Imagine your network suddenly goes down at the worst possible moment. How quickly can you bounce back?
If you want to keep your business running smoothly and avoid costly downtime, having solid network failover strategies is essential. You’ll discover simple yet powerful ways to protect your network. These strategies will help you stay connected, keep your data safe, and give you peace of mind.
Ready to make your network stronger and more reliable? Let’s dive in.
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Network Failover Basics
Network failover helps keep systems running when a connection breaks. It switches to backup links to avoid downtime.
Failover is important for businesses that need constant internet or network access. It prevents data loss and service interruptions.
What Is Network Failover
Network failover is a process that changes network traffic to a backup system. It works when the main network fails.
This process helps keep websites, applications, and services online without stopping or losing data.
Importance Of Failover
Failover keeps networks reliable and available. It helps avoid business losses caused by downtime.
It also improves user experience by providing continuous access to online services and data.
Types Of Failover Mechanisms
There are different ways to switch to backup networks. Each type works best for certain systems.
- Automatic Failover:Switches to backup without human help.
- Manual Failover:Needs a person to change the network.
- Hot Standby:Backup runs ready at the same time as the main system.
- Cold Standby:Backup starts only after failure happens.
Common Failover Techniques
Network failover helps keep systems working during failures. It switches connections to a backup system.
Many techniques exist to handle failover. Each works best in different situations.
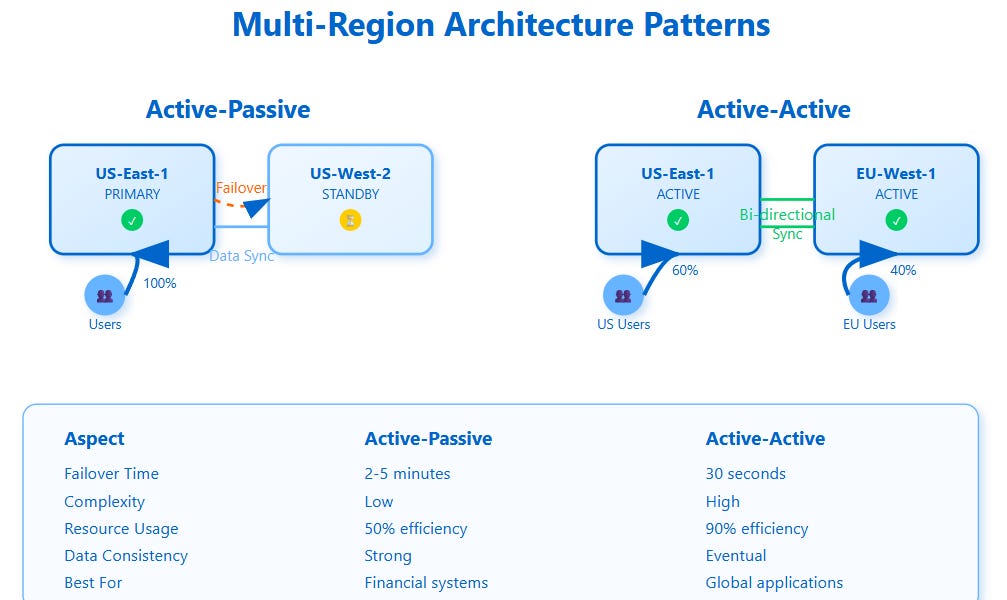
Active-passive Setup
In this setup, one system is active and handles traffic. The other system stays idle as a backup.
If the active system fails, the passive system takes over. This switch usually happens quickly.
- Simple to configure and manage
- Backup system uses no resources until needed
- Failover may cause a short downtime
Active-active Setup
Both systems run at the same time and share the load. They back each other up if one fails.
This setup improves resource use and reduces downtime. It needs more complex management.
- Higher availability and faster failover
- Load is balanced between systems
- Requires synchronization between systems
Load Balancing Approaches
Load balancers distribute traffic across multiple servers. They help prevent overload and failures.
If one server fails, the load balancer redirects traffic to others. This keeps services running smoothly.
- Round-robin sends requests in order
- Least connections send to the least busy server
- IP hash sends requests based on client IP
Failover Protocols
Failover protocols help networks stay online if one part fails. They switch traffic to backup systems quickly.
These protocols keep services running without interruption. They are key for reliable network performance.
