and limit access. They must also have plans to handle data breaches quickly.
- Encrypt health information both stored and in transit
- Control who can access patient data
- Create a breach response plan
- Keep audit logs of data access
Iso Standards
ISO standards help organizations manage security risks. ISO 27001 is the main standard for information security management.
Cloud storage following ISO standards uses policies and controls to protect data. It requires regular checks to stay secure.
- Implement security management systems
- Use risk assessment and treatment plans
- Perform regular security audits
- Train staff on security policies
Choosing A Secure Cloud Provider
Picking a safe cloud provider is key to protect your data. You must check many parts before making a choice.
Security in the cloud means your information stays private and safe from threats. This guide helps you find a trusted provider.
Security Features To Look For
Strong security features keep your data safe in the cloud. Look for providers with good protection tools.
Important features include encryption, access control, and monitoring. These stop hackers and data leaks.
- Data encryption during storage and transfer
- Multi-factor authentication for accounts
- Regular security updates and patches
- Activity monitoring and alert systems
- Data backup and disaster recovery options
Service Level Agreements
Service Level Agreements, or SLAs, set clear rules between you and the cloud provider. They explain what to expect.
Check SLAs for uptime guarantees, data handling, and support response times. Good SLAs protect your interests.
- Guaranteed uptime percentage (like 99.9%)
- Data privacy and security commitments
- Support availability and response time
- Penalties for service failures
- Clear data ownership terms
Reputation And Reviews
A provider’s reputation shows how well it protects data. Look at reviews from real users and experts.
Good reviews mean reliable service and strong security. Avoid providers with many complaints or breaches.
- Read user feedback on trusted review sites
- Check expert analysis and security reports
- Look for any past data breach incidents
- Ask for references from similar businesses
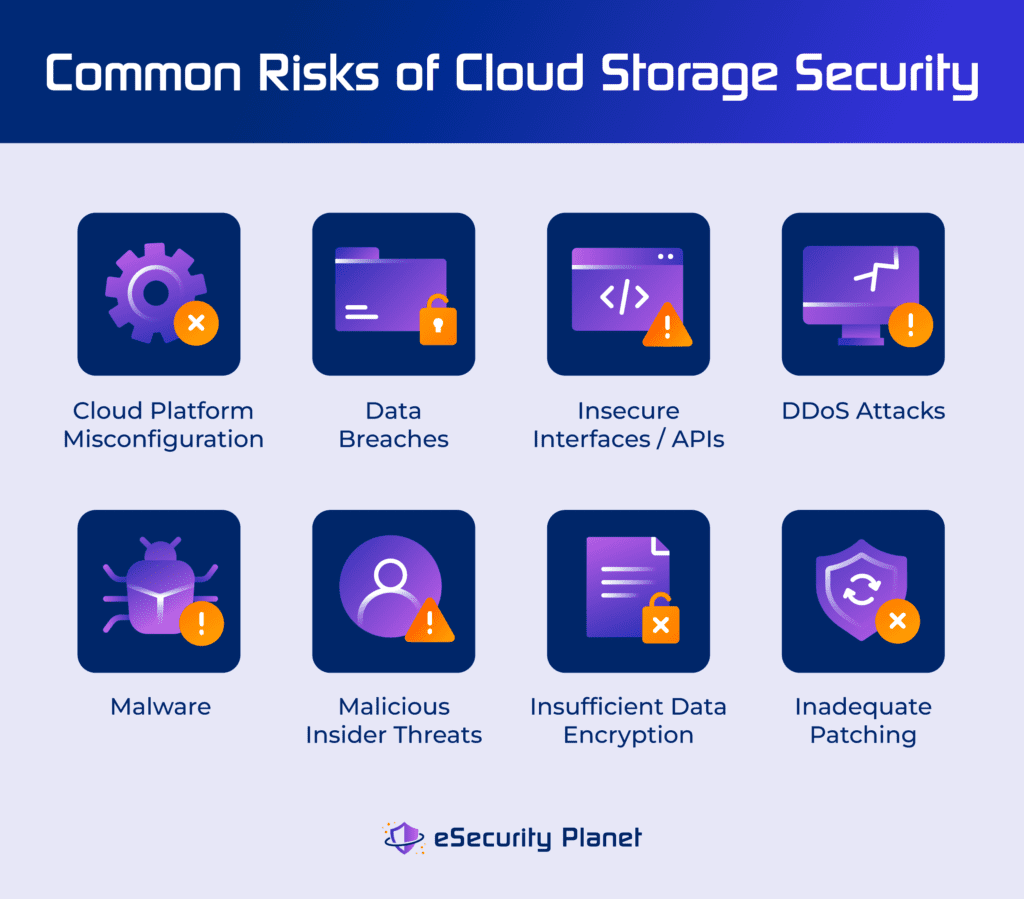
Credit: www.esecurityplanet.com
Best Practices For Cloud Security
Cloud security storage keeps your data safe in the cloud. Following best practices helps protect information.
Strong security stops hackers and data loss. Use simple steps to make your cloud storage safer.
Regular Security Audits
Check your cloud security often to find weak spots. Audits help fix problems before they cause harm.
Look at access controls, data encryption, and software updates during audits. Keep records for future checks.
- Review user permissions
- Test data encryption methods
- Check system updates and patches
- Analyze past security incidents
Employee Training
Teach employees how to protect cloud data. Training reduces mistakes that lead to security risks.
Train staff on strong passwords, recognizing phishing, and safe data handling. Update training regularly.
- Create clear security policies
- Run security awareness sessions
- Test staff with fake phishing emails
- Encourage reporting of suspicious activity
Monitoring And Logging
Track cloud storage activity to spot unusual behavior. Logs help find and fix security issues fast.
