When it comes to protecting your important data, you can’t afford to leave anything to chance. Your network holds valuable information that, if lost, could disrupt your work or business.
So, what’s the best way to keep it safe? Understanding your network backup options is the first step to making smart, reliable choices. You’ll discover simple, effective methods to secure your data. By the end, you’ll feel confident about protecting your network and avoiding costly downtime.
Ready to take control of your data’s safety? Let’s dive in.
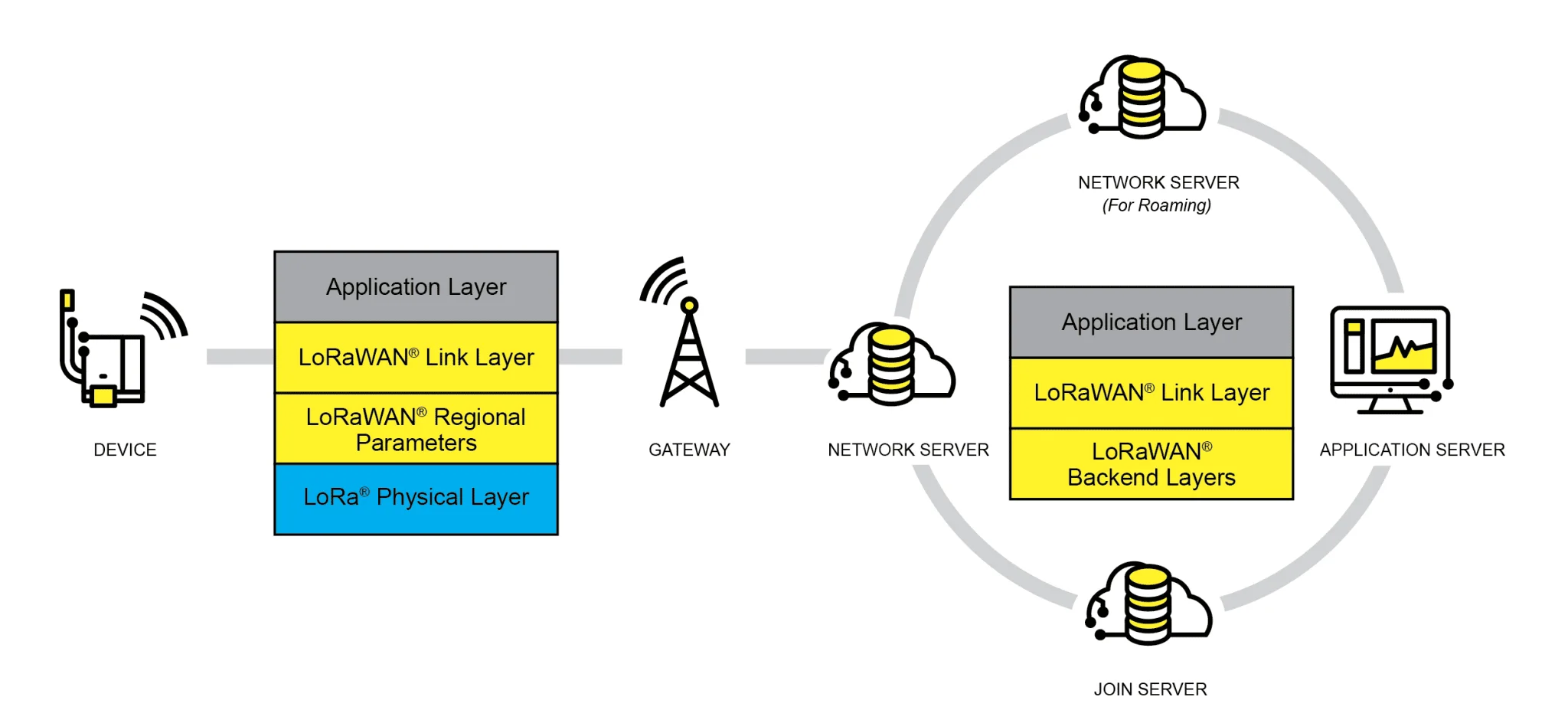
Credit: petri.com
Local Backup Solutions
Local backup solutions store your data on devices near you. They help protect your files from loss or damage.
These solutions are fast and give you easy access to your backups. They work well for home or small business use.
External Hard Drives
External hard drives are portable storage devices. You can connect them to your computer via USB or other ports.
They offer a simple way to back up important files. You can copy data manually or set automatic backups.
