Are you struggling to get your devices or apps to communicate properly? Sometimes, the problem lies in the network ports that are closed or blocked.
Knowing which network ports to open can make all the difference in improving your connection, boosting security, and unlocking new features. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about network ports, so you can take control of your network with confidence.
Keep reading, and you’ll discover simple steps to open the right ports and avoid common pitfalls that slow you down. Your smooth, hassle-free connection starts here.
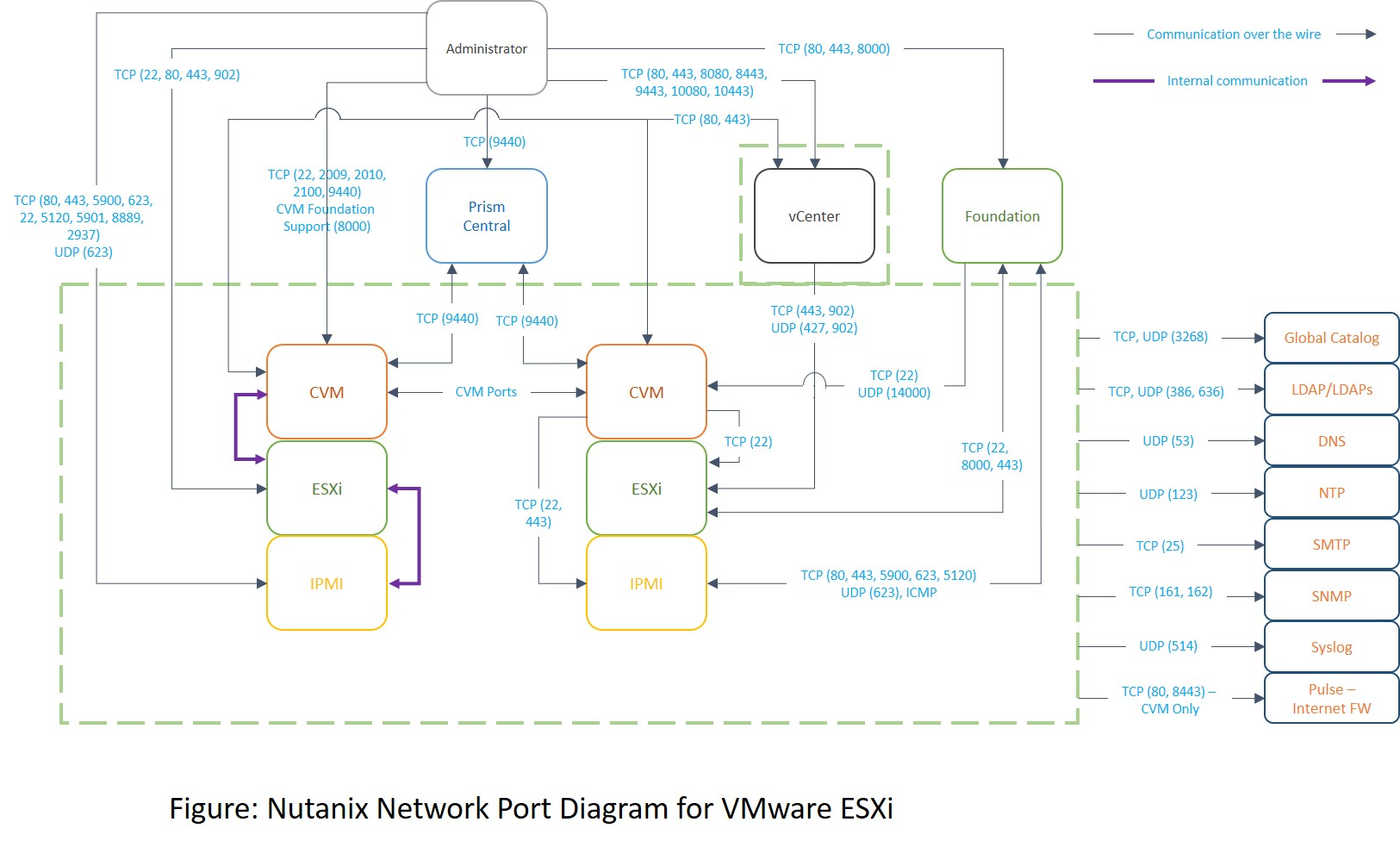
Credit: next.nutanix.com
Common Network Ports
Network ports help computers talk to each other over the internet. They are like doors for different services.
Opening the right ports is important for network communication and security.
Well-known Ports
Well-known ports range from 0 to 1023. They are used by common services and protocols.
