Have you ever wondered how your computer talks to other devices on the internet? The answer lies in something called an IP address.
It’s a simple string of numbers, but it plays a huge role in connecting you to websites, apps, and even your friends online. Understanding what an IP address is can help you feel more in control of your online world.
Keep reading, and you’ll discover how this small piece of information impacts your everyday internet experience in ways you might not expect.
Credit: surfshark.com
Basics Of Ip Addresses
An IP address is a unique number for each device on a network. It helps computers find and talk to each other.
Every device connected to the internet has an IP address. This address tells where the device is located.
Definition And Purpose
An IP address stands for Internet Protocol address. It is like a home address for devices on a network.
The main purpose of an IP address is to identify devices and help them send data to the right place.
Ipv4 Vs Ipv6
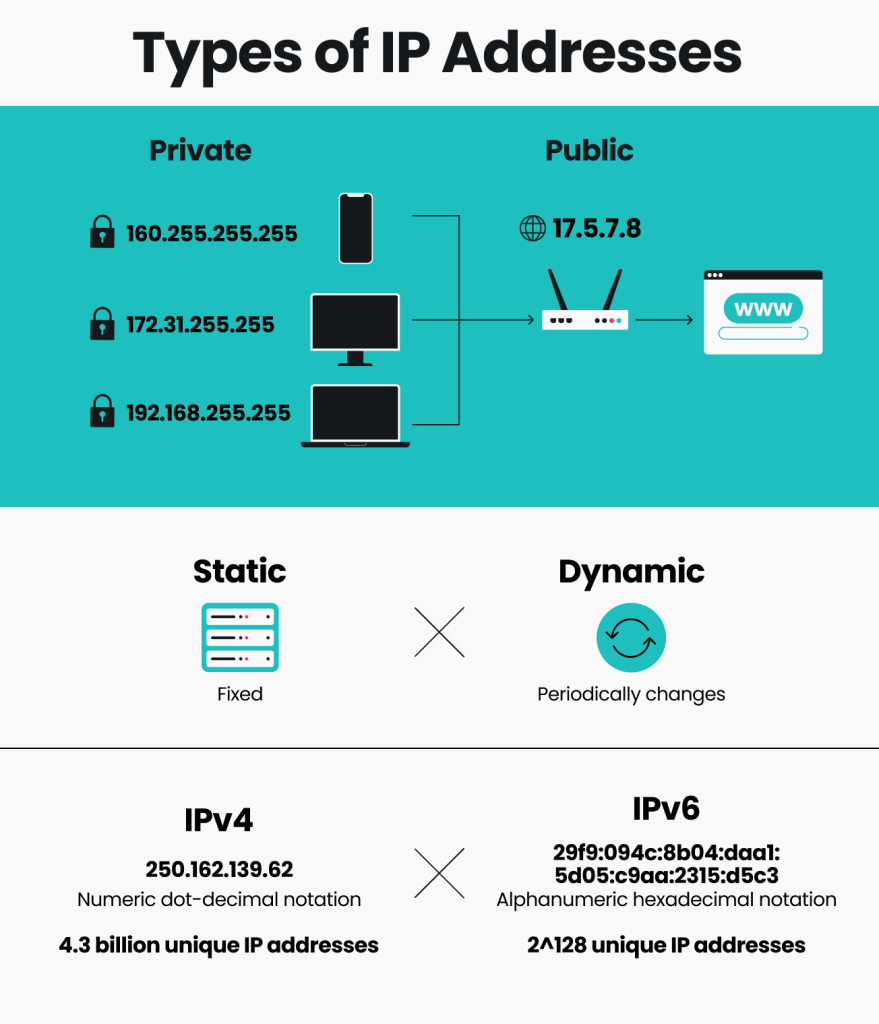
IPv4 and IPv6 are two types of IP addresses. IPv4 uses four groups of numbers separated by dots.
IPv6 is newer and uses longer addresses with letters and numbers. It can support more devices than IPv4.
- IPv4 example: 192.168.1.1
- IPv6 example: 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334
- IPv4 has about 4 billion addresses
- IPv6 has a much larger number of addresses
Public Vs Private Ips
Public IP addresses are visible on the internet. Devices use them to communicate outside their local network.
Private IP addresses are used inside local networks. They help devices connect without using the internet.
- Public IP example: 203.0.113.1
- Private IP example: 192.168.0.1
- Private IPs are not unique globally
- Public IPs must be unique worldwide
How Ip Addresses Work
An IP address is a unique number for each device on the internet. It helps computers find and talk to each other.
Every device like a phone or computer has an IP address. This address lets data travel from one device to another.
Role In Networking
IP addresses identify devices on a network. They make sure data goes to the right place.
Without IP addresses, devices could not find each other. The network would be like a city without street addresses.
Address Allocation
IP addresses are given out by special organizations. They assign blocks of addresses to internet providers.
Internet providers then give IP addresses to users and devices. These addresses can change or stay the same.
- Static IP: stays the same all the time
- Dynamic IP: changes each time you connect
Routing And Communication
Routers use IP addresses to send data to the right device. They act like traffic controllers on the internet.
When you send a message online, it travels in small parts called packets. Each packet has the sender and receiver IP address.
- Packets travel through many routers
- Each router reads the IP to forward packets
- Packets arrive and join back at the device
Types Of Ip Addresses
An IP address is a unique number that identifies a device on a network. It helps devices communicate with each other.
There are different types of IP addresses. Each type has a specific role and use in networks.
Static Vs Dynamic
Static IP addresses stay the same all the time. Devices keep the same address every time they connect.
Dynamic IP addresses change each time a device connects. They are assigned by a server called DHCP.
