Imagine your network suddenly goes down, and your business grinds to a halt. What if you had a safety net that keeps your data flowing smoothly, no matter what?
That’s exactly what configuring network backup routes can do for you. You’ll discover simple, practical steps to set up backup routes that protect your network from unexpected failures. Stay with me, and you’ll gain the confidence to keep your network reliable and your work uninterrupted—because your business deserves nothing less.
Credit: www.youtube.com
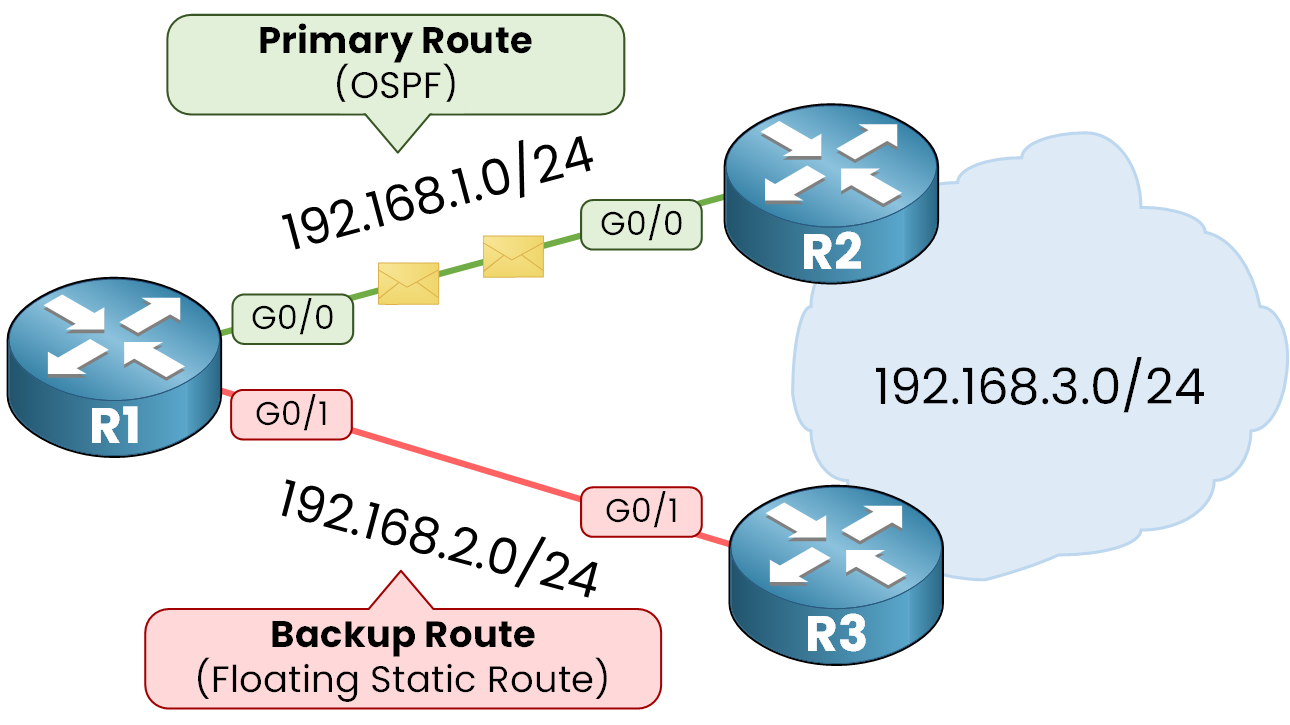
Importance Of Backup Routes
Backup routes are extra paths in a network. They help keep the network running if one path fails.
Configuring backup routes is key to a strong and safe network. It stops problems before they grow.
Minimizing Downtime
Backup routes reduce the time a network is offline. If the main route breaks, traffic switches to the backup quickly.
This fast switch helps users keep working without delays or loss of access.
- Switches data paths automatically
- Prevents long service interruptions
- Keeps business running smoothly
Ensuring Data Integrity
Backup routes protect data from being lost or damaged. They give a safe way to send information if the main path fails.
This makes sure data stays correct and complete during network problems.
- Prevents data loss during failures
- Maintains accurate data transfer
- Supports secure communication
Enhancing Network Reliability
Backup routes make networks more reliable. They give extra paths that keep connections strong and steady.
This reliability helps users trust the network for important tasks and services.
- Reduces chance of network failure
- Improves overall network performance
- Increases user satisfaction
Types Of Backup Routes
Backup routes help keep networks working if the main path fails. They provide a second way to send data.
There are different types of backup routes. Each type works in a unique way to protect the network.
Static Backup Routes
Static backup routes are fixed routes set by a network administrator. They do not change unless manually updated.
These routes are simple to set up. They work well in small or stable networks with few changes.
- Manually configured with a lower priority than main routes
- Used when dynamic routing is not available
- Reliable for predictable network paths
Dynamic Backup Routes
Dynamic backup routes change automatically based on network conditions. Routers share information to find new paths.
