Have you ever wondered how your devices get their internet addresses automatically? That’s where a DHCP server comes into play.
Understanding what a DHCP server is can save you time and frustration, especially if you manage a network or want to troubleshoot connection issues. You’ll discover exactly what a DHCP server does and why it’s essential for keeping your devices connected smoothly.
Stick around—you’ll find out how this technology works behind the scenes to make your digital life easier.
Credit: medium.datadriveninvestor.com
Basics Of Dhcp
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. It helps devices get an IP address automatically.
This system makes connecting to networks easy and fast. Devices do not need manual setup for IP addresses.
Role In Network Management
DHCP manages the IP addresses in a network. It assigns addresses so no two devices have the same one.
This helps keep the network organized. It reduces errors and saves time for network administrators.
How Dhcp Works
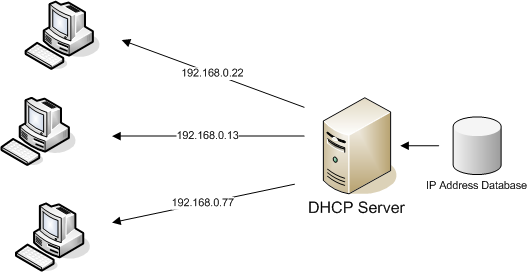
A device sends a request when it joins a network. The DHCP server replies with an IP address.
The device uses the address for a set time called a lease. The server manages these leases automatically.
- Device sends a discovery message
- Server offers an IP address
- Device requests the offered IP
- Server confirms the lease
Dhcp Vs Static Ip
DHCP gives IPs automatically. Static IPs are set by a person and stay the same.
Static IPs are good for devices that need a fixed address. DHCP suits most other devices.
| Feature | DHCP | Static IP |
|---|---|---|
| Setup | Automatic | Manual |
| IP Address | Changes with lease | Fixed |
| Best Use | Most devices | Servers, printers |
| Management | Easier for large networks | Needs more work |

Credit: medium.datadriveninvestor.com
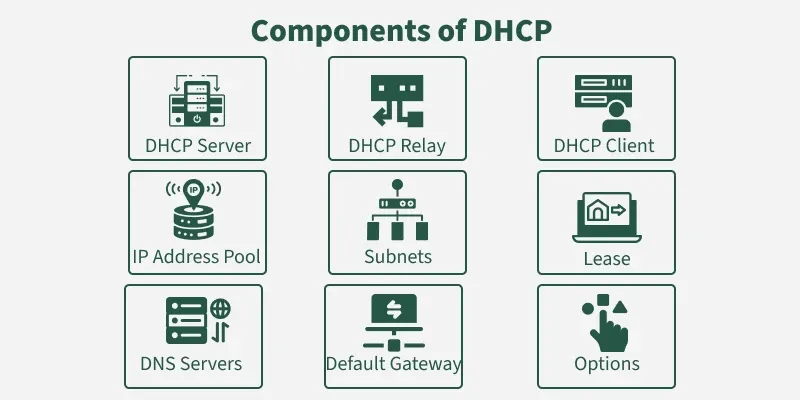
Key Components Of Dhcp Server
A DHCP server helps devices get IP addresses automatically. It manages network settings for many devices.
Understanding its main parts shows how it assigns addresses and settings to devices.
Ip Address Pool
The IP address pool is a set of addresses the server can give out. Each device gets one address from this pool.
The pool limits the number of devices that can connect at the same time. It keeps addresses organized.
Lease Time
Lease time is how long a device can use an IP address. After this time, the address must be renewed or given to another device.
This helps the network recycle addresses and avoid conflicts between devices.
Dhcp Options
DHCP options are extra settings the server sends to devices. These include information like the default gateway and DNS servers.
Options help devices connect properly and use the network services they need.
- Default gateway address
- DNS server addresses
- Subnet mask
- Time server
- Domain name
Setting Up A Dhcp Server
A DHCP server gives IP addresses to devices on a network. It helps devices connect easily.
Setting up a DHCP server needs careful steps. This guide will help you do it right.
