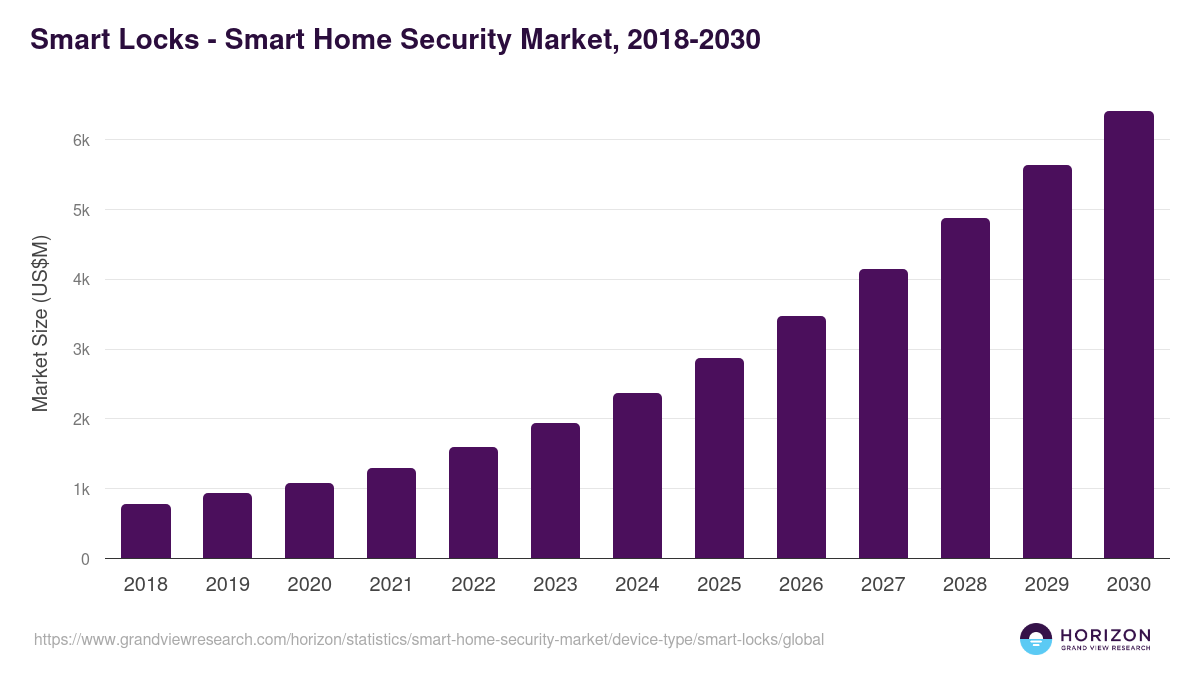
Is your internet slowing down when you need it most? Network congestion can turn simple tasks into frustrating delays.
But what if you could stop this problem before it starts? You’ll discover easy, effective ways to avoid network congestion and keep your connection smooth and fast. Keep reading, and you’ll learn practical tips that make a real difference—no technical jargon, just straightforward advice you can use right now.
Your online experience is about to get a lot better.

Credit: www.expereo.com
Causes Of Network Congestion
Network congestion happens when too much data tries to use the same network. This slows down the internet and causes delays.
Several reasons cause network congestion. Understanding these helps avoid problems and keeps the network running smoothly.
High Traffic Volume
High traffic volume means many devices send data at the same time. This overloads the network and causes slow speeds.
Traffic spikes happen during busy hours or big events. Too many users can cause the network to get congested quickly.
Insufficient Bandwidth
Bandwidth is the data capacity of a network. If bandwidth is too low, it cannot handle all the data traffic.
Low bandwidth causes delays and packet loss. Upgrading bandwidth helps reduce network congestion.
Hardware Limitations
Old or weak network devices cannot handle large data loads. This leads to slow processing and congestion.
Hardware like routers and switches must be updated to support more traffic and faster speeds.
Network Configuration Issues
Wrong network settings can cause data to be delayed or lost. Poor configuration leads to bottlenecks.
Proper setup and regular checks help fix configuration problems and reduce congestion.
Signs Of Network Congestion
Network congestion happens when too much data travels through the network. This causes slowdowns and connection problems.
Knowing the signs of network congestion helps you fix issues faster. Look out for these common problems.
Slow Internet Speeds
Slow internet speeds are a clear sign of congestion. Pages take longer to load, and downloads slow down.
Speed tests show lower than normal results. Streaming videos may buffer often or play in low quality.
Frequent Disconnects
Network congestion can cause your device to lose connection often. This can disrupt work or entertainment.
Wi-Fi signals may drop or switch between networks. Wired connections can also disconnect without warning.
High Latency
High latency means there is a delay in data transfer. This makes online games and video calls lag.
You might notice slow responses when clicking links or sending messages. Latency over 100 ms affects real-time activities.
