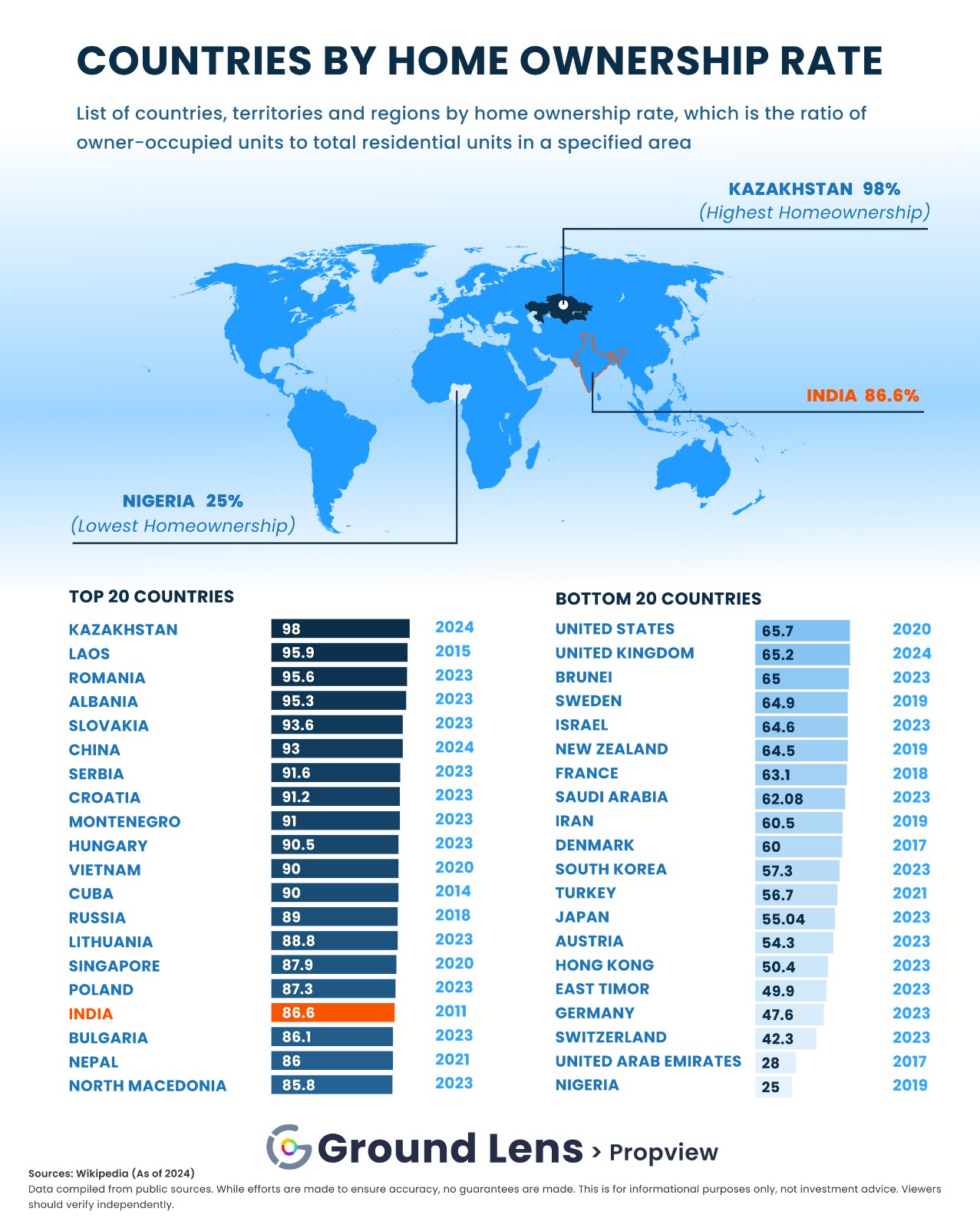
Do you ever wonder what makes your internet connection work smoothly or how your devices talk to each other? The answer lies in network devices.
Knowing how to identify these devices can help you understand your home or office network better. This knowledge puts you in control, making troubleshooting easier and boosting your confidence with technology. Keep reading, and you’ll discover simple ways to spot the key players in your network and why each one matters to you.
Network Devices Overview
Network devices are tools that help computers and other gadgets talk to each other. They move data from one place to another in a network.
