Have you ever wondered why your internet feels slow or why a website won’t load? Knowing how to ping and trace route can give you quick answers.
These simple tools help you check if your connection is working and find where problems might be hiding. You’ll learn easy steps to use ping and trace route like a pro. By the end, you’ll have the power to fix many common network issues all by yourself.
Ready to take control of your internet? Let’s dive in!
Ping Basics
Ping is a simple tool to check if a device is online. It helps test the connection between computers.
This tool sends small messages and waits for a reply to measure the network speed and quality.
What Ping Does
Ping checks if a computer or server is reachable over a network. It shows if the device is active.
It also measures how long it takes to send a message and get a response back.
- Tests network connectivity
- Measures response time
- Helps find connection problems
How Ping Works
Ping sends a small packet called an ICMP Echo Request to the target device.
The target device replies with an ICMP Echo Reply if it is online and working.
- The time between sending and receiving shows the network delay.
- If no reply comes, the device may be offline or blocked.
- Ping repeats the process several times to check consistency.
Common Ping Commands
Most computers use the command line to run ping. The command is simple and quick.
Here are some common ping commands and what they do.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| ping [IP or domain] | Sends 4 ping requests by default |
| ping -t [IP or domain] | Ping continuously until stopped (Windows) |
| ping -c [number] [IP or domain] | Send a set number of pings (Linux/macOS) |
| ping -i [seconds] [IP or domain] | Set wait time between pings |

Credit: apps.apple.com
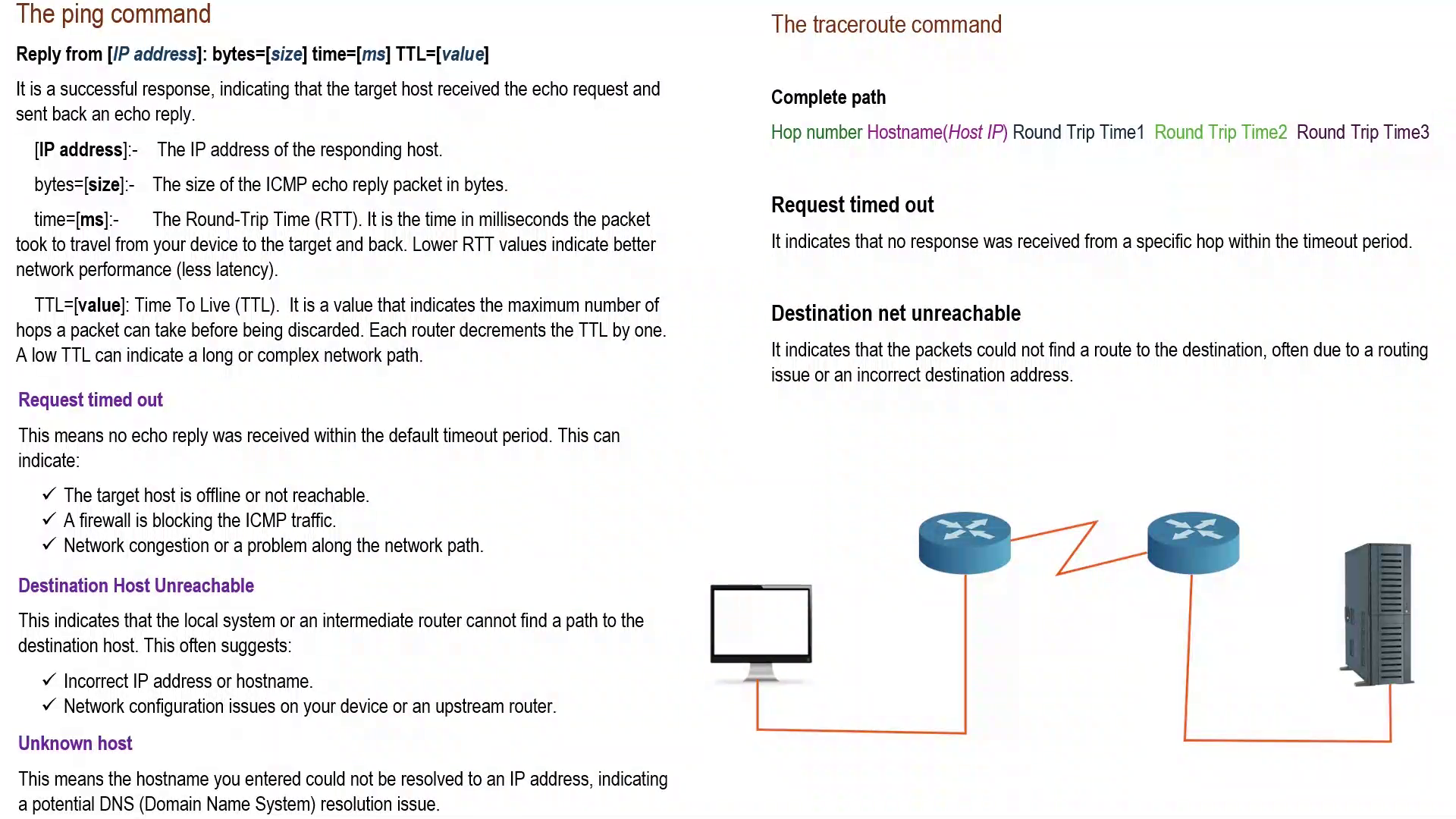
Trace Route Essentials
Trace route is a tool that shows the path data takes on the internet. It helps find where delays or problems happen.