Choosing The Right Server
Pick a server that fits your network size. It should handle many devices without slowing down.
Check if your server supports your network type. Some servers work better with certain systems.
- Use a dedicated machine for large networks
- Choose software that is easy to manage
- Consider security features on the server
Configuration Steps
Start by installing DHCP server software on your machine. Follow the setup instructions carefully.
Set the IP address range your server will assign. Avoid conflicts by excluding static addresses.
- Install the DHCP server application
- Define the IP address pool
- Set lease time for IP addresses
- Configure DNS and gateway settings
- Activate the DHCP service
Common Setup Mistakes
One mistake is setting the IP range too small. This causes devices to fail getting addresses.
Another error is not excluding static IPs. This leads to address conflicts on the network.
- Using overlapping IP ranges
- Forgetting to start the DHCP service
- Ignoring firewall rules blocking DHCP traffic
- Not setting correct DNS or gateway info
Dhcp In Network Automation
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. It helps assign IP addresses to devices on a network automatically.
In network automation, DHCP servers play a key role. They reduce manual work and errors in IP address management.
Automating Ip Management
DHCP servers assign IP addresses without human help. This saves time and avoids address conflicts.
Automation lets networks grow easily. Devices get addresses as soon as they connect.
- Auto assign IPs to new devices
- Prevent duplicate IP addresses
- Track IP usage automatically
Integration With Network Tools
DHCP servers work with other network tools. This helps monitor and control the network better.
Integrations allow easy data sharing. Network admins get real-time info on device connections and IP status.
- Connects with network monitoring software
- Supports security tools for device control
- Works with automation scripts and APIs
Benefits For Large Networks
Large networks have many devices. DHCP servers keep IP management simple and error-free.
They reduce manual setup and speed up device onboarding. This helps networks run smoothly every day.
- Handles thousands of IP addresses easily
- Improves network reliability and uptime
- Reduces admin workload and mistakes
Security Aspects Of Dhcp
DHCP servers assign IP addresses to devices on a network automatically. This helps devices connect to the internet or other network resources easily.
While DHCP makes networking simple, it also brings security risks. Understanding these risks helps protect your network.
Potential Threats
Attackers can exploit DHCP to disrupt networks or steal information. Some common threats include fake DHCP servers and IP address conflicts.
- Rogue DHCP servers give wrong IP addresses to users.
- DHCP starvation attacks use up all available IPs.
- Man-in-the-middle attacks intercept network traffic.
- IP conflicts cause network interruptions and errors.
Securing Dhcp Servers
Protecting a DHCP server is important to keep the network safe. This means controlling who can access the server and how it handles requests.
Use tools and settings that check each device before giving it an IP address. Monitor the network for unusual DHCP activity.
- Enable DHCP snooping to filter untrusted devices.
- Use network access control to verify devices.
- Keep DHCP server software updated with patches.
- Limit which devices can connect to the network.
Best Practices
Follow rules that reduce DHCP security risks. These practices help keep the network stable and safe from attacks.
- Assign fixed IP addresses to important devices.
- Use strong passwords for DHCP server access.
- Regularly review DHCP logs for suspicious activity.
- Separate guest and main networks with VLANs.
- Backup DHCP server settings often.
Troubleshooting Dhcp Issues
A DHCP server assigns IP addresses to devices on a network. Sometimes, it can have problems. Troubleshooting helps fix these issues fast.
This guide explains common DHCP problems and tools to find errors. It also shows ways to fix IP assignment failures.
Common Problems
DHCP servers face several common problems. These include no IP address assignment and IP conflicts. Network devices may lose connection.
- Server not responding to client requests
- IP address conflicts on the network
- Lease expiration issues causing disconnections
- Incorrect DHCP scope or settings
- Network hardware failures affecting DHCP communication
Diagnostic Tools
Several tools help find DHCP issues quickly. These tools check if the server works and see IP assignments on clients.
