Are you curious about the difference between Wi-Fi and Li-Fi? You rely on wireless connections every day, but do you really know how these technologies work and which one could be better for you?
Understanding Wi-Fi and Li-Fi can change the way you connect to the internet, making your experience faster, safer, and more reliable. Keep reading to discover how these two technologies stack up and which one fits your needs perfectly. Your next connection could be smarter than you think.
Wi-fi Technology
Wi-Fi is a wireless technology that lets devices connect to the internet. It uses radio waves to send data between devices.
Many homes and businesses use Wi-Fi to access the internet without wires. It is common in many gadgets like phones and laptops.
How Wi-fi Works
Wi-Fi works by sending data over radio signals. A router sends these signals to devices in its range.
The devices receive the signals and connect to the internet. The router links to the internet through a wired connection.
Common Uses Of Wi-fi
People use Wi-Fi to browse the internet on phones, tablets, and computers. It also connects smart home devices.
Businesses use Wi-Fi for emails, video calls, and cloud services. Public places offer Wi-Fi to attract customers.
- Internet browsing
- Streaming videos and music
- Online gaming
- Smart home device control
- Business communication
Advantages Of Wi-fi
Wi-Fi lets you connect many devices without wires. It gives freedom to move around while staying online.
It is easy to set up and works with many devices. Wi-Fi supports fast internet speeds for daily tasks.
- Wireless connection for many devices
- Easy to install and use
- Supports high-speed internet
- Works indoors and outdoors
- Cost-effective for homes and offices
Li-fi Technology
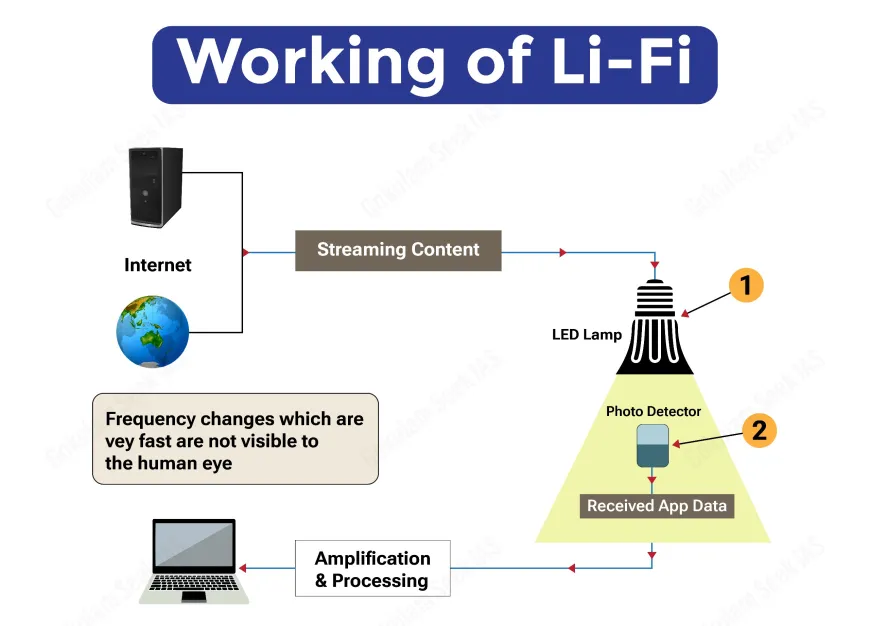
Li-Fi is a wireless communication technology that uses light to send data. It works by changing the brightness of LED bulbs very fast.
Li-Fi is different from Wi-Fi because it uses light instead of radio waves. It offers faster speeds and more security.
How Li-fi Works
Li-Fi sends data by turning LED lights on and off quickly. The changes are too fast for the human eye to see.
A receiver detects the light signals and converts them back into data for devices to use. This allows fast and secure communication.
- LED lights transmit data by blinking
- Light signals carry information
- Receivers convert light into data
- Requires line of sight between sender and receiver
Applications Of Li-fi
Li-Fi can be used in places where Wi-Fi is weak or not allowed. It works well in hospitals, airplanes, and offices.