This tool is useful for network troubleshooting and understanding how data moves between computers.
Purpose Of Trace Route
Trace route finds the route data takes from your device to a website or server. It shows each step along the path.
This helps find where slowdowns or failures happen in the network connection.
How Trace Route Operates
Trace route sends small data packets with increasing time limits. Each device on the path sends back a reply.
This way, trace route learns about each hop between your device and the target address.
- Packets start with a low time to live (TTL)
- Each hop reduces TTL by one
- When TTL reaches zero, the hop sends a response
- Trace route records the time and address of each hop
Key Trace Route Commands
Different systems use commands to run trace route. These commands show the path and time for each hop.
- Windows:Use
tracert [address] - Mac/Linux:Use
traceroute [address] - You can add options to change packet size or max hops
- Common options help diagnose network issues clearly
Running Ping Tests
Ping tests check if a device can reach another device on a network. They help find connection problems.
Running a ping test sends small data packets to a target. It then measures how long they take to return.
Using Ping On Windows
Open the Command Prompt to run ping on Windows. Type pingfollowed by the website or IP address.
The command sends four test packets by default. You see the time each packet took to return.
- Press Windows key + Rto open Run.
- Type
cmdand press Enter. - Type
ping example.comand press Enter. - Read the results shown in the window.
Using Ping On Mac And Linux
Open the Terminal app on Mac or Linux to use ping. Type pingwith the target address.
Ping keeps running until you stop it with Ctrl + C. You can add options to send a set number of packets.
- Open Terminal from Applications or press
Ctrl + Alt + Ton Linux. - Type
ping example.comand press Enter. - To send 4 packets, use
ping -c 4 example.com. - Stop the test with
Ctrl + Cif needed.
Interpreting Ping Results
Ping results show if the target is reachable and how fast it responds. Look for time and packet loss.
Low time means a fast connection. Packet loss means some data did not reach the target.
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Reply from | The target responded to the ping. |
| Time | How long the packet took in milliseconds. |
| TTL (Time to Live) | Number of hops the packet can take before being discarded. |
| Request timed out | No response from the target. |
| Packet loss | Percentage of packets lost during the test. |

Credit: www.youtube.com
Executing Trace Route Checks
Trace route helps find the path data takes to reach a website or server. It shows each stop between your computer and the target.
This tool is useful to check network problems and delays in data travel. You can run trace route on different operating systems.
Trace Route On Windows
Open the Command Prompt on your Windows PC. You can do this by typing “cmd” in the search bar and pressing Enter.
Type tracertfollowed by the website or IP address you want to check. Press Enter to start the trace route.
- Example:
tracert google.com - Each line shows a hop from your PC to the target.
- Look for delays or errors in the results.
Trace Route On Mac And Linux
Open the Terminal app on your Mac or Linux system. You can find it in the Utilities folder or use a search tool.
Type traceroutefollowed by the website or IP address. Press Enter to run the trace route command.
- Example:
traceroute google.com - Results show each step the data takes to reach the target.
- Check for any long delays or missing hops.
Analyzing Trace Route Output
Each line in the trace route shows a hop. A hop is a stop at a router or server between you and the target.