- Static IP: fixed and does not change
- Dynamic IP: changes with each connection
- Static IPs are good for servers
- Dynamic IPs are common for home users
Shared Vs Dedicated
A shared IP address is used by many devices or websites at the same time. It is common in hosting services.
A dedicated IP address is used by only one device or website. It offers more control and privacy.
- Shared IP: many users share one address
- Dedicated IP: one user has exclusive use
- Shared IP is cheaper and more common
- Dedicated IP is better for security
Loopback And Link-local
Loopback IP addresses are used by a device to talk to itself. The common loopback IP is 127.0.0.1.
Link-local IP addresses work only inside a local network. Devices use them to communicate without needing a router.
- Loopback IP: device talks to itself
- Link-local IP: works in a local network only
- Loopback IP helps test network software
- Link-local IP helps devices connect easily

Credit: bevijaygupta.medium.com
How To Find Your Ip Address
An IP address is a unique number that identifies your device on the internet or a local network. It helps computers find and communicate with each other.
Finding your IP address is easy. You can do it on different devices like Windows, Mac, Linux, or mobile phones.
On Windows
To find your IP address on Windows, open the Command Prompt. Type a simple command to see your network details.
This shows your IPv4 and IPv6 addresses if available.
- Click the Start menu and type “cmd”.
- Press Enter to open Command Prompt.
- Type
ipconfigand press Enter. - Look for “IPv4 Address” under your network adapter.
On Mac And Linux
On Mac or Linux, use the Terminal to find your IP address. A simple command will show your network information.
You can check both local and public IP addresses using different tools.
- Open Terminal from your applications.
- Type
ifconfigand press Enter. - Find your active network adapter (like en0 or eth0).
- Look for the “inet” value; this is your IP address.
On Mobile Devices
Mobile devices show IP addresses in their settings. The steps differ slightly between Android and iOS.
You can find your IP address for Wi-Fi or mobile data connections.
- Android:Go to Settings > Network & internet > Wi-Fi. Tap the connected network and look for IP address.
- iOS:Open Settings > Wi-Fi. Tap the “i” next to your network. Find the IP address under IPv4 Address.
Security And Privacy Concerns
An IP address is a unique number that identifies your device on the internet. It helps websites know where to send data.
Your IP address can reveal your location and online activities. This raises concerns about security and privacy.
Ip Tracking Risks
Many websites and online services track IP addresses to monitor users. This tracking can expose personal information.
Hackers can also use your IP address to launch attacks like hacking or spying on your internet activity.
- Location tracking by advertisers or websites
- Targeted ads based on browsing habits
- Potential hacking attempts from exposed IPs
- Unwanted monitoring by third parties
Using Vpns And Proxies
VPNs and proxies hide your real IP address by routing your internet traffic through other servers. This helps protect your identity.
They can make it harder for trackers to see your location and browsing habits. VPNs also encrypt your data for extra security.
- Hide your real IP address
- Mask your location from websites
- Encrypt data to protect privacy
- Access content restricted by region
Best Practices For Protection
Protect your IP address by using strong security habits and tools. This reduces risks from hackers and trackers.
Always keep your software updated and use VPNs or proxies. Avoid sharing your IP address on public platforms.
- Use VPNs or proxies for online privacy
- Keep your devices and apps updated
- Avoid clicking unknown links or attachments
- Do not share your IP address publicly
Future Of Ip Addresses
IP addresses are numbers that identify devices on the internet. They help computers talk to each other.
The future of IP addresses is changing because of new technology and more internet users.
Transition To Ipv6
IPv4 is the old system for IP addresses. It has a limited number of addresses.
IPv6 is the new system with many more addresses. It will help the internet grow.
- IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses
- IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses
- IPv6 supports billions more devices
- IPv6 improves security features
Impact Of Iot
The Internet of Things (IoT) connects many devices to the internet. These include smart homes and cars.
IoT needs more IP addresses to work well. This puts pressure on current IP systems.
- Smart devices need unique IP addresses
- IoT growth increases IP demand
- IPv6 helps connect many IoT devices
Evolving Network Needs
Networks today need faster and safer ways to connect devices. IP addresses must support this.
New uses like video calls and cloud computing need better IP systems that handle more data.
- More devices need more IP addresses
- Security in IP addressing is very important
- Networks must handle more data traffic
- IPv6 offers better support for new tech

Credit: infosecwriteups.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is An Ip Address?
An IP address is a unique numerical label assigned to each device connected to a computer network. It serves two main functions: identifying the host or network interface, and providing the location address. IP addresses are essential for devices to communicate with each other over the internet.
How Does An Ip Address Work?
An IP address works by identifying devices on a network and enabling communication between them. When you access a website, your device sends a request to the server’s IP address. The server then sends the requested data back to your device’s IP address, completing the connection.
Why Is My Ip Address Important?
Your IP address is important because it allows your device to communicate on the internet. It identifies your device, enabling data exchange between your device and other servers. Additionally, it helps websites and services tailor content to your location, enhancing your online experience.
Can My Ip Address Be Traced?
Yes, your IP address can be traced to your internet service provider. While it doesn’t reveal personal details, it can indicate your general location. Law enforcement agencies can request further details from ISPs if necessary. Using a VPN can help mask your IP address for enhanced privacy.
Conclusion
An IP address helps identify devices on the internet. It acts like a home address for your computer. This makes communication between devices possible and safe. Knowing what an IP address is can help you understand how the internet works.
It also helps protect your privacy online. Keep this simple idea in mind next time you connect to the web. Understanding IP addresses makes using the internet easier for everyone.
17 min read