Packet Loss
Packet loss happens when some data does not reach its destination. This causes errors and poor connection quality.
You may hear choppy sound in calls or see broken video streams. Packet loss is a strong indicator of congestion.
Optimizing Network Hardware
Network congestion slows down internet speed. It causes delays and dropped connections.
Optimizing network hardware helps reduce congestion. It improves overall network performance.
Upgrading Routers And Switches
Old routers and switches may not handle high traffic well. Upgrading to newer models boosts speed.
New devices support faster data transfer and better traffic management. This reduces congestion on the network.
- Choose routers with higher bandwidth capacity
- Use switches that support gigabit speeds
- Select devices with multiple ports for better connections
Using Quality Of Service (qos)
Quality of Service controls how network traffic flows. It gives priority to important data.
QoS settings can reduce delays for video calls or gaming. It helps avoid congestion during peak times.
- Set higher priority for real-time applications
- Limit bandwidth for less important services
- Adjust QoS rules based on user needs
Regular Firmware Updates
Firmware updates improve device performance and security. They fix bugs that may cause slowdowns.
Keeping routers and switches updated ensures smooth traffic flow. Updates add new features for better handling.
- Check for updates regularly
- Install updates during low network use
- Follow manufacturer instructions carefully
Proper Placement Of Devices
Where you place routers and switches affects signal quality. Poor placement causes weak connections.
Place devices in open areas and away from metal objects. This reduces interference and improves speed.
- Keep devices central to the coverage area
- Avoid placing near microwaves or cordless phones
- Elevate devices for better signal reach
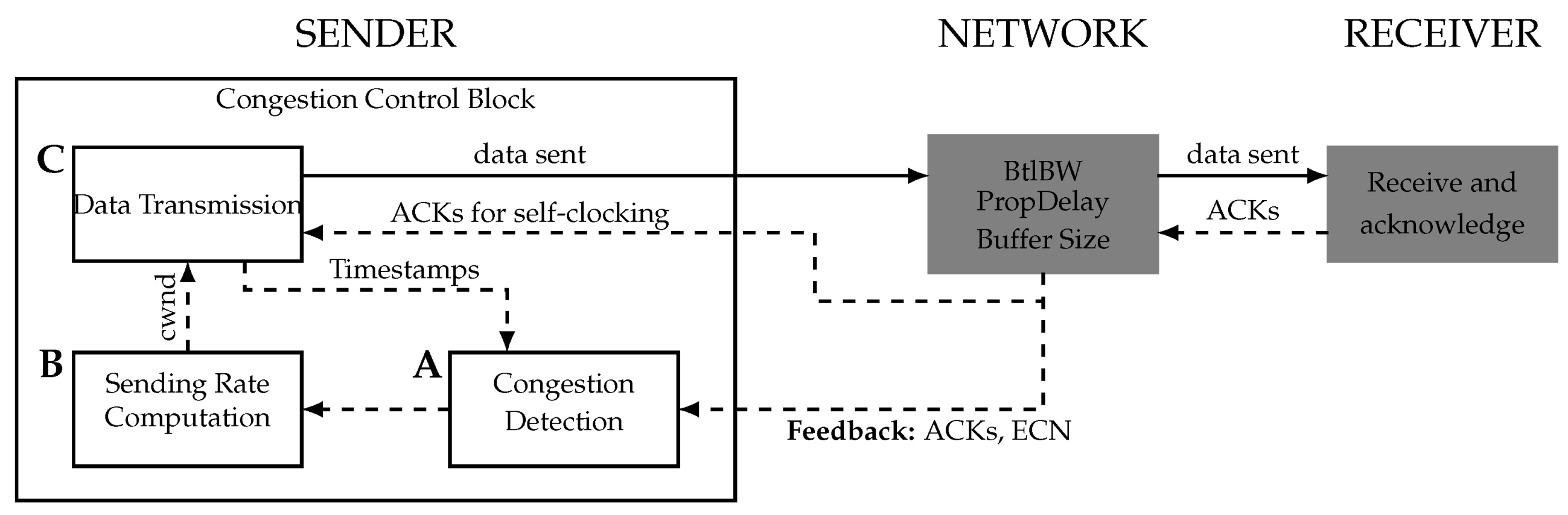
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Managing Network Traffic
Network congestion slows down data flow and causes delays. Managing traffic helps keep networks fast and reliable.
Good traffic management controls data flow and prevents overload. This improves user experience and service quality.
Traffic Shaping Techniques
Traffic shaping controls data flow by delaying some packets. It smooths out bursts and avoids network overload.
This method ensures important data moves smoothly while less urgent traffic waits. It balances network use efficiently.
- Delay low-priority traffic during peak times
- Limit data rate for certain applications
- Use buffers to handle sudden traffic spikes
Prioritizing Critical Applications
Some applications need fast network access to work well. Prioritizing these apps reduces delays and failures.
Networks assign higher priority to important traffic. This ensures critical apps get enough bandwidth to run smoothly.
