Have you ever noticed your video calls freezing or your online game lagging at the worst moments? The culprit might be network packet loss.
When your data packets fail to reach their destination, it disrupts your entire online experience. Understanding what causes packet loss can help you fix these frustrating issues and keep your connection smooth. You’ll discover the main reasons behind network packet loss and learn how to tackle them effectively.
Keep reading to take control of your network and say goodbye to those annoying interruptions.
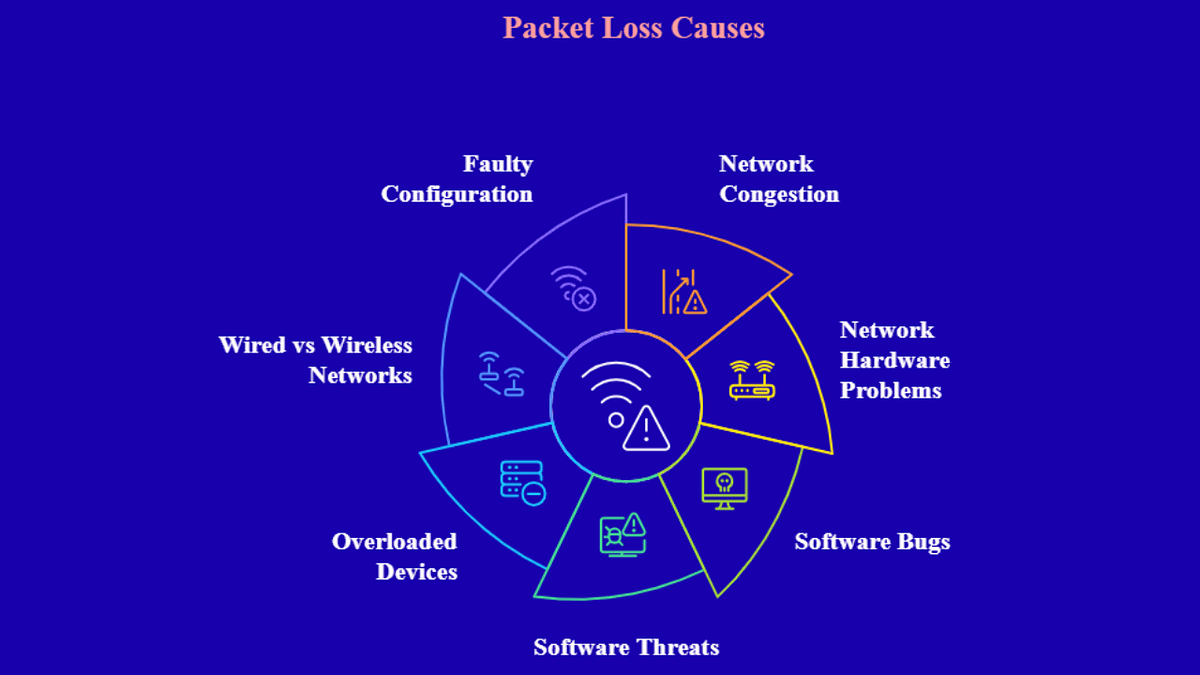
Common Causes Of Packet Loss
Packet loss happens when data packets do not reach their destination. This problem can slow down your internet and cause interruptions.
Understanding what causes packet loss helps you fix network issues faster. Several common reasons can lead to this problem.
Hardware Failures
Hardware problems like broken routers or damaged network cards cause packet loss. These devices may stop sending or receiving data correctly.
Old or worn-out hardware also increases the chance of losing packets during transmission.
Network Congestion
Too many devices using the network at once can overload it. This congestion causes delays and lost packets.
High traffic can happen during peak hours or when many users stream videos or download files simultaneously.
Faulty Cables And Connectors
Damaged or poor-quality cables and connectors reduce data signal strength. This damage leads to packet loss.
- Cracked or bent cables
- Loose connectors
- Old cables not meeting speed standards
Wireless Interference
Wireless signals can be blocked or weakened by walls, other devices, or appliances. This interference causes packets to drop.
Common sources include microwaves, cordless phones, and nearby Wi-Fi networks.
Software Bugs And Configuration Errors
Errors in network software or wrong settings can cause packet loss. These bugs affect how data is sent or received.
Incorrect firewall rules or outdated drivers often cause problems in data flow.
Overloaded Routers And Switches
Routers and switches can only handle a certain amount of traffic. Too much data causes overload and packet drops.
Devices working beyond their capacity fail to forward packets properly.
Isp Issues
Sometimes, your Internet Service Provider has network problems. These issues cause packet loss outside your control.
ISP maintenance, faulty equipment, or routing errors can interrupt data transfer.
Impact Of Packet Loss On Network Performance
Packet loss happens when data packets fail to reach their destination. This issue can slow down your network and cause problems.
Even a small amount of packet loss can affect how well your network works. It can change how fast and reliable your internet feels.
Reduced Data Throughput
Packet loss lowers the amount of data sent successfully over a network. This means less information moves in the same time.
When packets are lost, devices resend data. This reduces the overall speed and efficiency of the network connection.
Increased Latency
Packet loss causes delays in data transmission. When packets fail, the network waits to resend them, adding extra time.
Higher latency means slower response times. This delay can affect real-time services like video calls and online gaming.
Application Performance Degradation
Applications may work poorly when packets are lost. They may freeze, crash, or show errors due to missing data.
Critical apps like VoIP and streaming rely on steady data. Packet loss disrupts their normal function and lowers quality.
User Experience Issues
Users notice packet loss as slow loading or interruptions. This can cause frustration and reduce satisfaction with the network.
Bad user experience can happen in websites, apps, and online services. Consistent packet loss harms trust and usability.
