Imagine your network suddenly goes down. How quickly can you get it back up and running?
Your business depends on smooth, uninterrupted connectivity. That’s why understanding network redundancy options is crucial. These options act like safety nets, keeping your systems alive when problems strike. You’ll discover simple and effective ways to protect your network from unexpected failures.
Ready to make your network stronger and more reliable? Let’s dive in.
Credit: clouddle.com
Types Of Network Redundancy
Network redundancy helps keep networks running during failures. It uses extra parts to avoid downtime.
There are several types of network redundancy. Each type focuses on different areas of the network.
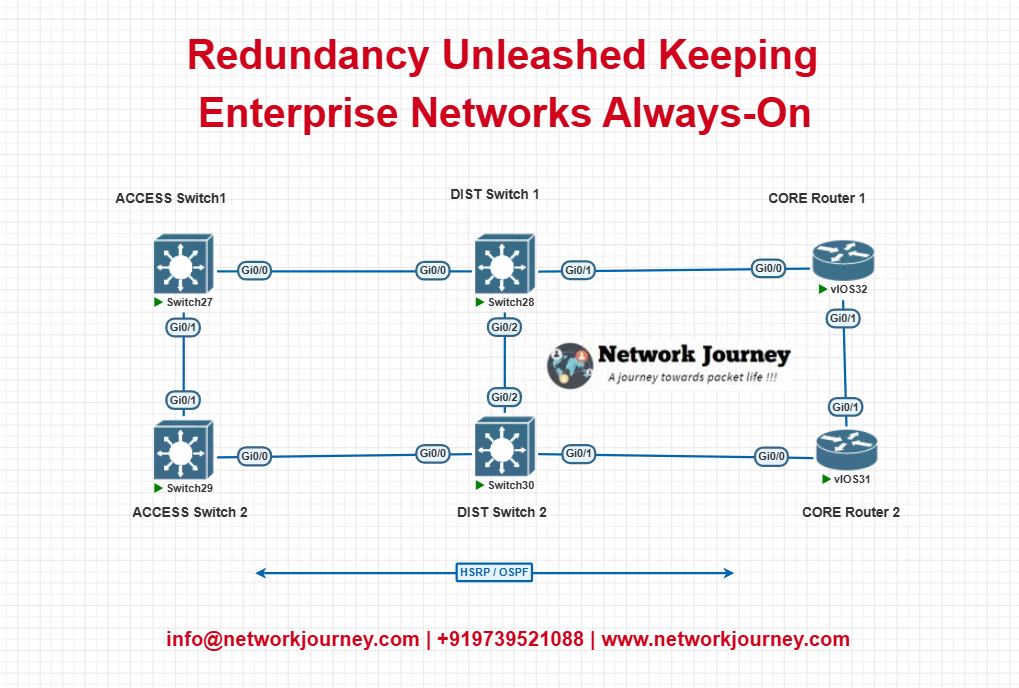
Hardware Redundancy
Hardware redundancy means using extra physical devices. These devices take over if one fails.
Common hardware parts include routers, switches, and power supplies. Backup devices reduce network downtime.
- Duplicate routers or switches
- Extra power supplies
- Backup servers
Software Redundancy
Software redundancy uses multiple programs to do the same task. This helps avoid failure if one program crashes.
It includes backup software, failover systems, and automatic recovery tools. These keep the network working smoothly.