It also helps in smart homes and cities by connecting devices through light. Schools and museums can use it for fast internet access.
- Hospitals for secure data transfer
- Airplanes to avoid radio interference
- Offices and conference rooms
- Smart homes and smart cities
- Schools and museums
Benefits Of Li-fi
Li-Fi provides very fast internet speeds. It can be up to 100 times faster than Wi-Fi.
It is more secure because light cannot pass through walls. This limits unwanted access to the network.
- High-speed data transmission
- Improved security with light signals
- Works where radio waves are blocked
- Less interference with other devices
- Energy-efficient using LED lights
Speed Comparison
Wi-Fi and Li-Fi are two different ways to send data wirelessly. Speed is a key difference between them.
Understanding how fast each technology transfers data helps choose the right option for different needs.
Data Transfer Rates
Wi-Fi uses radio waves to send data and usually has speeds up to 1 Gbps. Newer Wi-Fi versions can go faster.
Li-Fi uses light waves and can reach speeds over 10 Gbps. This makes Li-Fi much faster than Wi-Fi.
- Wi-Fi: up to 1 Gbps in common use
- Li-Fi: over 10 Gbps in ideal conditions
- Li-Fi speed depends on light source quality
- Wi-Fi speed depends on signal strength and interference
Latency Differences
Latency is the delay before data starts to transfer. Lower latency means faster response times.
Li-Fi has lower latency than Wi-Fi because light travels faster and faces less interference.
- Wi-Fi latency is usually around 10 to 50 milliseconds
- Li-Fi latency can be less than 1 millisecond
- Low latency is good for gaming and video calls
- Wi-Fi latency varies with network traffic and obstacles
Range And Coverage
Range and coverage are key factors when comparing Wi-Fi and Li-Fi. These technologies use different signals to send data.
Understanding how far their signals travel helps choose the right option for different spaces.
Wi-fi Coverage Area
Wi-Fi uses radio waves to transmit data through the air. These waves can pass through walls and furniture.
Wi-Fi signals cover a wide area, making them useful for homes, offices, and public places.
- Typical indoor range is about 100 to 150 feet
- Outdoor range can reach up to 300 feet
- Walls and obstacles may reduce signal strength
- Signal quality decreases with distance from router
Li-fi Coverage Limitations
Li-Fi sends data using visible light from LED bulbs. Light cannot pass through walls or objects.
This limits Li-Fi coverage to the area lit by the light source. It works best in small, open spaces.
- Range is usually a few meters, depending on light strength
- Light must have a clear line of sight
- Signal stops when light is blocked or turned off
- Less suitable for large or cluttered areas
Security Aspects
Wi-Fi and Li-Fi are both ways to send data wirelessly. They have different security features. Understanding these helps keep data safe.
This section explains the security risks of Wi-Fi and the security benefits of Li-Fi.
Wi-fi Security Risks
Wi-Fi sends data using radio waves. These waves can pass through walls. This makes Wi-Fi easy to access from outside your home or office.
Hackers can intercept Wi-Fi signals if the network is not secure. They may steal personal information or inject harmful data.
- Weak passwords allow easy access to Wi-Fi networks
- Unencrypted data can be seen by attackers
- Public Wi-Fi hotspots often lack strong security
- Malware can spread through unsecured Wi-Fi connections
Li-fi Security Advantages
Li-Fi uses light waves to send data. Light cannot pass through walls. This limits access to the network to the room with the light source.
This physical barrier makes Li-Fi more secure. Only people inside the lit area can connect and see the data.
- Data stays within the room due to light confinement
- Harder for hackers to intercept signals remotely
- Reduced risk of unauthorized access
- Less chance of data leaks through physical walls
Interference And Reliability
Wi-Fi and Li-Fi are two ways to send data without wires. Both face challenges with interference and reliability.
Understanding these challenges helps us see which technology works best in different places.