These devices make sure that information flows smoothly and safely between users and systems.
Role In Network Infrastructure
Network devices connect different parts of a network. They control the flow of data to keep communication clear and fast.
They also protect the network by managing access and stopping unwanted traffic.
- Connect devices within a network
- Manage data traffic efficiently
- Secure the network from threats
- Help devices communicate across distances
Common Types And Functions
There are many types of network devices, each with a special job. They work together to keep the network running well.
| Device | Function |
|---|---|
| Router | Routes data between different networks |
| Switch | Connects devices inside a network |
| Firewall | Blocks unwanted access to the network |
| Access Point | Provides wireless connection to devices |
| Modem | Connects a network to the internet |
Routers
Routers are devices that connect different networks together. They help send data from one place to another.
They are important for home and business internet connections. Routers control how data moves across networks.
Routing Basics
Routing means finding the best path for data to travel. Routers read data addresses and send data to the right place.
They use tables to decide where to send information. This helps devices communicate quickly and correctly.
Types Of Routers
There are many types of routers. Each type works for different network sizes and needs.
- Home Routers: Used in houses for internet access.
- Core Routers: Handle large amounts of data in big networks.
- Edge Routers: Connect internal networks to outside networks.
- Virtual Routers: Software-based routers in cloud networks.
Key Features
Routers have features that help manage data traffic well. These features keep networks fast and secure.
- Routing Protocols: Help routers share route information.
- Firewall: Protects networks from threats.
- Quality of Service (QoS): Prioritizes important data.
- Wireless Support: Connects devices without cables.
- Multiple Ports: Connect many devices at once.
Switches
Switches are devices used to connect multiple devices in a network. They help send data to the right device quickly.
Switches work by creating a network that allows devices to communicate efficiently and safely.
Switching Concepts
Switches use MAC addresses to send data only to the correct device. This saves time and bandwidth.
They work in full-duplex mode, so devices can send and receive data at the same time.
- Learn device addresses to direct traffic
- Use separate channels for sending and receiving
- Reduce network collisions and delays
Managed Vs Unmanaged Switches
Managed switches let users control settings and monitor the network. They are flexible for large setups.
Unmanaged switches work right out of the box. They have no extra controls but are easy to use.
- Managed switches offer security and traffic control
- Unmanaged switches are simple and cost-effective
- Choose based on network size and needs
Use Cases
Switches are used in homes, offices, and data centers to connect devices. They make networks faster and stable.
Small offices often use unmanaged switches. Large companies prefer managed switches for better control.
- Home networks connect computers and printers
- Offices manage many devices with managed switches
- Data centers handle heavy traffic and security
Credit: www.geeksforgeeks.org
Hubs And Repeaters
Network devices help computers talk to each other. Hubs and repeaters are simple devices used in networks.
They both help send signals but work in different ways. Knowing how they work helps you choose the right one.
Basic Operations
A hub connects many devices in a network. It sends data to all connected devices at once.
A repeater boosts the signal. It catches weak signals and sends them stronger to reach far devices.
Differences Between Hub And Repeater
A hub shares data with all devices. It does not check who should get the data.
A repeater only increases signal strength. It does not share data or connect devices.
- Hub broadcasts data to all ports
- Repeater strengthens signal for long distances
- Hub works at the physical layer
- Repeater works only to extend signal reach
- Hub connects multiple devices
- Repeater does not connect devices, only boosts signals
When To Use Them
Use a hub to connect many devices in small networks. It is simple and easy to use.
Use a repeater when the network signal is weak. It helps signals travel further without loss.
- Hub: Connects devices in the same room or area
- Repeater: Extends signal over long distances
- Hub: Good for small, simple networks
- Repeater: Good for large spaces needing signal boost
Firewalls
Firewalls protect networks by controlling incoming and outgoing traffic. They help keep bad data out and safe data in.
They are important devices in network security. Firewalls stop hackers and harmful software from entering a network.
Purpose And Importance
Firewalls check data that tries to enter or leave a network. They block dangerous or unwanted traffic.
They protect sensitive information and prevent attacks. Without firewalls, networks are open to threats and damage.
Hardware Vs Software Firewalls
Hardware firewalls are physical devices placed between a network and the internet. They protect the whole network.
Software firewalls run on individual computers. They protect one device by controlling its network traffic.
- Hardware firewalls are good for large networks.