- Failover software
- Backup and recovery tools
- Load balancing programs
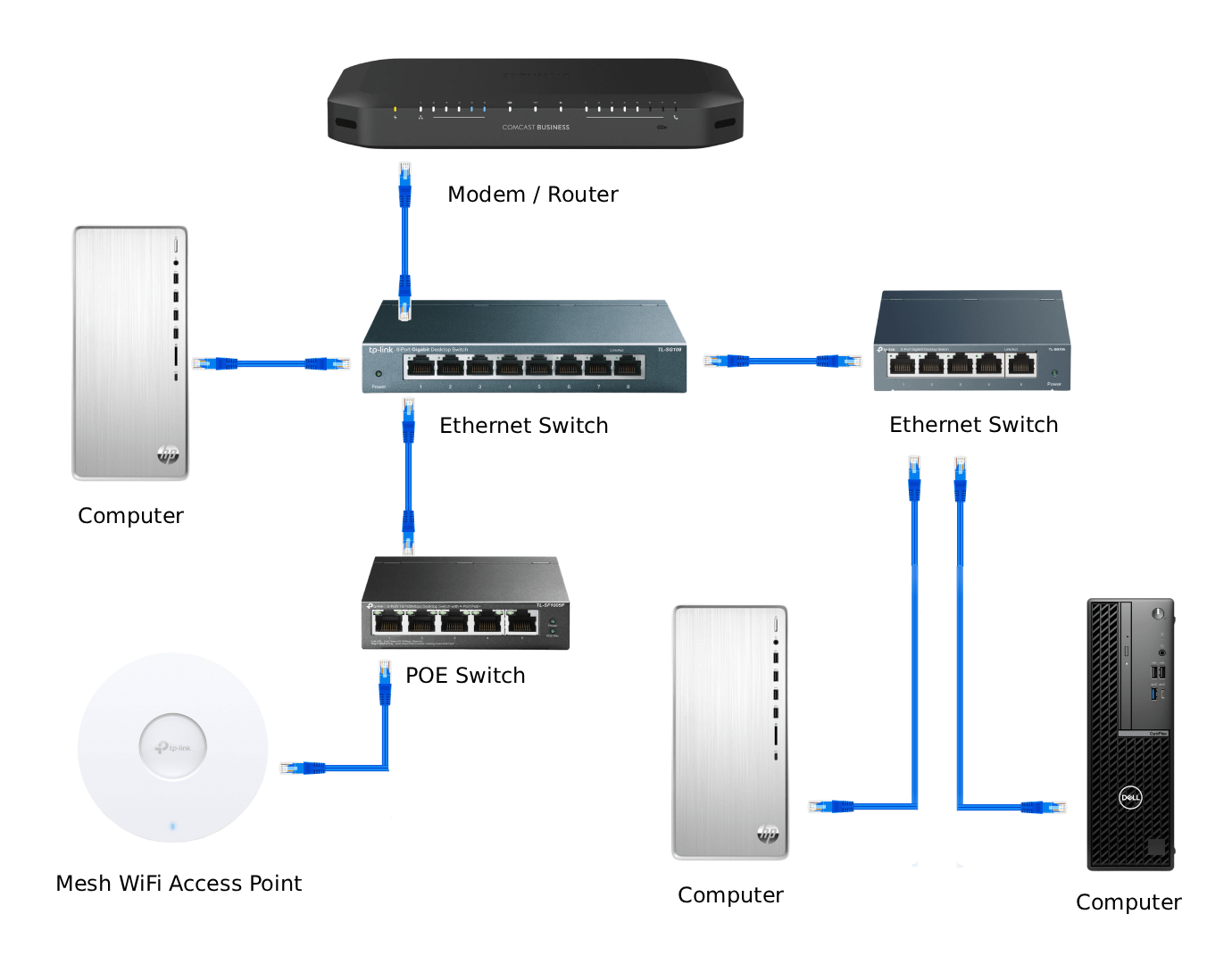
Path Redundancy
Path redundancy means having multiple routes for data to travel. If one path breaks, another path is used.
This type avoids network failure caused by cable cuts or link problems. It ensures constant network access.
- Multiple network cables
- Alternative wireless links
- Redundant internet connections
Redundancy Protocols
Network redundancy protocols keep networks working if one part fails. They help avoid downtime and data loss.
These protocols create backup paths and devices. They make sure data reaches its destination safely.
Spanning Tree Protocol
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) stops loops in network switches. Loops can cause data to circle endlessly.
STP finds the best path and blocks others. If one path fails, it opens a backup path.
- Prevents broadcast storms
- Ensures one active path between switches
- Automatically adjusts to network changes
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) lets routers work together as one. It picks a main router and backups.
If the main router fails, a backup takes over quickly. This keeps the network running without interruption.
- Provides router failover
- Improves network uptime
- Uses virtual IP to hide router changes
Hot Standby Router Protocol
Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) is a Cisco protocol. It creates a virtual router with one active and one standby router.
If the active router stops working, the standby router takes control fast. This avoids network downtime.
- Supports router redundancy
- Uses hello messages to check router status
- Switches routers smoothly if failure happens
Redundant Network Designs
Network redundancy helps keep systems working if one part fails. It adds extra paths to avoid downtime.
Different designs offer ways to build this backup into your network. Each design has strengths and uses.
Ring Topology
Ring topology connects devices in a circular path. Data travels in one or both directions.