These ports are usually reserved for system or standard applications.
| Port Number | Service | Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| 80 | HTTP | TCP |
| 443 | HTTPS | TCP |
| 25 | SMTP | TCP |
| 22 | SSH | TCP |
| 53 | DNS | UDP/TCP |
Registered Ports
Registered ports range from 1024 to 49151. They are assigned to user applications.
These ports are not as tightly controlled as well-known ports.
- Used by software programs for specific functions
- Examples include game servers and database services
- Can be opened to allow application traffic
Dynamic And Private Ports
Dynamic and private ports range from 49152 to 65535. They are used temporarily.
These ports are often chosen by the operating system for short connections.
- Used for temporary communication sessions
- Not assigned to any specific service
- Usually closed by default for security

Credit: pinggy.io
Purpose Of Opening Ports
Network ports allow computers to communicate over the internet or local networks. Opening ports helps data flow between devices and services.
Without opening the right ports, some programs or services cannot work properly. This guide explains why opening ports is important.
Allowing Remote Access
Opening network ports lets users connect to a device from another location. This remote access is useful for managing computers or servers.
Remote work and troubleshooting depend on open ports to reach systems safely and efficiently.
- Access computers from home or office
- Control servers without physical presence
- Support team can fix problems remotely
Enabling Services And Applications
Many apps need specific ports open to work right. Opening these ports allows services to send and receive data smoothly.
This helps apps like web servers, email clients, and games connect to the internet without issues.
- Websites use port 80 or 443 for traffic
- Email apps need ports for sending and receiving
- Online games require ports for player connections
Facilitating Data Transfer
Open ports help move data between devices quickly. File sharing, backups, and streaming rely on these open channels.
Without open ports, data transfers can be blocked or slowed down by firewalls.
- Send files between computers
- Stream videos and music smoothly
- Backup data to cloud or local servers
Risks Of Open Ports
Open network ports allow data to enter and leave a computer or network. They help run services like websites and email.
But open ports can cause problems. They can let attackers access your system and slow down your network.
Potential Security Threats
Open ports create entry points for hackers. They can use these to steal data or damage your system.
Attackers scan for open ports to find weak spots. They may then send harmful software or try to break in.
- Unauthorized access to sensitive data
- Installation of malware or ransomware
- Use of your system for illegal activities
- Disruption of normal network services
Vulnerabilities Exploited By Attackers
Attackers look for open ports with weak security. They exploit flaws in software running on these ports.
Common vulnerabilities include outdated software, weak passwords, and unpatched bugs. These let attackers enter your system easily.
- Unpatched security holes in services
- Default or weak login credentials
- Misconfigured firewall or network settings
- Exposed management interfaces
Impact On Network Performance
Open ports can slow down your network. Attackers can use them to send large amounts of traffic.
This traffic overloads your system and reduces speed. It can cause downtime and affect users’ experience.
- Increased network congestion
- Slower response times for users
- Possible crashes from overload
- Higher costs for bandwidth and maintenance
Best Practices For Secure Port Management
Network ports allow computers to send and receive data. Open ports can be entry points for hackers. Managing ports carefully helps keep your network safe.
Use these best practices to control and protect your network ports. This reduces risks and improves security.
Limit Open Ports To Essentials
Only open the ports your system really needs. Each open port is a possible risk for attacks. Close all unused ports quickly.
Check your open ports regularly. Remove any that are not necessary. This limits access points for intruders.
Regularly Update Firewall Rules
Firewalls control which ports can send or receive data. Update firewall rules often to match your current needs. Old rules may allow unsafe access.
Review rules after network changes. Remove rules that are no longer needed. This keeps your firewall strong and relevant.
Use Strong Authentication Methods
Authentication checks who can use open ports. Use strong methods like passwords and keys. Avoid weak or default passwords.
Combine authentication with encryption if possible. This protects data and access from attackers.
- Use complex passwords
- Enable multi-factor authentication
- Change passwords regularly
Implement Network Segmentation
Network segmentation splits a network into smaller parts. This limits open ports to each segment only. It stops attackers from moving easily inside the network.
Use firewalls and switches to create segments. Control open ports for each segment separately. This improves security and performance.
- Separate user devices from servers
- Isolate sensitive data areas
- Limit port access between segments
Tools To Monitor And Manage Ports
Network ports control data flow between devices. Monitoring and managing these ports keeps networks safe.
Different tools help check open ports and protect against unwanted access. These tools make network management easier.
Port Scanners
Port scanners check which ports are open on a device. They help find weak spots in network security.
These tools send requests to ports and report if the ports respond. This helps detect unauthorized open ports.