Vrrp And Hsrp
VRRP and HSRP are protocols that manage router failover. They let routers work together for backup.
VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol) creates a virtual router. One router acts as the main, others as backups.
HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol) is similar but made by Cisco. It also uses a virtual router IP for failover.
- Both use a virtual IP address shared by routers
- Main router handles traffic normally
- Backup router takes over if main fails
- Failover happens quickly to avoid downtime
Bgp For Failover
BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) controls how data moves between networks. It can reroute traffic during failures.
BGP detects if a network path is down. It then chooses another path to keep data flowing smoothly.
- Used by internet service providers and big networks
- Shares routing info to find best paths
- Switches routes if a link or device fails
- Supports multiple failover paths for reliability
Link Aggregation Control Protocol
Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) combines several network links. This creates one logical link for more speed and backup.
If one link in the group fails, traffic moves to the others. This keeps the network connected without stopping data flow.
- Aggregates multiple physical links into one
- Increases bandwidth and provides failover
- Detects link failures automatically
- Works with switches and routers that support LACP
Designing Failover Systems
Network failover systems keep services running when problems happen. They switch to backup systems fast.
Good design helps avoid downtime and data loss. It ensures users have a smooth experience.
Redundancy Planning
Redundancy means having extra hardware and paths. This prevents a single failure from stopping your network.
Plan backup routers, switches, and internet connections. Use diverse paths to avoid common failures.
- Use multiple internet service providers
- Have backup power supplies
- Duplicate critical hardware components
- Place backups in different locations
Failover Testing Methods
Testing failover ensures the system works in an emergency. Test often to find problems early.
Run tests that simulate failures without affecting users. Check if systems switch over smoothly.
- Perform planned failover drills
- Use automated failover testing tools
- Check failover time and recovery speed
- Review logs for errors during tests
Monitoring And Alerts
Monitoring keeps track of network health in real time. Alerts notify staff when issues arise.
Use clear alerts for failures and slow performance. Quick responses reduce downtime.
- Set up monitoring for all key devices
- Create alerts for link failures and errors
- Use dashboards to view network status
- Test alert systems regularly
Challenges And Solutions
Network failover strategies help keep systems running during failures. They switch traffic to backup systems quickly.
Failover faces many challenges. We will look at some common problems and how to solve them.
Latency And Downtime Issues
Latency can slow down failover response. High delay causes longer downtime and user frustration.
To reduce latency, place backup servers close to users. Use fast detection tools to spot failures early.
- Deploy backups in multiple locations
- Use monitoring to detect issues fast
- Automate failover to cut delay
- Test failover regularly to find slow points
Handling Split-brain Scenarios
Split-brain happens when two network parts think they are main. It causes data conflicts and errors.
Prevent split-brain by using clear master election rules. Use quorum systems to decide which side stays active.
- Set priority for active nodes
- Use quorum or voting mechanisms
- Monitor network links to detect splits
- Automate recovery to fix split-brain fast
Security In Failover Networks
Failover networks must stay secure during switchovers. Unprotected failovers risk data leaks or attacks.
Encrypt data between primary and backup systems. Use strong access controls and keep software updated.