If one link breaks, data can travel the other way. This keeps the network running without stops.
- Simple layout with easy connection
- Backup path if a link fails
- Works well for small to medium networks
Mesh Topology
Mesh topology connects every device to many others. This creates many paths for data.
If one device or link fails, data can find a new route. This makes mesh very reliable and strong.
- High redundancy with multiple connections
- Good for critical systems needing strong backup
- More complex and costly to build
Star Topology
Star topology uses one central device to connect all others. Each device has its own link.
Redundancy happens by adding backup links or devices at the center. This protects the network.
- Easy to set up and manage
- Central point can be a weakness
- Backup central devices improve reliability
Load Balancing Techniques
Load balancing helps distribute network traffic evenly. It keeps systems running smoothly and avoids overload.
There are different ways to balance loads. Each technique works best in certain network setups.
Round Robin
Round Robin sends requests to servers in order. It cycles through each server one by one.
This method is simple and fair. It works well when servers have similar capacity.
Least Connections
Least Connections sends traffic to the server with the fewest active connections. This helps balance load better.
This method suits networks where some servers handle tasks slower than others. It prevents overload on busy servers.
Ip Hash
IP Hash uses the client’s IP address to decide the server. It sends the same client to the same server each time.
This technique is good for sessions that need to stay on one server. It keeps user data consistent across visits.
Cloud-based Redundancy
Cloud-based redundancy helps keep networks running without interruptions. It uses cloud services to back up systems and data.
This type of redundancy protects against failures by spreading resources across the cloud.
Multi-cloud Strategies
Multi-cloud means using more than one cloud provider. This reduces risks if one provider has problems.
It also lets businesses choose the best services from different clouds to fit their needs.
- Distributes workloads across several clouds
- Prevents total service failure
- Offers flexibility and cost control
Failover Automation
Failover automation switches traffic to a backup system when the main one fails. It happens without human help.
This process reduces downtime and keeps services available to users.
- Monitors system health constantly
- Triggers automatic switch to backup
- Restores normal function quickly
Geographic Distribution
Geographic distribution means placing data centers in different locations. This protects data from local disasters.