- Software firewalls are easy to install on personal devices.
- Both types work together for better security.
Common Firewall Rules
Firewalls use rules to decide which traffic is allowed or blocked. Rules are simple instructions for filtering data.
- Allow trusted IP addresses to access the network.
- Block unknown or suspicious IP addresses.
- Permit traffic on safe ports like HTTP and HTTPS.
- Deny traffic on risky or unused ports.
- Allow outgoing traffic but monitor incoming requests.

Credit: medium.com
Access Points
Access points are devices that allow wireless devices to connect to a wired network. They help extend the range of a Wi-Fi network.
Access points are important in offices, schools, and homes to provide better wireless coverage.
Wireless Connectivity
Access points send and receive wireless signals to connect devices like phones and laptops. They create a Wi-Fi network that devices use to access the internet.
Good wireless connectivity means fast and reliable internet without cables. Access points manage this connection by communicating with many devices at once.
Types Of Access Points
There are different types of access points. Some are simple, while others have advanced features for bigger networks.
- Standalone Access Points: Work alone and are easy to set up.
- Controller-Based Access Points: Managed by a central controller for large networks.
- Mesh Access Points: Connect to each other to cover wide areas without wires.
- Cloud-Managed Access Points: Controlled through the internet using cloud software.
Deployment Tips
Place access points where they can send signals without obstacles. Avoid walls and metal objects that block Wi-Fi.
Use enough access points to cover the whole area. Too few cause weak signals; too many cause interference.
- Mount access points high for better signal spread.
- Check for overlapping channels to reduce interference.
- Secure access points with strong passwords.
- Update firmware to keep devices safe and fast.
Modems
A modem is a device that connects your home or office to the internet. It changes digital signals from your computer into signals that travel over phone or cable lines.
Modems help computers talk to internet service providers. Without a modem, your devices cannot access the web.
Function In Networks
Modems turn digital data into signals that can travel on phone or cable lines. They also convert incoming signals back to digital data.
This process allows devices to send and receive information through the internet. Modems act as a bridge between your local network and the wider internet.
Types Of Modems
There are several types of modems based on the technology and connection they use. Each serves a different network setup.
- Dial-up modems use phone lines to connect to the internet.
- Cable modems connect through cable TV lines and offer faster speeds.
- DSL modems use telephone lines but provide faster internet than dial-up.
- Fiber optic modems connect to fiber optic cables for very high-speed internet.
- Wireless modems use cellular networks like 4G or 5G for internet access.
Integration With Other Devices
Modems often work with routers to share internet with many devices. Some modems combine both functions in one device.
They connect to computers, routers, or switches using Ethernet cables. Wireless modems can also connect devices via Wi-Fi.
- Modem connects to internet service provider
- Router connects to modem to share internet
- Computers and phones connect to the router or modem
Credit: www.geeksforgeeks.org
Gateways
Gateways are important devices in computer networks. They connect different networks and help data flow between them.
They act as bridges between networks that use different protocols or structures. Gateways allow communication beyond local networks.
Role In Network Communication
Gateways manage data transfer between separate networks. They translate information so devices can understand each other.
They control traffic, ensuring data reaches the correct destination. Gateways also improve security by filtering data between networks.
Types And Examples
There are different types of gateways for various tasks. Some connect local networks to the internet, while others link different network types.
- Internet Gateway: Connects private networks to the internet.
- VoIP Gateway: Converts voice signals for phone networks.
- Cloud Gateway: Connects on-premise networks to cloud services.
- Protocol Gateway: Translates data between different network protocols.
Use In Enterprise Networks
Enterprises use gateways to link multiple office networks. They allow secure and efficient communication inside and outside the company.
Gateways help manage data flow between cloud services and local systems. They also support remote work by connecting distant locations securely.
Network Interface Cards
Network Interface Cards (NICs) connect computers to a network. They help devices send and receive data.
NICs come in different types and speeds. They are important for network communication.
Purpose And Types
The main purpose of a NIC is to link a device to a network. It controls data flow between the device and the network.
NICs vary by speed, connection type, and technology. Different types suit different network needs.
- Ethernet NICs connect to wired networks using cables.
- Wireless NICs connect to Wi-Fi networks without cables.
- Fiber NICs use fiber optics for high-speed connections.
- Virtual NICs work within virtual machines for network access.