- Easy to use and widely available
- Varied storage sizes to fit your needs
- Good for quick, local backups
Network Attached Storage (nas)
A NAS device connects to your home or office network. It stores data centrally for multiple users or devices.
NAS offers more storage and features than external drives. You can access your backups from any device on the network.
- Supports multiple users and devices
- Can run backup tasks automatically
- Often includes extra security options
Backup Software Tools
Backup software helps you manage and automate your backups. It works with external drives or NAS devices.
These tools can schedule backups and keep track of file changes. They make local backups easier and more reliable.
- Automates backup processes
- Allows file versioning and recovery
- Offers encryption for data safety
Credit: www.veeam.com
Cloud Backup Services
Cloud backup services store your data on internet servers. They keep your files safe from loss or damage.
These services offer easy access to your data anytime. They help businesses protect important information.
Public Cloud Providers
Public cloud providers offer backup services to many users. They run large data centers and share resources.
These providers give fast setup and flexible storage options. Users pay only for the space they use.
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- IBM Cloud
Private Cloud Options
Private clouds are dedicated to one organization. They offer more control and security for backup data.
Companies can host private clouds on their own servers. This keeps data inside the company’s network.
- Higher security and privacy
- Custom backup policies
- Greater control over data
- Usually higher cost and maintenance
Hybrid Cloud Strategies
Hybrid cloud mixes public and private clouds. It gives businesses flexible backup options.
This strategy lets companies store sensitive data privately. Less sensitive data goes to public clouds.
- Balance between security and cost
- Improves disaster recovery plans
- Supports data compliance rules
- Allows easy scaling of backup storage
Backup Techniques
Network backup helps protect data from loss. It saves copies of files and systems on a network.
There are different backup techniques. Each has its own way of copying data and saving time.
Full Backup
A full backup copies all files every time it runs. This creates a complete copy of your data.
It takes more time and space but is easy to restore. You only need the latest full backup.
- Copies all files
- Takes longer to complete
- Uses more storage space
- Simple to restore data
Incremental Backup
Incremental backup saves only changed or new files after the last backup. It is faster than full backup.
This method uses less space but needs all increments plus the last full backup to restore data.
- Backs up changed files only
- Faster backup process
- Needs less storage space
- Restore requires all increments
Differential Backup
Differential backup saves all changes since the last full backup. It grows larger over time.
It takes more time and space than incremental but needs only the last full and last differential to restore.
- Backs up all changes since full backup
- Faster than full but slower than incremental
- Uses moderate storage space
- Easier restore than incremental

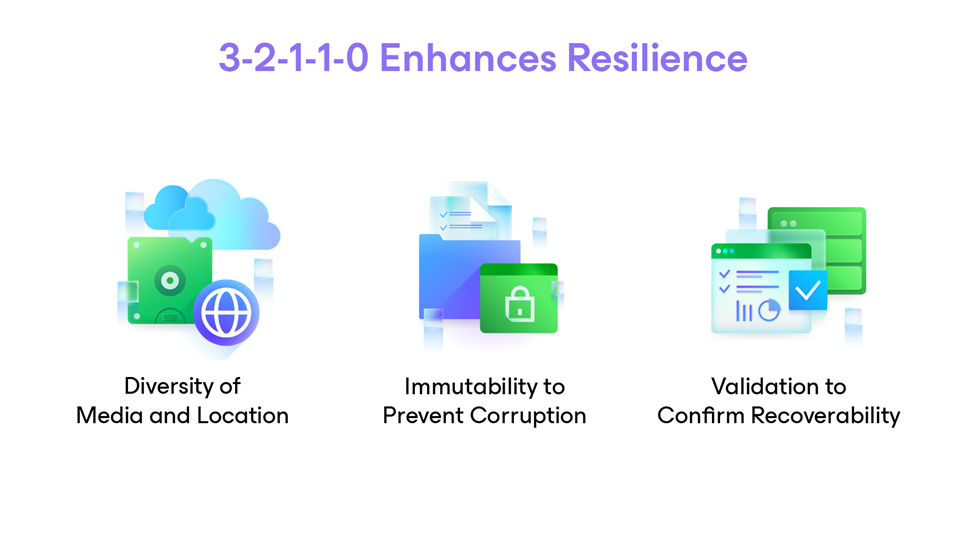
Credit: stevemats.medium.com
Security Measures For Backups
Network backups store important data offsite or on different devices. Protecting these backups is key to avoid data loss or theft.
Security measures help keep backup data safe from hackers and accidental damage. Let’s look at some main ways to protect backups.
Data Encryption
Data encryption changes backup data into a secret code. Only people with the key can read the data.
