Your network is the gateway to everything important—your data, your devices, and your privacy. But how safe is it really?
Understanding the basics of network security isn’t just for tech experts anymore; it’s something you need to protect what matters most. Imagine stopping threats before they reach you, keeping hackers out, and feeling confident every time you go online. This article will give you clear, simple steps to secure your network right now.
Keep reading, and take control of your digital safety today.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Common Network Threats
Network security protects computers and data from harm. Many threats can damage or steal information.
Knowing common threats helps you stay safe online. Attackers use different tricks to break security.
Malware And Viruses
Malware is software made to harm your device. Viruses are a type of malware that spread quickly.
They can delete files, steal data, or slow your system. Malware often comes from bad downloads or emails.
- Viruses attach to files and spread
- Worms spread across networks without help
- Trojans pretend to be safe software
- Ransomware locks data until you pay
Phishing Attacks
Phishing tricks people into giving private info. Attackers use fake emails or websites to steal passwords.
These attacks look real but aim to fool users. They can lead to identity theft or money loss.
- Fake emails ask for personal details
- Links lead to fake login pages
- Urgent messages cause quick actions
Denial Of Service
Denial of Service (DoS) attacks block access to websites. Attackers overload servers with many requests.
Users cannot reach the site during the attack. This can stop business or prevent important services.
- Flooding servers with traffic
- Using many computers in an attack (DDoS)
- Causing slow or no response from servers
Man-in-the-middle
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks spy on communication. The attacker intercepts messages between two parties.
They can steal or change information without being noticed. Public Wi-Fi is a common place for MitM attacks.
- Intercepting data in transit
- Stealing login details or credit cards
- Changing messages before they reach the receiver
Securing Network Access
Network security is important to keep data safe from attackers. Securing network access helps protect sensitive information.
Only authorized users should connect to the network. This prevents unauthorized access and reduces risks.
Strong Password Practices
Using strong passwords is the first step to secure network access. Weak passwords are easy to guess or crack.
Strong passwords have a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols. They should be at least eight characters long.
- Use uppercase and lowercase letters
- Add numbers and special characters
- Avoid common words and phrases
- Change passwords regularly
Multi-factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds extra security. It asks users to provide more than one proof of identity.
MFA makes it harder for attackers to access accounts, even if passwords are stolen.
- Something you know, like a password
- Something you have, like a phone or token
- Something you are, like a fingerprint or face ID
User Access Controls
User access controls limit what users can see and do on a network. This reduces the risk of accidental or harmful actions.
Access should be given based on roles and responsibilities. This follows the principle of least privilege.
- Assign permissions based on job needs
- Review access rights regularly
- Remove access for inactive users
- Use strong authentication methods
Network Encryption Methods
Network encryption helps keep data safe as it moves across networks. It changes information into a secret code.
This makes it hard for others to read or steal the data. Many tools use encryption to protect networks.
Vpn Usage
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, creates a secure link between your device and the internet. It hides your data from outsiders.
VPNs use encryption to keep your online actions private. This stops hackers from spying on your connection.
- Encrypts all data sent and received
- Hides your IP address
- Protects public Wi-Fi connections
Ssl/tls Protocols
SSL and TLS are protocols that encrypt data between a web browser and server. They make websites safe to visit.
These protocols create a secure channel to stop data from being stolen or changed during transfer.
- SSL is the older version, mostly replaced by TLS
- TLS offers stronger encryption and better security
- Used in HTTPS websites to protect passwords and payments
Wireless Encryption Standards
Wireless encryption protects data sent over Wi-Fi networks. It stops others from accessing your connection without permission.
Common standards include WEP, WPA, and WPA2. WPA2 is the most secure and widely used today.
- WEP is outdated and easy to crack
- WPA improved security but has some flaws
- WPA2 uses strong encryption and is the current standard
- WPA3 is the newest and offers even better protection
Firewalls And Intrusion Detection
Network security is important to keep data safe. Firewalls and intrusion detection help protect computers from attacks.
They monitor traffic and stop harmful activity. Understanding how they work helps keep networks secure.
Types Of Firewalls
Firewalls control network traffic by rules. They can be hardware, software, or both.
Each type works in a different way to block threats and allow safe data.
- Packet-Filtering Firewalls:Check data packets and block suspicious ones.