- Ping: Tests if DHCP server is reachable
- IPconfig /renew: Requests a new IP from DHCP
- DHCP logs: Shows errors and lease info
- Wireshark: Captures DHCP network packets
- Network scanner: Detects IP conflicts
Fixing Assignment Failures
Fix DHCP failures by checking network settings and server status. Restarting services often helps. Clear old leases if needed.
- Verify DHCP server is running and reachable
- Check DHCP scope has available IP addresses
- Restart DHCP service to reset processes
- Clear or delete expired or conflicting leases
- Ensure network devices are connected properly
Advanced Dhcp Features
DHCP servers have many features that help manage IP addresses easily. These features improve network efficiency and security.
Understanding advanced DHCP features helps network admins control devices and IP assignments better.
Dhcp Relay Agents
DHCP relay agents forward requests between clients and servers. They work when clients and servers are on different networks.
This feature reduces the need for many DHCP servers in each network segment. Relay agents save resources and simplify setup.
- Listens for DHCP requests from clients
- Forwards requests to the DHCP server
- Sends responses back to clients
- Allows centralized DHCP management
Dynamic Dns Updates
Dynamic DNS updates let DHCP servers automatically update DNS records. This links hostnames with their IP addresses.
It helps keep DNS information current. Devices can be found by name without manual updates.
- Updates DNS when IP addresses change
- Reduces errors in DNS records
- Improves network name resolution
- Works with both forward and reverse DNS zones
Ipv6 Dhcp
IPv6 DHCP works with the new internet protocol version. It assigns IPv6 addresses to devices on a network.
IPv6 DHCP supports more devices and bigger address spaces. It also offers options like prefix delegation and DNS settings.
- Assigns IPv6 addresses automatically
- Supports large networks with many devices
- Works with IPv6 prefix delegation
- Provides DNS and other network info
Future Trends In Dhcp
DHCP servers assign IP addresses automatically to devices on a network. This helps devices connect without manual setup.
As networks grow, DHCP is changing to meet new needs. These changes make DHCP more flexible and easier to manage.
Evolving Protocols
New versions of DHCP are being developed to support more devices and better security. These protocols work with IPv6 and IoT devices.
The updates improve how DHCP handles address leasing and renewals. This reduces errors and network conflicts.
Cloud-based Dhcp Solutions
Cloud DHCP lets organizations manage IP addresses from anywhere. It removes the need for physical servers.
This approach scales easily and supports remote work. It also offers better backup and disaster recovery options.
- Central control of IP addresses
- Faster deployment of network changes
- Lower hardware costs
Automation Enhancements
Automation helps DHCP servers assign addresses faster and with fewer mistakes. It uses AI to predict network needs.
Automatic monitoring alerts admins about issues before they affect users. This keeps networks running smoothly.
- AI-driven IP address management
- Auto-detection of network problems
- Self-healing network configurations
Credit: www.geeksforgeeks.org
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Primary Function Of A Dhcp Server?
A DHCP server automatically assigns IP addresses to devices on a network. It simplifies network management by reducing manual configuration and preventing IP conflicts.
How Does A Dhcp Server Improve Network Efficiency?
It dynamically allocates IP addresses, reducing errors and saving time. Devices can join networks quickly without manual setup, enhancing overall network performance.
Can A Dhcp Server Assign Other Network Information?
Yes, besides IP addresses, DHCP servers provide subnet masks, gateways, and DNS server details. This helps devices communicate effectively within and outside the network.
Is Dhcp Server Necessary For All Networks?
While not mandatory, DHCP servers are essential for large or dynamic networks. Small networks may use static IPs, but DHCP offers convenience and scalability.
Conclusion
Understanding DHCP servers boosts network efficiency. They assign IP addresses automatically. This simplifies network management. Users face fewer connectivity issues. Smooth, uninterrupted internet access becomes a reality. Businesses benefit, too. Reduced IT workload saves time and resources. A key tool in modern networks.
DHCP servers ensure seamless communication. Their role in networks is crucial. Grasping their function enhances tech knowledge. Make networks run smoothly. Easy network management is within reach. No need for complex setups. DHCP servers make things straightforward. A valuable component for any network setup.
18 min read