- Use VPN or encrypted tunnels for backups
- Apply strict authentication for failover tools
- Regularly update security patches
- Monitor failover activity for unusual events

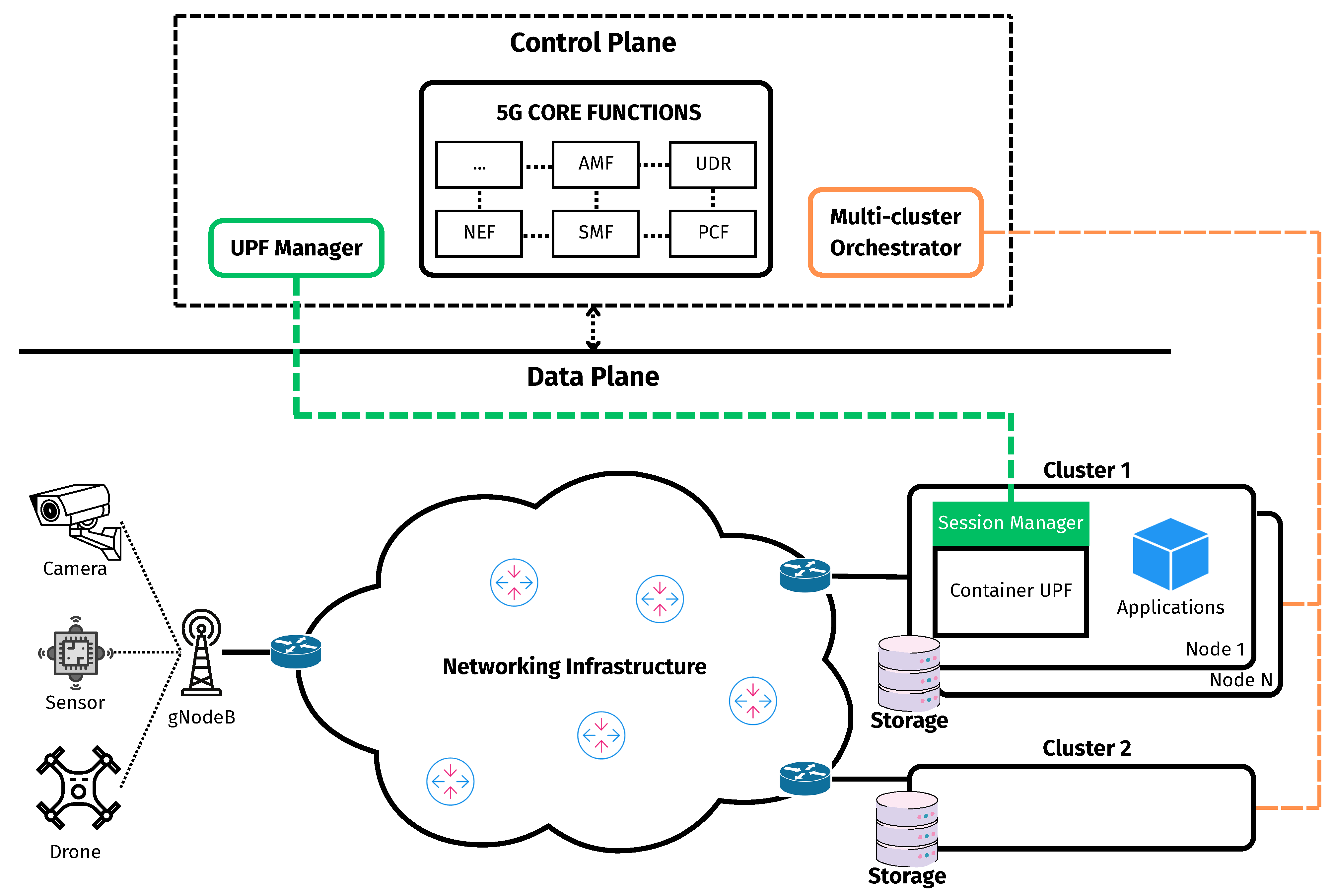
Credit: medium.com
Real-world Applications
Network failover strategies help keep systems running during outages. They switch traffic to backup networks quickly.
Different setups need different approaches. We will look at how failover works in real settings.
Enterprise Networks
Enterprises use failover to avoid downtime that can cost money. They often use multiple connections and routers.
Failover tools monitor network health. If one link fails, traffic moves to a backup instantly.
- Use redundant routers and switches
- Employ dynamic routing protocols like OSPF or BGP
- Monitor network status continuously
- Test failover systems regularly
Cloud Infrastructure
Cloud providers use failover to keep services available. They spread resources across many data centers.
If one server or region goes down, traffic moves to another place. This keeps apps running without delay.
- Use multiple availability zones
- Deploy load balancers for traffic distribution
- Automate failover with cloud management tools
- Keep data synchronized across sites
Isp Failover Strategies
Businesses rely on internet service providers (ISPs). Failover helps switch between ISPs if one fails.
This keeps internet access stable. Failover can be automatic or manual depending on the setup.
- Use dual ISP connections for redundancy
- Configure routers to detect ISP outages
- Switch traffic automatically to the active ISP
- Test failover regularly to ensure uptime
Future Trends
Network failover strategies are evolving with new technology. These changes help keep systems online during failures.
Future trends focus on smarter, faster, and more flexible failover methods. This improves network reliability and user experience.
Ai-driven Failover
AI helps networks detect problems quickly. It can predict failures before they happen and switch to backup systems.