- Stateful Inspection Firewalls:Track active connections and filter packets accordingly.
- Proxy Firewalls:Act as a middleman to filter requests between networks.
- Next-Generation Firewalls:Use deep inspection and can block advanced threats.
Ids And Ips Systems
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) watch network traffic for suspicious activity. They alert admins about possible attacks.
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) also block threats automatically. They act faster to stop attacks.
- Network-based IDS/IPS:Monitor traffic on the whole network.
- Host-based IDS/IPS:Protect a single computer or device.
- Signature-based Systems:Detect known attack patterns.
- Anomaly-based Systems:Detect unusual behavior that may mean an attack.
Configuring Firewall Rules
Firewall rules tell the system what traffic to allow or block. Good rules keep networks safe and working well.
Rules should be clear and simple. Avoid letting all traffic pass without checks.
- Define allowed and blocked IP addresses.
- Set rules for specific ports and protocols.
- Use a default deny rule to block unknown traffic.
- Review and update rules regularly.
Regular Updates And Patch Management
Network security depends on keeping software and devices up to date. Regular updates fix security holes.
Patches help protect systems from new threats. Managing them well reduces risks of attacks.
Software Updates
Software updates improve security and add new features. They close vulnerabilities hackers use.
Installing updates on time helps keep your network safe. Many attacks exploit outdated software.
- Operating systems need frequent updates
- Applications also require regular patches
- Update browsers and plugins for safety
Firmware Upgrades
Firmware controls hardware devices like routers and switches. Upgrading firmware fixes bugs and holes.
Old firmware can let attackers enter your network. Regular upgrades keep devices running securely.
- Check device maker for firmware releases
- Backup settings before upgrading
- Follow instructions carefully to avoid issues
Automated Patch Tools
Automated tools help manage patches faster and easier. They scan and apply updates across devices.
Using these tools reduces human error and saves time. They keep your network updated consistently.
- Schedule scans for missing patches
- Test patches before full deployment
- Report patch status for security checks
Credit: www.geeksforgeeks.org
Backup And Recovery Plans
Backup and recovery plans protect important data from loss or damage. They help keep networks safe during problems.
Good plans make sure data is saved and can be restored quickly after a failure.
Data Backup Strategies
Data backup means making copies of files to keep them safe. Backups should happen often to avoid big losses.
There are different ways to backup data to fit your needs and resources.
- Full Backup: Copies all data every time. It takes more space and time.
- Incremental Backup: Saves only new or changed files since last backup. It is faster and uses less space.
- Differential Backup: Backs up changes since last full backup. It is a balance between full and incremental.
- Cloud Backup: Stores data on remote servers. It adds extra protection from local damage.
Disaster Recovery
Disaster recovery is the process to restore data and systems after a failure. It helps reduce downtime and losses.
A good disaster recovery plan has clear steps to follow. It includes roles, tools, and timelines.
- Identify critical data and systems to restore first.
- Set up backup locations and recovery tools.
- Assign team members to specific tasks.
- Practice the plan regularly to improve response time.
Testing Backup Integrity
Testing backup integrity means checking if backups are complete and usable. It prevents surprises during recovery.
Regular tests help find problems early and ensure data can be restored correctly.
- Verify backup files are not corrupted.
- Try restoring data to a test system.
- Check backup logs for errors.
- Update backup methods if tests show issues.
Employee Training And Awareness
Employees play a key role in keeping networks safe. Training helps them understand risks and protect data.
Awareness programs teach workers how to spot dangers and act safely online. This lowers security problems.
Recognizing Threats
Employees should know common threats like phishing emails and fake websites. They must watch for unusual messages.
Signs of threats include spelling mistakes, urgent requests, and unknown senders. Being cautious helps avoid attacks.
- Emails asking for passwords or personal info
- Links leading to strange websites
- Unexpected attachments or downloads
- Pop-ups asking to install software
Safe Browsing Habits
Employees should use secure websites and avoid clicking unknown links. This keeps data safe from hackers.
Using strong passwords and logging out after work stops others from accessing accounts. Regular updates improve security.
- Check for “https” in website addresses
- Avoid downloading files from unknown sources
- Use unique passwords for each account
- Clear browser history and cookies often
Reporting Suspicious Activity
Employees must report anything unusual to IT staff. Quick reports stop security problems from growing.