Installation And Configuration
Installing a NIC usually means plugging it into the computer’s slot. Desktop PCs use PCI or PCIe slots.
After installation, configure the NIC by installing drivers and setting network details. This helps the device work on the network.
- Insert NIC into the correct slot on the motherboard.
- Turn on the computer and install NIC drivers.
- Set IP address and network settings if needed.
- Test the connection to ensure NIC works properly.
Performance Considerations
NIC performance affects how fast data moves on a network. Choose NICs that match your network speed.
Factors like speed, duplex mode, and cable quality impact NIC performance. Good settings improve network reliability.
- Speed: Common speeds are 100 Mbps, 1 Gbps, and 10 Gbps.
- Duplex: Full duplex allows sending and receiving at once.
- Cable type: Use proper cables for the NIC and network type.
- Driver updates: Keep NIC drivers updated for best performance.
Identifying Devices In Practice
Identifying network devices is important for managing any network. It helps keep track of devices and fix problems fast.
You can identify devices by looking at them, using tools, and keeping good records. Each way makes your work easier.
Physical Identification Tips
Look at the device’s shape, size, and ports to tell what it is. Different devices have unique features to spot.
Check the labels or stickers on the device. They often show the model number and manufacturer.
- Notice the number and type of ports
- Look for brand logos or model names
- Observe device size and form factor
- Find serial numbers or MAC addresses on labels
Using Network Tools
Network tools help find devices and get details about them. These tools scan the network and list connected devices.
Tools like network scanners, ping, and traceroute give useful info. They show IP addresses, device names, and types.
- Use network scanners to detect all devices
- Ping devices to check if they are online
- Run traceroute to see device paths
- Use SNMP tools for detailed device data
Labeling And Documentation
Label devices clearly to help identify them later. Use tags or stickers with device names or numbers.
Keep documentation like spreadsheets or diagrams. Record device info such as location, type, and IP address.
- Attach readable labels on each device
- Note device details in a document
- Update records when devices change
- Use diagrams to map device positions
Enhancing It Skills With Device Knowledge
Knowing network devices helps IT workers fix problems faster. It also improves how networks run every day.
Understanding devices like routers and switches builds strong skills. These skills make work easier and more efficient.
Troubleshooting Techniques
Knowing device functions helps find network issues quickly. IT staff can check the right parts without guessing.
Using device knowledge, you can test connections and settings. This reduces downtime and fixes errors faster.
- Identify device roles to isolate problems
- Check device indicators for error signs
- Use device manuals to guide fixes
Optimizing Network Performance
Knowing devices helps adjust settings for better speed. IT staff can balance loads to avoid slowdowns.
Proper use of devices ensures smooth data flow. This keeps the network fast and stable for users.
- Configure routers for efficient traffic routing
- Use switches to reduce network congestion
- Monitor device health to prevent failures
Keeping Up With Technology Trends
Learning about new devices keeps IT skills current. This helps adapt to changes in network technology.
Following trends lets IT workers recommend better hardware. This improves network security and speed.
- Read updates on new network devices
- Attend workshops on emerging technology
- Practice using new tools in test environments
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Common Types Of Network Devices?
Common network devices include routers, switches, hubs, modems, and access points. Each device serves a unique role in managing data flow and connectivity within a network, enhancing communication and performance.
How To Identify A Network Device By Its Function?
Identify network devices by their functions: routers direct traffic, switches connect devices, hubs broadcast signals, and modems translate signals. Understanding these roles helps in recognizing and troubleshooting network components effectively.
Why Is Identifying Network Devices Important?
Identifying network devices ensures proper network setup, security, and maintenance. It helps in diagnosing issues, optimizing performance, and managing resources efficiently, leading to a reliable and secure network environment.
Can Software Tools Help Identify Network Devices?
Yes, software tools like network scanners and monitoring applications can detect and identify devices on a network. These tools provide detailed information, aiding in network management and troubleshooting.
Conclusion
Understanding network devices is crucial for managing any IT setup. Each device plays a key role in connectivity and communication. Routers direct data traffic efficiently. Switches connect devices within the same network. Firewalls protect your data from threats. Identifying these devices helps maintain a secure and efficient network.
Always keep your devices updated. This prevents vulnerabilities and ensures optimal performance. Proper identification can save time and resources. It also enhances security. Stay informed and proactive in managing your network. This will lead to a more reliable and efficient system.
25 min read