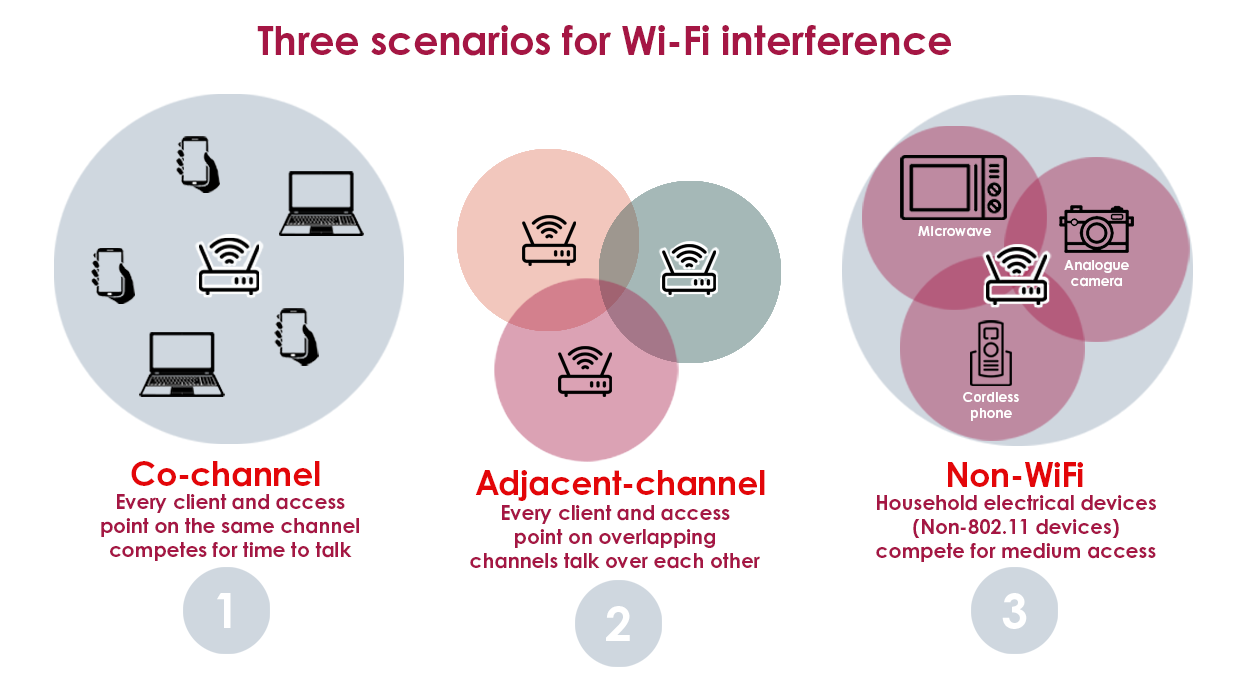
Wi-fi Signal Interference
Wi-Fi uses radio waves to send signals through the air. These waves can be blocked or mixed up by objects and devices.
Common sources of interference include walls, microwaves, and other Wi-Fi networks nearby. This can slow down or drop your connection.
- Walls and furniture weaken Wi-Fi signals
- Microwave ovens cause signal noise
- Other Wi-Fi devices share the same frequencies
- Signals can overlap and cause slow speeds
Li-fi Stability Factors
Li-Fi uses light to send data. It depends on a clear line of sight between the light source and receiver.
Li-Fi works well in places without physical barriers but can be affected by changes in lighting and obstacles.
- Light must reach the receiver directly
- Objects blocking light cause signal loss
- Strong sunlight can interfere with Li-Fi signals
- Stable lighting keeps Li-Fi reliable
Cost And Implementation
Wi-Fi and Li-Fi are two wireless communication technologies. They differ in cost and how easy they are to set up.
Understanding the expenses and maintenance helps choose the right option for your needs.
Installation Expenses
Wi-Fi uses radio waves and common hardware like routers. It is cheaper to install in most places.
Li-Fi uses light to send data. It needs special LED lights and sensors, which cost more upfront.
- Wi-Fi routers are widely available and affordable
- Li-Fi requires new lighting systems and receivers
- Wi-Fi installation fits existing setups easily
- Li-Fi may need wiring changes for lights
Maintenance Considerations
Wi-Fi equipment needs regular updates and occasional repairs. It may need signal adjustments over time.