This type adapts quickly if the main route fails. It suits large or complex networks with frequent changes.
- Uses routing protocols like OSPF or EIGRP
- Adjusts routes when network devices go down
- Reduces manual work for network admins
Policy-based Routing
Policy-based routing sends traffic based on rules, not just the destination address. It allows custom backup paths.
This method uses policies like source IP or application type. It gives more control over how data flows.
- Defines backup routes by traffic type or source
- Improves network performance and security
- Requires careful planning and configuration
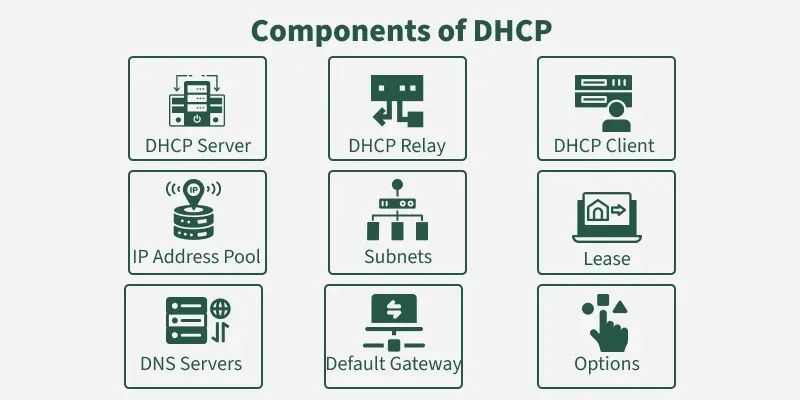
Key Components For Failover
Network backup routes keep data moving if the main path breaks. Failover means switching to a backup route fast.
Good failover needs the right parts working together. This stops downtime and keeps networks stable.
Routing Protocols
Routing protocols help devices find the best path for data. They update routes when changes happen in the network.
Protocols like OSPF and BGP support backup routes. They share route info quickly to avoid delays.
- OSPF: Uses link-state info to find fast backup paths
- BGP: Manages routes between different networks and finds alternatives
- RIP: Simple but slower to react to network changes
Failover Mechanisms
Failover mechanisms switch traffic to backup routes automatically. They keep the network running without manual work.
Common failover types include active-passive and active-active setups. Each type suits different network needs.
- Active-passive: Backup route is idle until needed
- Active-active: Multiple routes run at the same time
- Load balancing: Shares traffic to avoid overloads
Health Checks And Monitoring
Health checks test network paths to see if they work. Monitoring tools watch routes and alert for problems.
Good health checks use ping or heartbeat signals. They find failures fast to trigger failover.
- Ping tests check if a route is reachable
- Heartbeat signals confirm devices are active
- Monitoring software tracks route status in real time
Step-by-step Configuration
Configuring network backup routes helps keep your network stable. It lets traffic flow even if one route fails.
This guide shows how to set up backup routes in three simple steps. Follow these steps to improve your network’s reliability.
Identifying Primary And Backup Paths
Start by finding the main route your data uses. This is the primary path for your network traffic.
Next, choose an alternate route for backup. This path will take over if the primary path fails.
- Check network maps to find possible paths
- Pick the fastest and most stable path as primary
- Choose a different but reliable path as backup
Setting Route Priorities
Assign priorities to your routes to tell the network which to use first. The primary route gets the highest priority.
Lower the priority number for backup routes. This way, the network switches only when the main route is down.
- Use a low number for primary route priority (like 1)
- Assign higher numbers to backup routes (like 10 or 20)
- Confirm the priority settings on your router or switch
Implementing Route Tracking
Route tracking checks if the primary path works. It sends signals to see if the route is active.
If the primary route fails, tracking helps the network use the backup route automatically. This keeps traffic flowing.
- Enable route tracking on your network device
- Set up health checks for the primary route
- Configure automatic failover to the backup route
Tools And Technologies
Configuring network backup routes needs the right tools and technology. These tools help keep data moving if the main path fails.
Using features in routers and switches, automation scripts, and management software makes backup setup easier and more reliable.
Router And Switch Features
Routers and switches have built-in features for backup routes. They detect failures and switch paths fast.
Common features include dynamic routing protocols like OSPF and BGP. These help routers find new paths automatically.
- Failover support to switch routes instantly
- Load balancing to share traffic among paths
- Redundancy protocols like VRRP and HSRP
- Link monitoring for quick failure detection
Automation Scripts
Automation scripts simplify backup route setup and changes. They reduce manual work and errors.
Scripts can run commands on devices to update routes or check status. They work with languages like Python or Bash.
- Automatically update routing tables
- Monitor network health and alert admins
- Schedule backups and failover tests
- Integrate with APIs for seamless control
Network Management Software
Network management software helps control backup routes from one place. It shows network status and route details.