- Scan all ports or specific port ranges
- Identify open, closed, or filtered ports
- Detect services running on open ports
Firewall Management Software
Firewall software controls which ports allow traffic. It blocks unwanted connections to protect the network.
This software lets you set rules for opening or closing ports. It helps manage network security easily.
- Create rules to allow or block ports
- Monitor port activity in real time
- Log all connection attempts for review
Intrusion Detection Systems
Intrusion detection systems watch network traffic on open ports. They alert you about suspicious activity.
These systems analyze data packets and look for patterns. They help stop attacks before damage occurs.
- Detect unusual port scanning attempts
- Alert on unauthorized access tries
- Provide detailed reports for security teams
Configuring Ports On Common Devices
Opening network ports helps devices communicate over the internet or local networks. Each device has different ways to configure these ports.
This guide explains how to open ports on Windows, Linux, and routers safely and correctly.
Windows Firewall Settings
Windows Firewall controls network access on your PC. You can open ports by creating rules that allow traffic through.
To open a port, you add a new inbound rule for the port number and protocol (TCP or UDP).
- Open Windows Defender Firewall from Control Panel
- Click “Advanced settings”
- Choose “Inbound Rules” and select “New Rule”
- Select “Port” and click Next
- Choose TCP or UDP and enter the port number
- Allow the connection and finish the wizard
Linux Iptables Configuration
Linux uses iptables to manage firewall rules. You can add rules to open specific ports for incoming traffic.
Use the iptables command to allow traffic on a port, then save the changes to keep them after reboot.
- Open a terminal on your Linux device
- Run:
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport PORT_NUMBER -j ACCEPT - Replace
PORT_NUMBERwith the port you want to open - Save the rules with
sudo iptables-save - Restart the firewall service if needed
Router Port Forwarding
Routers block many ports by default. Port forwarding sends incoming traffic on certain ports to a device inside your network.
You need your router’s IP address and login to set up port forwarding rules.
- Log in to your router’s web interface
- Find the Port Forwarding or Virtual Server section
- Add a new rule with the port number and protocol (TCP/UDP)
- Enter the local IP address of the device to receive traffic
- Save the settings and reboot the router if needed
Troubleshooting Port Issues
Network ports are essential for communication between devices. Sometimes, these ports may not work properly.
Fixing port problems helps restore network connections quickly and easily.
Checking For Blocked Ports
Blocked ports stop data from reaching your device. Firewalls or security apps often block these ports.
Check your firewall and router settings to see if the needed port is blocked.
- Open your firewall control panel
- Look for inbound and outbound rules
- Allow traffic on the specific port number
- Save changes and restart your device
Diagnosing Connectivity Problems
Connectivity issues can come from closed or filtered ports. Use tools to test if the port is open.
Ping and port scanning software help check if the port responds to requests.
- Use the command prompt or terminal
- Run “ping” to check device reachability
- Use “telnet” or port scanner apps to test port status
- Record results to find the source of the problem
Resolving Conflicts Between Applications
Two apps may want the same port number. This causes conflicts and stops both from working.
Change the port number for one app or close the app that blocks the port.
- Identify apps using the port with system tools
- Close or disable one app if not needed
- Change port settings in app preferences
- Restart apps and test the connection
Credit: www.purevpn.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are The Most Common Network Ports To Open?
Common network ports include 80 (HTTP), 443 (HTTPS), 22 (SSH), and 25 (SMTP). Opening these ports enables web access, secure connections, remote management, and email services.
How Do I Know Which Ports To Open For My Application?
Check your application’s documentation for required ports. Only open essential ports to minimize security risks. Use tools like netstat to verify active ports.
Can Opening Too Many Ports Affect Network Security?
Yes, opening unnecessary ports increases vulnerability to attacks. Limit open ports to essential services only. Regularly monitor and close unused ports to enhance security.
What Is The Difference Between Tcp And Udp Ports?
TCP ports provide reliable, connection-based communication. UDP ports offer faster, connectionless data transfer. Choose based on your application’s speed and reliability needs.
Conclusion
Understanding network ports is crucial for smooth connectivity. This guide simplifies that. Open the right ports to ensure secure and efficient data flow. Avoid unnecessary risks by knowing which ports to open. Keep your network safe and effective. Knowledge of network ports empowers better decisions.
Always stay informed about port configurations. This reduces potential security threats. With these basics, managing your network becomes easier. Remember, practice makes perfect. Continue learning to enhance your network skills. Your network’s performance depends on it. Stay proactive and keep exploring more about network ports.
18 min read