It also improves speed by serving users from the nearest data center.
- Reduces risk from natural disasters
- Improves load balancing
- Enhances user experience worldwide
Credit: clouddle.com
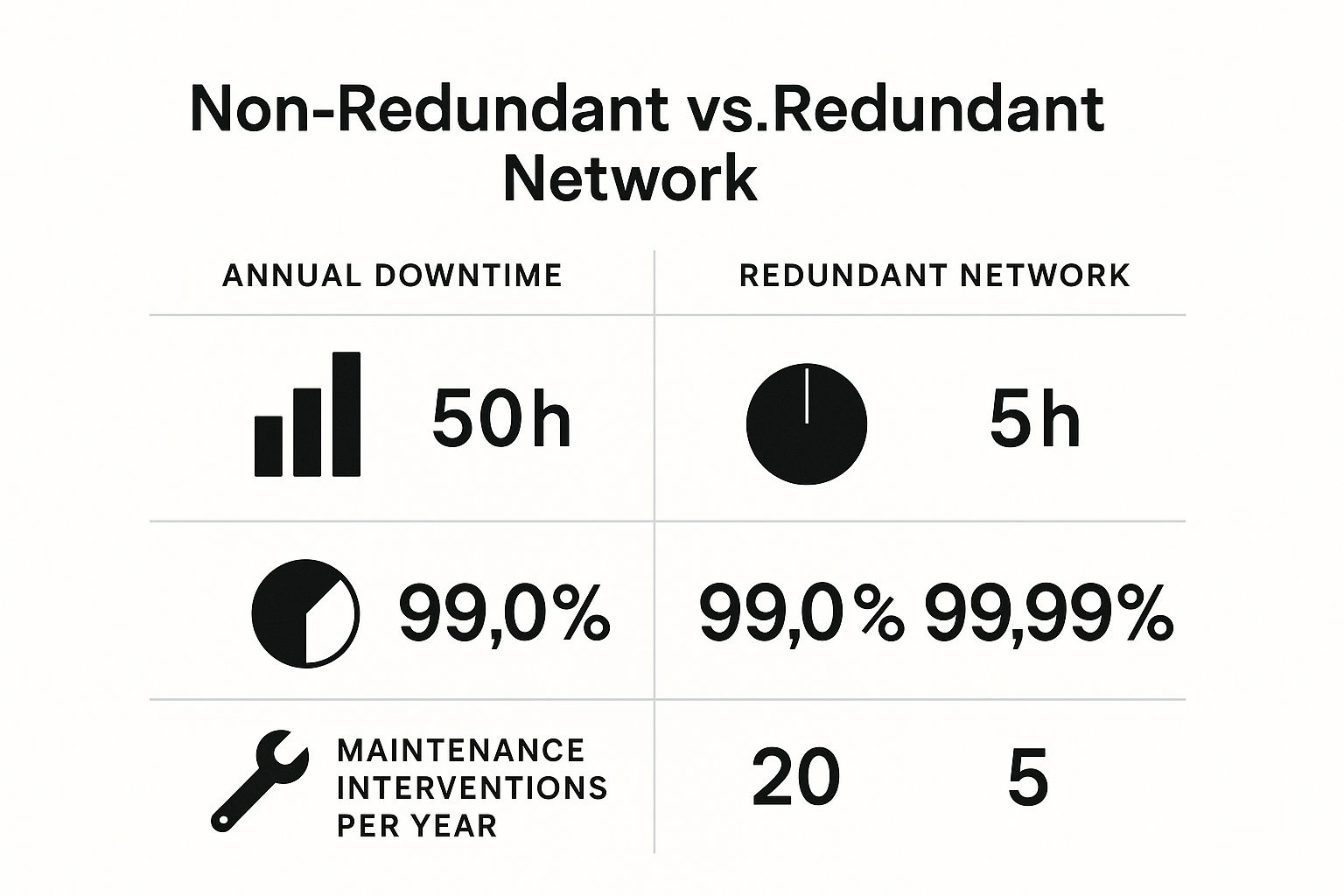
Challenges In Network Redundancy
Network redundancy helps keep systems running when one part fails. It adds backup paths and devices to avoid downtime.
Despite benefits, network redundancy faces several challenges. These affect cost, management, and performance.
Cost Implications
Adding extra hardware and connections increases expenses. Backup devices, cables, and software all add to costs.
Ongoing maintenance and power use also raise costs. Budget limits can restrict how much redundancy a network has.
- More devices mean higher initial investment
- Extra power and cooling add to operational costs
- Software licenses for redundancy features cost money
- Maintenance requires skilled staff and time
Complexity Management
Network redundancy makes setups more complex. More devices and links create harder systems to manage.
Managing many backup paths can cause configuration errors. Troubleshooting takes longer when systems are complicated.
- Multiple backup routes increase configuration tasks
- More devices require detailed monitoring
- Failure detection becomes harder with many components
- Staff need training for complex network setups
Latency Issues
Backup paths may add delay to network traffic. Switching to redundant links can cause slowdowns.
Latency affects user experience and application performance. Networks must balance redundancy with speed.
- Longer routes increase data travel time
- Failover processes add brief pauses
- Extra devices can cause processing delays
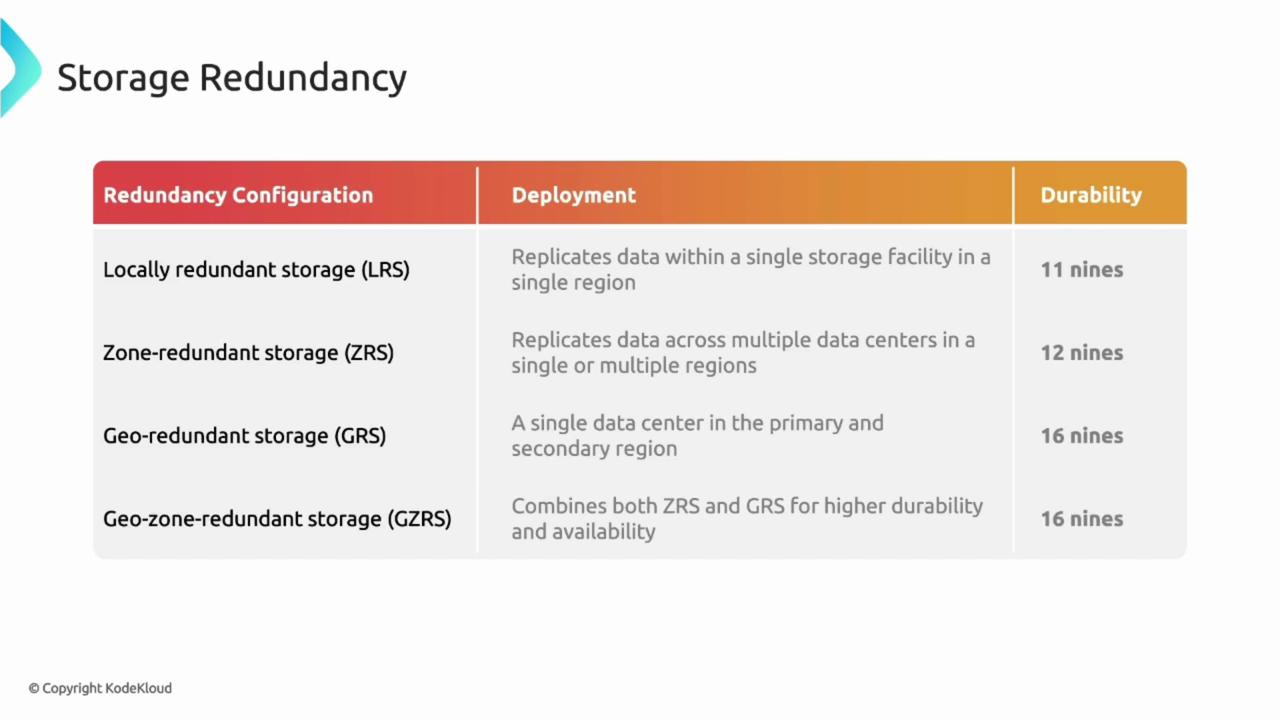
Best Practices For Redundancy
Network redundancy helps keep systems running during failures. It reduces downtime and improves reliability.
Following best practices ensures your redundancy plan works well. This guide covers key areas to focus on.
Regular Testing
Test your redundancy systems often to find issues early. Testing shows if backups and failovers work as expected.
Schedule tests during low traffic times to avoid disruptions. Document results and fix problems quickly.
- Run failover drills regularly
- Check backup hardware and software
- Verify data synchronization
- Test alert and notification systems
Documentation And Monitoring
Keep detailed documents of your network setup and redundancy processes. Clear records help teams understand the system.
Monitor network performance and alerts in real time. Quick detection of problems allows faster recovery.