- Voice calls get priority to avoid lag
- Video conferences use higher bandwidth
- File downloads run with lower priority
Load Balancing Methods
Load balancing spreads network traffic across multiple paths. This stops any one link from getting overloaded.
It helps use network resources evenly. This improves speed and prevents bottlenecks.
- Distribute traffic based on current network load
- Use multiple servers to share user requests
- Switch to backup links if one fails
Implementing Bandwidth Limits
Setting bandwidth limits stops users from using too much data. This protects network speed for everyone.
Limits can be set by user, device, or application. This controls traffic and reduces congestion risk.
- Limit streaming quality during busy hours
- Cap data use for guest devices
- Restrict large file transfers on slow links
Improving Network Configuration
Network congestion slows down data flow and affects user experience. Improving network configuration helps avoid these issues.
Good configuration keeps the network fast and reliable. It reduces delays and packet loss.
Segmentation And Vlans
Segmentation divides a large network into smaller parts. VLANs (Virtual LANs) separate traffic logically without extra hardware.
This reduces congestion by limiting broadcast domains. Devices in one VLAN do not send traffic to others unless needed.
- Improves security by isolating sensitive data
- Reduces unnecessary traffic between devices
- Makes network easier to manage and troubleshoot
Optimizing Ip Addressing
Use IP addressing schemes that fit your network size. Avoid large subnets that increase broadcast traffic.
Proper subnetting creates smaller groups of devices. This controls traffic and improves overall performance.
- Assign IP ranges logically by location or department
- Use DHCP to manage addresses automatically
- Plan for future growth to avoid reconfigurations
Reducing Broadcast Traffic
Broadcast traffic reaches all devices in a subnet. High broadcast levels cause congestion and slow the network.
Limit broadcast domains with VLANs and smaller subnets. Disable unnecessary protocols that generate extra broadcasts.
- Use switches instead of hubs to reduce collisions
- Turn off unused services like NetBIOS or SSDP
- Monitor broadcast storms and fix their sources quickly
Monitoring And Analysis Tools
Use tools to watch network traffic and spot congestion early. Monitoring helps find problems before they worsen.
Analyze data to adjust settings and improve flow. Tools show which devices or apps use the most bandwidth.
- Network analyzers track packet flow and errors
- SNMP tools provide device status and alerts
- Traffic monitors identify bandwidth hogs
Preventive Measures
Network congestion slows down data flow and affects user experience. Preventive measures keep networks running smoothly.
Taking steps early helps avoid delays and reduces downtime in your network.
Regular Network Audits
Network audits check the health and performance of your system. They find weak spots before problems start.
Audits help track traffic patterns and spot unusual activity that could cause congestion.
- Review bandwidth use monthly
- Check hardware and software updates
- Analyze traffic flow and bottlenecks
Capacity Planning
Capacity planning predicts network needs based on growth and usage trends. It helps avoid overloads.
Adding resources before reaching limits keeps the network fast and reliable.
- Estimate future traffic volumes
- Upgrade bandwidth and hardware as needed
- Plan for peak usage times
Employee Training
Training employees improves network use and security. They learn to avoid actions that cause congestion.
Well-informed staff can spot and report network issues early.
- Teach proper data usage rules
- Explain safe internet practices
- Train on recognizing network problems
Using Advanced Security Protocols
Security protocols block unwanted traffic and attacks that slow networks. They keep data flowing smoothly.
Strong security reduces risks of congestion caused by malware or hackers.
- Use firewalls and intrusion detection
- Apply encryption for data protection
- Regularly update security software

Credit: blog.devops.dev
Frequently Asked Questions
What Causes Network Congestion?
Network congestion occurs when data traffic exceeds a network’s capacity. This can be due to high demand, inefficient routing, or outdated infrastructure. Heavy usage during peak times also contributes to congestion, slowing down network performance.
How Can I Monitor Network Traffic?
Monitoring network traffic involves using tools like Wireshark or NetFlow. These tools help analyze data flow, identify bottlenecks, and optimize performance. Regular monitoring ensures network efficiency and helps prevent congestion.
What Is The Role Of Qos In Congestion?
Quality of Service (QoS) prioritizes critical data traffic, ensuring essential services receive bandwidth. By managing traffic effectively, QoS reduces congestion and improves overall network performance. Implementing QoS policies helps maintain efficient data flow.
How Do Load Balancers Prevent Congestion?
Load balancers distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers. This reduces strain on any single server, preventing congestion. By optimizing resource use, load balancers improve network efficiency and reliability.
Conclusion
Avoiding network congestion keeps your internet fast and reliable. Regularly check your devices and update software to prevent slowdowns. Manage traffic by prioritizing important tasks and limiting heavy downloads. Using wired connections can also reduce congestion. Small steps make a big difference in network performance.
Stay proactive to enjoy smooth and steady online experiences every day.
16 min read