Li-Fi systems require maintenance of LED lights and sensors. Bulbs may need replacing more often than Wi-Fi gear.
- Wi-Fi needs software updates to stay secure
- Li-Fi needs light fixtures kept clean and functional
- Wi-Fi has more spare parts available
- Li-Fi may need specialist technicians for repairs

Credit: en.m.wikipedia.org
Future Trends
Wi-Fi and Li-Fi are two ways to connect devices to the internet. Both have strong futures as technology grows fast.
New updates in Wi-Fi and Li-Fi will change how we use the internet every day.
Innovations In Wi-fi
Wi-Fi is getting faster and smarter. New versions will offer better speed and cover more areas.
Wi-Fi 7 is coming soon. It will let many devices connect without slowing down. This helps homes and offices work better.
- Higher data rates for smooth video and gaming
- Improved energy use for longer device battery life
- Better security to protect user data
- More stable connections in crowded places
Emerging Li-fi Developments
Li-Fi uses light to send data. It can be faster than Wi-Fi and works well in places with many devices.
New Li-Fi tech will expand its use. It will connect more devices and improve indoor internet access.
- Better LED lights that send data faster
- Integration with smart home and office systems
- Use in hospitals and planes where Wi-Fi is weak
- Lower costs to make it easier to use everywhere
Choosing The Right Option
Wi-Fi and Li-Fi are two ways to send data wirelessly. Both have strong points and limits.
Knowing when to use each helps you pick the best for your needs.
Use Case Scenarios
Wi-Fi works well in most homes and offices. It covers wide areas and connects many devices.
Li-Fi suits places needing fast, secure connections. It uses light, so it works best in small spaces.
- Wi-Fi is good for internet browsing and streaming on many devices.
- Li-Fi fits well in hospitals to avoid radio interference.
- Li-Fi can help in airplanes where radio waves are limited.
- Wi-Fi is better outdoors or large spaces.
Environmental Factors
Wi-Fi uses radio waves that pass through walls and objects. This makes it flexible indoors and outdoors.
Li-Fi depends on light. It needs clear line of sight and can be blocked by walls or objects.
- Wi-Fi works well with walls and obstacles around.
- Li-Fi needs direct light, so it is best in open, well-lit areas.
- Li-Fi is safer in places with radio wave restrictions.
- Wi-Fi signals can suffer from interference from other devices.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Credit: www.imv-imaging.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Main Difference Between Wi-fi And Li-fi?
Wi-Fi uses radio waves for wireless communication, while Li-Fi utilizes visible light. Li-Fi can achieve faster data transmission rates than Wi-Fi. However, Li-Fi requires line-of-sight and cannot pass through walls. Wi-Fi, on the other hand, can penetrate walls, offering greater coverage but potentially slower speeds.
Is Li-fi Faster Than Wi-fi?
Yes, Li-Fi can be significantly faster than Wi-Fi. It uses visible light, allowing for higher data transmission rates. While Wi-Fi is limited by radio wave bandwidth, Li-Fi’s light waves provide a wider spectrum. This results in speeds that can surpass Wi-Fi by multiple times.
Can Li-fi Replace Wi-fi Completely?
Li-Fi is unlikely to replace Wi-Fi entirely. While Li-Fi offers faster speeds, it requires direct line-of-sight. This makes it less practical for widespread use in environments with obstacles. Wi-Fi’s ability to penetrate walls ensures broader coverage, making it more versatile for general use.
Does Li-fi Work Outdoors?
Li-Fi can work outdoors but with limitations. It depends on visible light, which can be affected by natural light conditions. Bright sunlight can interfere with Li-Fi signals, reducing effectiveness. However, in controlled outdoor environments, Li-Fi can still offer high-speed communication.
Conclusion
Wi-Fi and Li-Fi both connect devices to the internet. Wi-Fi uses radio waves and works through walls. Li-Fi uses light and is faster but needs line of sight. Each has good points and limits. Choosing depends on your needs and space.
Both technologies will keep improving soon. Stay aware of these options for better connections.
20 min read