- Record network configurations and changes
- Use monitoring tools for uptime and traffic
- Set alerts for failures and performance drops
- Review logs regularly to spot issues
Scalable Architecture
Design your network to grow with your needs. Scalability means adding redundancy without major changes.
Use modular components and flexible protocols. This approach makes upgrades easier and keeps downtime low.
- Choose hardware that supports expansion
- Implement protocols that allow load balancing
- Plan for future traffic increases
- Design redundant paths for easy scaling
Credit: notes.kodekloud.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Network Redundancy?
Network redundancy involves using multiple paths or components to ensure continuous network operation. It minimizes downtime and maintains connectivity during failures. Implementing redundancy can involve backup systems, alternative pathways, or duplicate hardware. This ensures reliability and stability, safeguarding against network disruptions and enhancing performance.
Why Is Network Redundancy Important?
Network redundancy is crucial to prevent downtime and ensure consistent connectivity. It provides alternative routes for data, maintaining operations during outages or failures. This enhances reliability, minimizes disruptions, and supports business continuity. Investing in redundancy safeguards against potential losses and improves user experience by ensuring seamless network availability.
How Does Network Redundancy Work?
Network redundancy works by using multiple pathways or systems to ensure network reliability. When a failure occurs, traffic is rerouted to alternative routes. This prevents disruptions and maintains connectivity. Redundancy can involve duplicate hardware, backup systems, or diverse paths, ensuring seamless operation and minimizing the impact of failures.
What Are Common Network Redundancy Options?
Common network redundancy options include load balancing, failover systems, and diverse routing paths. Load balancing distributes traffic, ensuring efficient resource use. Failover systems switch to backup components during failures. Diverse routing paths provide alternative data paths, enhancing reliability. These options help maintain connectivity and minimize downtime.
Conclusion
Network redundancy keeps your network safe and working well. It helps stop downtime and data loss. Choosing the right option depends on your needs and budget. Simple methods work for small setups. Larger systems need stronger plans. Always plan and test your backup paths.
This way, your network stays reliable and fast. Good redundancy protects your business and saves money. Think ahead and stay prepared for any issue.
16 min read