This software helps plan, monitor, and fix network issues. It can automate failover and keep backups ready.
- Visualize network maps and routes
- Alert on route failures or slowdowns
- Automate route changes during outages
- Generate reports for network health
Credit: medium.com
Testing And Validation
Testing and validation are key steps for network backup routes. They ensure routes work correctly during failures.
Proper testing helps avoid downtime and keeps your network reliable.
Simulating Failures
Simulating failures means creating fake problems to test backup routes. This shows if routes switch correctly.
Try shutting down main routes or devices to see if backups take over smoothly.
- Disable primary network links
- Disconnect routers or switches
- Use software tools to mimic failures
- Check if backup routes activate
Monitoring Route Switchover
Monitoring route switchover means watching how quickly the network changes paths. Fast switchover avoids data loss.
Use monitoring tools to track delays and errors during route changes.
- Check network devices’ logs
- Use real-time monitoring software
- Measure time taken for switchover
- Look for packet loss or delays
Analyzing Performance Metrics
Analyze performance metrics to see how well backup routes work. Metrics show network speed and reliability.
Focus on metrics like latency, packet loss, and uptime during tests.
| Metric | What It Shows |
|---|---|
| Latency | Delay in data transmission |
| Packet Loss | Data packets lost during transfer |
| Uptime | How long the route stays active |
| Switchover Time | Speed of switching to backup |
Best Practices
Configuring network backup routes is essential for keeping your network reliable. Backup routes help your network stay connected if the main path fails.
Using best practices ensures your backup routes work well under stress. This guide covers key points to keep your network safe and efficient.
Regular Updates And Maintenance
Keep your network backup routes updated to avoid failures. Regular checks catch problems before they cause outages.
Update routing tables and backup configurations after any network change. Test backup routes often to ensure they work correctly.
- Schedule routine reviews of backup routes
- Apply software updates promptly
- Test failover paths regularly
- Monitor network performance for issues
Documentation And Change Management
Keep clear records of your backup route setups and changes. Good documentation helps teams understand the network layout.
Use change management to track updates. This reduces errors and keeps the network stable.
- Document all backup route configurations
- Log changes with dates and reasons
- Share documentation with your team
- Review changes before applying them
Scalability Considerations
Design backup routes to grow as your network expands. Scalable routes prevent slowdowns and failures.
Plan for more devices and higher traffic. Use flexible routing protocols that handle growth smoothly.
- Choose routing protocols that support scaling
- Use hierarchical network designs
- Plan capacity for future traffic loads
- Review backup routes after network growth
Common Challenges
Configuring network backup routes is important for keeping networks stable. It helps make sure data moves smoothly if the main path fails.
This process can face some common problems. These problems can affect how well the backup routes work and can cause delays or errors.
Route Flapping
Route flapping happens when a network route goes up and down quickly. This causes confusion in the network and can slow down data flow.
Frequent changes make routers use extra resources. This can lower network performance and cause delays in switching to backup routes.
- Causes include unstable links or hardware problems
- Leads to high CPU use on routers
- Can cause network instability and packet loss
Latency Issues
Latency is the delay before data starts moving through the network. High latency in backup routes can slow down communication.
Backup routes often have longer paths. This adds to the time data takes to travel, affecting real-time services like video calls.
- Longer backup paths increase delay
- Network congestion adds to latency
- Poor route selection can cause slow response
Configuration Errors
Errors in network settings can stop backup routes from working. Incorrect IP addresses or wrong routing rules cause failures.
Even small mistakes can block traffic or cause loops. Careful checking and testing of configurations is needed to avoid these problems.
- Wrong subnet masks can misroute data
- Missing backup routes cause no failover
- Incorrect priorities lead to wrong route use
Credit: medium.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Network Backup Route Configuration?
Network backup route configuration involves setting alternative paths for data. It ensures continuous connectivity during primary route failures, enhancing network reliability and uptime.
Why Are Backup Routes Important In Networking?
Backup routes prevent network downtime by providing failover paths. They maintain data flow, improve performance, and protect against single points of failure.
How Do I Configure Backup Routes On Routers?
Configure backup routes by setting route priorities or metrics. Use routing protocols or static routes to define secondary paths for failover.
What Protocols Support Network Backup Routes?
Routing protocols like OSPF, EIGRP, and BGP support backup routes. They automatically switch traffic to backup paths when primary routes fail.
Conclusion
Configuring network backup routes keeps your data safe. It ensures minimal downtime. Backups act as a safety net. They prevent data loss. Regular testing of routes is crucial. It maintains their reliability. A simple and effective setup saves time. It also reduces stress.
Make sure to update configurations as needed. This adapts to network changes. Reliable backups enhance network stability. They also ensure seamless operations. With proper configuration, your network stays secure. It also stays efficient. Invest time in this process. It pays off in long-term security.
Stay proactive with your network management. Keep your data protected.
19 min read