Look at the time values on each hop. High numbers show delays or slow network parts. Asterisks mean the hop did not respond.
- Low times mean fast connections
- High times may cause slow loading or errors
- Missing hops can mean network blocks or issues
Advanced Tips
Ping and trace route are tools to check network paths and delays. Using them well helps find network problems quickly.
This guide gives tips for advanced use of ping and trace route. It helps fix latency, packet loss, and more.
Troubleshooting Network Latency
Network latency means delays in data travel between devices. Ping shows how long data takes to reach a target.
To find latency issues, use multiple ping tests over time. Look for high or changing response times.
- Run ping to different targets to compare delays
- Check ping times during busy network hours
- Use the “-t” option on Windows to ping continuously
- Look for spikes or slow responses that last
Identifying Packet Loss
Packet loss means some data packets do not reach their destination. This causes slow or broken connections.
Ping helps spot packet loss by showing missed replies. Losing even a few packets can cause problems.
- Run ping tests with many packets (e.g., 100 packets)
- Use the “-n” option on Windows or “-c” on Linux to set packet count
- Check the summary for lost packets and loss percentage
- Trace route can show where packets are lost on the path
Combining Ping And Trace Route
Ping checks if a device responds and how fast. Trace route shows the path packets take to reach that device.
Use both tools to find where delays or packet loss happen on the network path.
- Start with trace route to map the route and find slow hops
- Ping each hop to test its response time and packet loss
- Compare ping times along the route to spot problem points
- Use repeated tests to confirm consistent issues
Tools And Alternatives
Ping and traceroute are common tools to check network connections. They help find if a device is reachable and how data moves through the network.
Besides built-in commands, many tools and apps offer easier ways to use ping and traceroute. These tools show results clearly and add extra features.
Third-party Network Tools
Third-party tools provide more detailed network testing than basic commands. They work on many platforms and offer extra options.
Examples include software that can run ping and traceroute tests with advanced settings and save the results for later review.
- PingPlotter: Combines ping and traceroute with graphs
- WinMTR: Simple tool showing live traceroute and ping stats
- Angry IP Scanner: Scans networks and includes ping tests
Graphical Interfaces For Diagnostics
Graphical user interfaces (GUIs) make network tools easier to use. They show ping and traceroute results in charts and maps.
These interfaces help users understand network issues quickly by visualizing data paths and response times.
- VisualRoute: Displays traceroute on world maps
- SolarWinds Ping Sweep: Network scanner with GUI
- Network Analyzer Pro: Combines tools in one app
Mobile Apps For Network Testing
Mobile apps let you run ping and traceroute tests on smartphones or tablets. They are useful for testing networks on the go.
These apps often include extra tools like port scanning and network speed tests to help diagnose problems quickly.
- Fing: Network scanner with ping and traceroute
- PingTools Network Utilities: Multiple network test tools
- Net Analyzer: Easy-to-use network diagnostics

Credit: www.youtube.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Purpose Of Pinging?
Pinging helps check the connectivity between two devices over a network. It sends packets to a target IP and measures response time. This tool is crucial for troubleshooting network issues and ensuring devices are reachable. Quick response times indicate a healthy connection, while delays suggest potential network problems.
How Does Traceroute Work?
Traceroute tracks the path data packets take to reach a destination. It reveals each hop along the route, showing transit delays. This tool helps diagnose network issues by identifying bottlenecks or failures. By understanding the path, users can optimize or troubleshoot network connections effectively.
Why Is Traceroute Important In Networking?
Traceroute identifies the path data takes across a network. It shows each hop and measures delays. This information helps in diagnosing network issues and optimizing performance. By understanding where delays occur, network administrators can address problems and improve overall connectivity.
Can Ping And Traceroute Improve Network Performance?
Ping and traceroute diagnose network issues, but they don’t directly improve performance. They identify connectivity problems and path delays. By analyzing this data, network administrators can make informed decisions to optimize or troubleshoot networks, leading to better performance over time.
Conclusion
Ping and trace route help find network problems fast. They show where data travels and where it stops. Anyone can use these tools with simple commands. Practice them to understand your internet better. These steps improve your troubleshooting skills. Keep exploring to fix connection issues easily.
Your network’s health depends on these tests. Try ping and trace route next time. You will see the difference.
18 min read