AI learns from past incidents to improve decision-making. This reduces downtime and keeps data safe.
- Real-time monitoring with AI
- Automatic failover decisions
- Reduced human intervention
Software-defined Networking
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) separates control from hardware. This allows quick changes to network paths during failure.
SDN makes networks more flexible and easier to manage. It can reroute traffic automatically to avoid problems.
- Centralized control for failover
- Dynamic traffic management
- Better resource use during outages
Edge Computing Impact
Edge computing moves data processing closer to users. This reduces delay and helps failover happen faster.
Networks with edge devices can handle failures locally. This lowers the risk of large-scale outages.
- Local failover at edge nodes
- Faster recovery times
- Less load on central servers
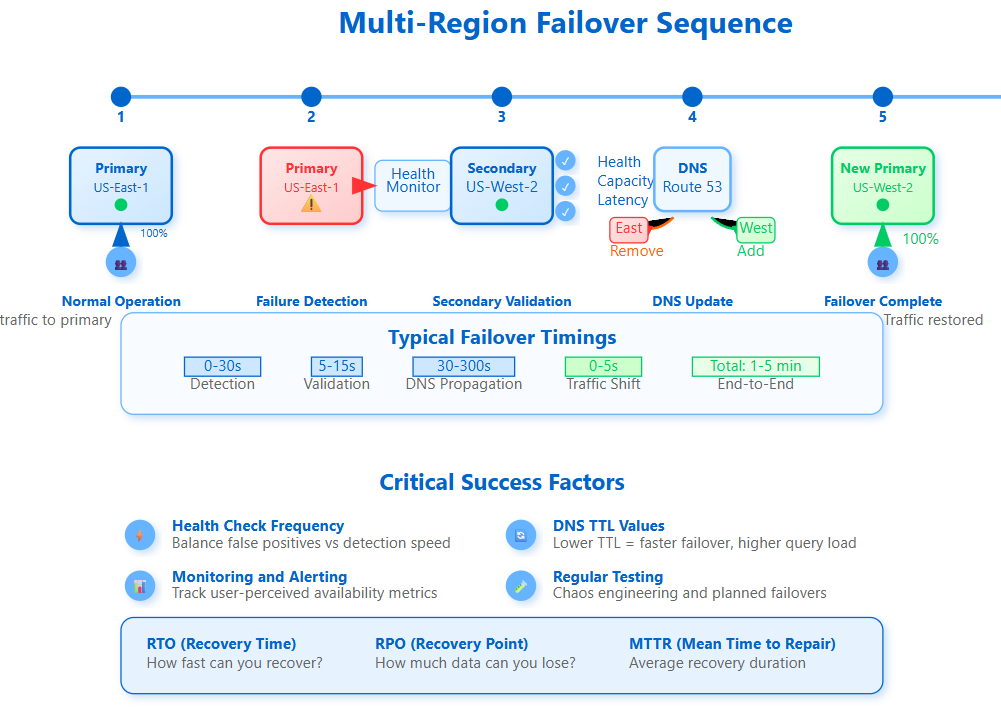
Credit: systemdr.substack.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Network Failover And Why Is It Important?
Network failover automatically switches to a backup connection when the primary fails. It ensures continuous network availability. This prevents downtime, data loss, and service disruption. Failover is crucial for businesses that rely on stable internet and network services.
How Do Network Failover Strategies Improve Reliability?
Failover strategies provide alternative paths for data during outages. They reduce downtime by quickly switching to backup systems. This boosts network resilience and user experience. Effective failover planning minimizes risks and maintains business continuity.
What Are Common Types Of Network Failover Methods?
Common methods include active-passive, active-active, and load balancing failovers. Active-passive uses a standby connection, while active-active runs multiple active links. Load balancing distributes traffic across connections. Each method suits different network needs and budgets.
How To Choose The Best Failover Strategy For Your Network?
Assess your network size, critical applications, and budget. Consider speed of failover, complexity, and maintenance needs. Choose strategies that align with your business goals. Testing and monitoring ensure the chosen method works effectively.
Conclusion
Network failover strategies keep your systems running without pause. They help avoid downtime and protect data. Choose a plan that fits your network size and needs. Test your setup often to ensure it works well. Simple steps can prevent big problems later.
Stay prepared and keep your network strong. Reliable failover means less stress and smooth operations.
17 min read