Tools To Detect Packet Loss
Packet loss happens when data packets fail to reach their destination. It can cause slow internet and poor call quality.
Using the right tools helps find where packet loss occurs. These tools check network health and diagnose issues.
Ping And Traceroute
Ping checks if a device is reachable by sending small data packets. It shows if packets are lost or delayed.
Traceroute tracks the path packets take to reach a target. It helps find where packet loss happens along the route.
- Ping measures packet loss and round-trip time.
- Traceroute identifies problematic network hops.
- Both are simple and built into most systems.
Network Analyzers
Network analyzers monitor traffic and check for packet loss in real time. They provide detailed reports.
These tools help spot patterns and pinpoint devices causing loss. They are useful for large networks.
- Show live data flow and error rates.
- Help troubleshoot network devices and links.
- Offer visual graphs and alerts.
Snmp Monitoring
SNMP stands for Simple Network Management Protocol. It gathers data from devices like routers and switches.
SNMP tools track packet loss by reading device counters. They give early warnings about network problems.
- Collect data automatically from many devices.
- Monitor bandwidth and error rates continuously.
- Send alerts when packet loss exceeds limits.
Packet Capture Tools
Packet capture tools record all data packets on a network. They let you analyze lost or corrupted packets deeply.
These tools are useful for detailed troubleshooting. They show exact packet details and timing.
- Capture packets for later analysis.
- Identify packet loss causes like collisions or errors.
- Require technical knowledge to interpret data.

Credit: splitpoint.io
Quick Fixes For Packet Loss
Packet loss happens when data packets do not reach their destination. This can cause slow internet and poor connections.
Some simple fixes can help reduce or stop packet loss quickly. Try these easy steps to improve your network.
Restarting Network Devices
Turning off your modem and router can clear errors and reset connections. This often solves packet loss issues fast.
Wait 30 seconds before turning them back on. This lets devices reset fully and start fresh.
Replacing Faulty Hardware
Old or broken cables and devices cause packet loss. Check all parts of your network for damage or wear.
Replace any faulty hardware like cables, routers, or network cards to improve your connection.
Updating Firmware And Drivers
Outdated software on routers and network cards can cause packet loss. Update firmware and drivers regularly.
Check the manufacturer’s website for the latest versions to keep your devices running well.
Optimizing Network Configuration
Incorrect network settings can cause packet loss. Adjust settings like MTU size and QoS to improve performance.
Use simple tools or guides to find the best settings for your network setup.
Reducing Network Congestion
Too many devices using the network at once cause congestion and packet loss. Limit heavy usage during important tasks.
- Pause large downloads or updates
- Close unused apps that use the internet
- Schedule high-data tasks for low-traffic times
Switching To Wired Connections
Wi-Fi can lose packets due to interference. Use Ethernet cables for a stable, fast connection.
Wired connections reduce packet loss and improve overall network speed.
Contacting Isp Support
Your internet provider can check for issues on their side. Contact them if packet loss continues after trying fixes.
They can run tests and help solve network problems beyond your control.
Preventing Future Packet Loss
Packet loss causes slow or interrupted internet connections. Preventing it helps keep networks fast and reliable.
To stop packet loss, follow simple steps like maintaining your network and upgrading hardware.
Regular Network Maintenance
Check your network devices regularly. Clean and update them to avoid errors.
Fix broken cables and replace old parts. Keep software and firmware up to date.
- Inspect cables and connections
- Update device firmware
- Remove unnecessary network traffic
- Restart devices when needed
Upgrading Network Infrastructure
Old network devices can cause packet loss. Upgrade routers, switches, and cables for better performance.
Use higher quality hardware that handles more traffic and reduces errors.
- Replace outdated routers
- Use Cat6 or better cables
- Choose switches with higher capacity
- Install modern wireless access points
Implementing Quality Of Service (qos)
QoS lets you prioritize important data. This reduces packet loss for critical apps.
Set rules to give priority to voice, video, or business traffic over less important data.
- Identify key applications
- Assign higher priority to critical data
- Limit bandwidth for non-essential traffic
- Adjust settings based on network needs
Monitoring Network Health Continuously
Watch your network all the time. Use tools that alert you to packet loss or other issues.
Quick detection helps fix problems before they affect users.
- Use network monitoring software
- Track packet loss and latency
- Set alerts for unusual activity
- Review logs regularly
Credit: www.pubnub.com

Credit: obkio.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Network Packet Loss?
Network packet loss occurs when data packets fail to reach their destination. This can lead to interrupted communication or degraded network performance. Causes include network congestion, faulty hardware, or software issues. Identifying the root cause is essential for troubleshooting and improving network efficiency.
How Does Packet Loss Affect Network Performance?
Packet loss can significantly degrade network performance. It leads to increased latency, jitter, and reduced data throughput. This can affect real-time applications like video calls or gaming. Ensuring minimal packet loss is crucial for maintaining optimal network functionality and user satisfaction.
What Causes Network Packet Loss?
Several factors can cause network packet loss. Common causes include network congestion, faulty routers, or interference. Additionally, outdated hardware or software can contribute. Regular maintenance and monitoring can help identify and mitigate these issues promptly.
Can Packet Loss Be Prevented?
While complete prevention isn’t possible, packet loss can be minimized. Network optimization, regular hardware checks, and using quality network devices help. Implementing redundancy and monitoring tools can also reduce packet loss. Consistent network management is key to maintaining performance.
Conclusion
Network packet loss can slow down your internet and cause frustration. It happens due to many reasons like weak signals, faulty hardware, or network congestion. Fixing these issues helps improve your connection speed and reliability. Regular checks and good equipment reduce packet loss risks.
Understanding its causes lets you act faster and keep your network stable. Keep your devices updated and monitor your connection often. A smooth online experience depends on a healthy network with minimal packet loss.
16 min read