This keeps information safe even if someone steals the backup files. Encryption protects both data in transit and stored data.
- Encrypt data before sending it over the network
- Use strong encryption standards like AES-256
- Keep encryption keys secure and separate from backups
Access Controls
Access controls limit who can view or change backup data. Only trusted users should have permissions.
Use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication to protect backup systems. Track who accesses or modifies backups.
- Set user roles with minimum required rights
- Require strong passwords and regular updates
- Enable audit logs for access tracking
Regular Audits
Regular audits check backup security and compliance. They find weaknesses and verify backup integrity.
Schedule audits to review access logs, encryption status, and backup success rates. Fix issues quickly to keep data safe.
- Review user access logs for unusual activity
- Check encryption is active on all backups
- Test backups by restoring sample files
Disaster Recovery Planning
Disaster recovery planning helps protect your data in case of an emergency. It ensures you can restore your systems quickly.
Network backup options are key parts of this plan. They keep your information safe and ready to recover.
Backup Frequency
Backup frequency means how often you save copies of your data. Regular backups reduce data loss risks.
Daily or weekly backups are common choices. Choose a schedule that matches how often your data changes.
- Hourly backups for critical data
- Daily backups for most business files
- Weekly backups for archives and less used data
Offsite Storage
Offsite storage means keeping backup copies away from your main site. It protects data from physical damage.
Use cloud storage or a secure remote location. This way, backups stay safe even if your office is affected.
- Cloud storage services
- Remote data centers
- Physical media stored offsite
Testing Restore Procedures
Testing restore procedures means checking if your backups can be used to recover data. It ensures your plan works.
Regular tests help find problems early. This keeps your disaster recovery plan reliable and effective.
- Schedule restore tests at least twice a year
- Verify all critical data can be recovered
- Document the testing process and results
Choosing The Right Backup Option
Choosing the right network backup option is important for data safety. You need to pick a solution that fits your needs.
This guide helps you decide based on data size, budget, and recovery needs.
Assessing Data Volume
Look at how much data you need to back up. Large data needs more storage space and time to copy.
Small data sets can use simple backup options. Large sets might need advanced solutions.
- Small data: local backups or cloud storage
- Medium data: network-attached storage (NAS)
- Large data: dedicated backup servers or tape drives
Evaluating Budget Constraints
Your budget limits the backup options you can choose. Some solutions cost more upfront or monthly.
Free or low-cost options work for small budgets but may lack features. Higher budgets allow for faster and safer backups.
- Low budget: basic cloud or external drives
- Medium budget: NAS devices or hybrid solutions
- High budget: professional backup software and hardware
Considering Recovery Time Objectives
Recovery Time Objective (RTO) means how fast you need to restore data after loss. Faster recovery needs better tools.
If you need quick access, choose backups that allow fast data restoration. Slower options may save money but increase downtime.
- Short RTO: real-time backups or snapshots
- Moderate RTO: scheduled daily backups
- Long RTO: weekly or monthly backups
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Network Backup Options?
Network backup options include cloud storage, network-attached storage (NAS), and remote server backups. These methods help secure data from loss or corruption. They offer automated scheduling, encryption, and easy restoration. Businesses can choose based on their needs, budget, and infrastructure.
Regular backups ensure data integrity and accessibility.
Why Is Network Backup Important?
Network backup is crucial for data protection, ensuring business continuity during failures. It safeguards against data loss from hardware malfunctions, cyberattacks, and accidental deletions. Regular backups prevent downtime, protect sensitive information, and support compliance with regulations. Investing in reliable network backup solutions is vital for maintaining operational efficiency.
How Does Cloud Backup Work?
Cloud backup involves storing data on remote servers accessed via the internet. Data is encrypted and transferred securely to cloud service providers. Users can automate backups and access files from any location. Cloud solutions offer scalability, data redundancy, and disaster recovery options, making them a popular choice for businesses.
What Is Nas In Network Backup?
Network-attached storage (NAS) is a dedicated device that provides centralized data storage. It connects to a network, allowing multiple users and devices to access files. NAS offers data redundancy, automated backups, and remote access. It is ideal for small to medium-sized businesses seeking cost-effective and scalable backup solutions.
Conclusion
Choosing the right network backup option protects your important data. Regular backups help avoid data loss and downtime. Cloud backups offer easy access and offsite safety. Local backups provide quick recovery for urgent needs. Combining both methods creates a stronger defense.
Always check your backup plan works well. Keep your data safe, secure, and ready. Take action today to protect your network.
17 min read