Use tools to monitor data access and changes. Keep logs safe and review them regularly for signs of trouble.
- Monitor login attempts
- Track file uploads and downloads
- Alert on unusual access times
- Keep logs for security reviews
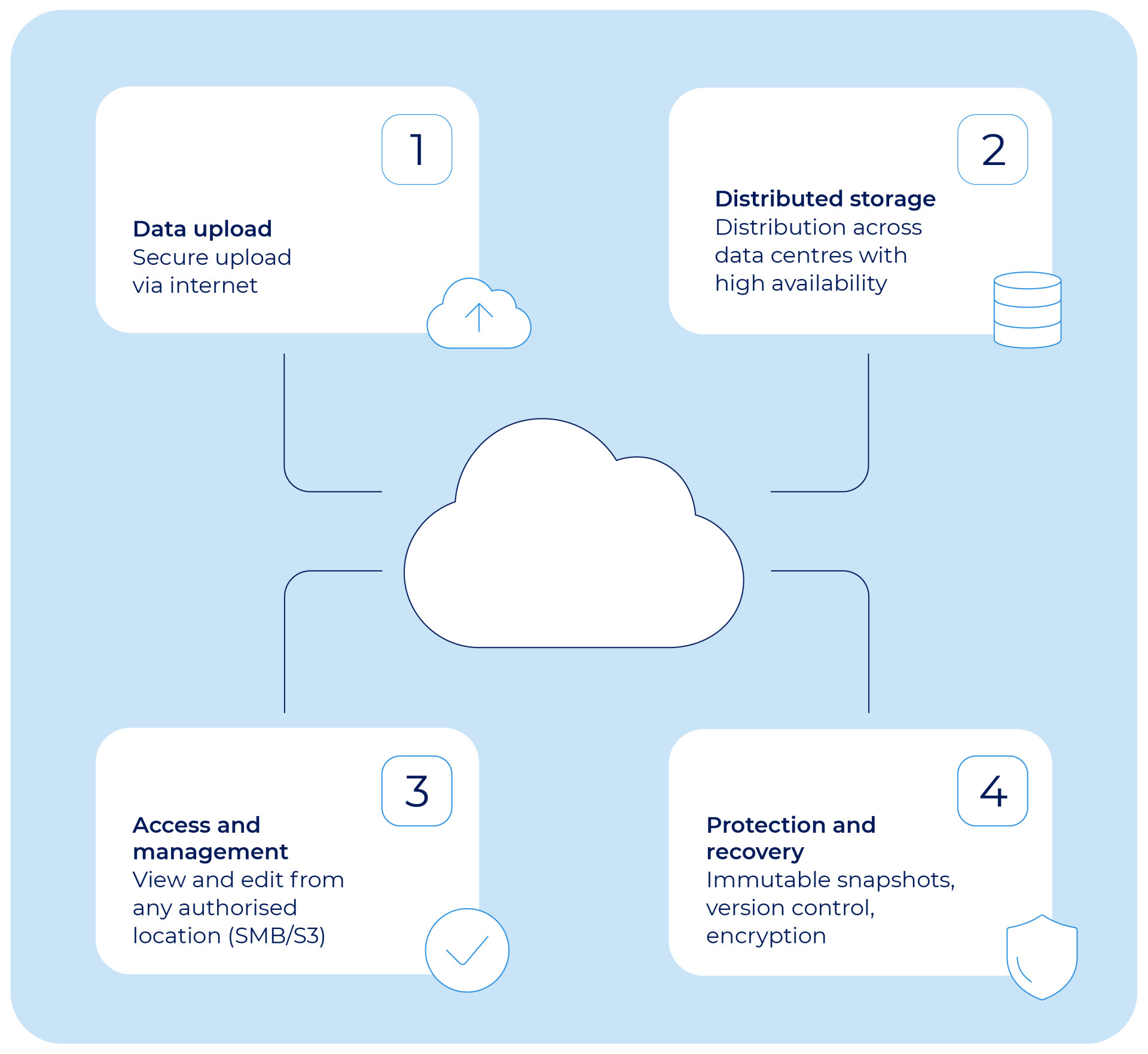
Credit: adam.es
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Cloud Security Storage And Why Is It Important?
Cloud security storage protects data stored on cloud servers from unauthorized access and breaches. It ensures confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data, which is vital for businesses to maintain trust and comply with regulations.
How Does Encryption Enhance Cloud Storage Security?
Encryption converts data into a secure code, making it unreadable without a key. It protects sensitive information during storage and transmission, reducing risks of data theft or unauthorized access in cloud environments.
What Are Common Threats To Cloud Storage Security?
Common threats include data breaches, insider threats, malware attacks, and misconfigured cloud settings. These risks can lead to data loss, theft, or exposure, emphasizing the need for robust security measures in cloud storage.
How Can Businesses Ensure Compliance In Cloud Storage?
Businesses must follow industry regulations like GDPR and HIPAA by implementing proper encryption, access controls, and regular audits. Compliance ensures legal protection and builds customer trust in cloud storage solutions.
Conclusion
Cloud security storage offers peace of mind. Data remains safe and accessible. Businesses benefit from its robust protection. Simple setup, yet highly effective. Costs stay manageable, even for small companies. Trust in cloud security keeps growing. No need for constant worry about data breaches.
Embrace the future with secure cloud storage. Your data’s safety is paramount. Choose wisely. Protect your information and business integrity. Reliable, secure, and efficient solutions await. Make informed decisions today. Secure your digital assets for tomorrow. Thank you for reading.
Stay safe in the digital world.
20 min read