Signs to report include strange emails, slow computers, or unexpected pop-ups. Reporting helps protect the whole network.
- Unfamiliar login attempts or password changes
- Unexpected software installations
- Emails asking for confidential information
- Devices acting strangely or slowing down
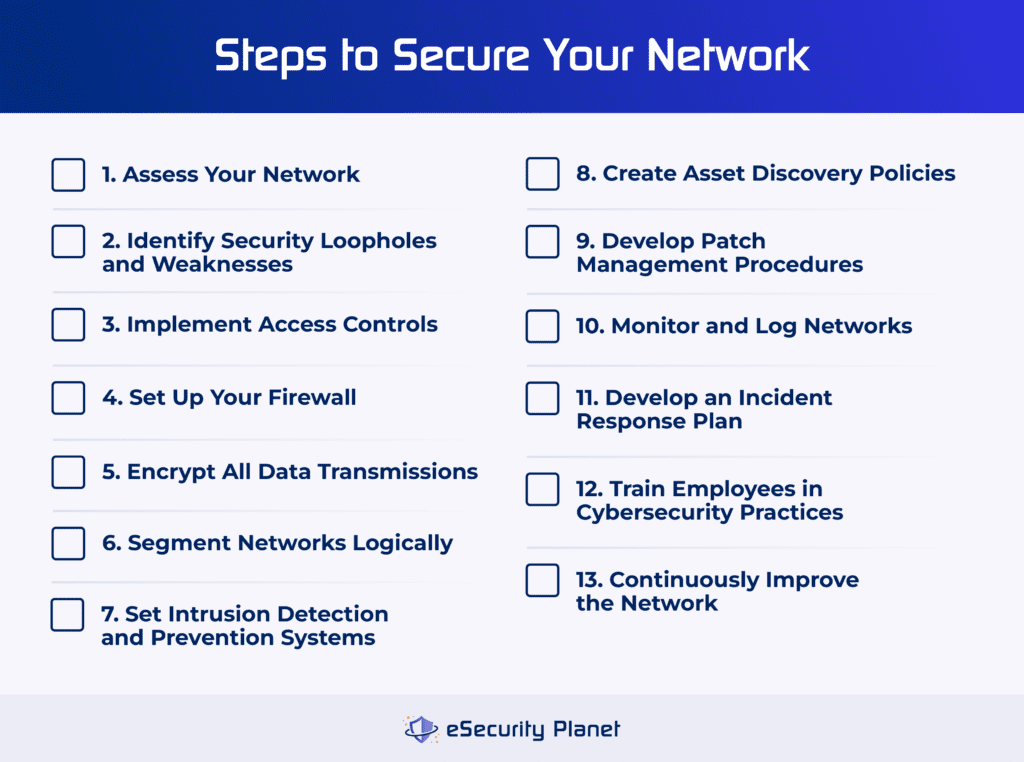
Credit: www.esecurityplanet.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Network Security?
Network security involves protecting data and resources from unauthorized access. It ensures the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of information. This is achieved through various measures like firewalls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems. Network security is crucial for safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining trust in digital communications.
Why Is Network Security Important?
Network security is vital for protecting data from cyber threats. It prevents unauthorized access, data breaches, and identity theft. Effective network security ensures business continuity and protects sensitive information. It also helps maintain customer trust and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Organizations can avoid costly damages by investing in robust network security measures.
How Does A Firewall Enhance Network Security?
A firewall acts as a barrier between trusted and untrusted networks. It monitors and controls incoming and outgoing traffic based on security rules. Firewalls help prevent unauthorized access to systems and data. They can also block malicious traffic, protecting networks from various cyber threats.
Firewalls are essential for maintaining a secure network environment.
What Are Common Network Security Threats?
Common network security threats include malware, phishing, and ransomware attacks. Hackers use these to steal sensitive information and disrupt operations. Denial-of-service (DoS) attacks can overload systems, causing disruptions. Insider threats, where employees misuse access, are also a concern. Regular updates and security measures help combat these threats effectively.
Conclusion
Strong network security keeps your data safe from threats. Use basic tools like firewalls and antivirus software. Keep your passwords strong and change them often. Regular updates fix weak spots in your system. Stay alert for unusual activity on your network.
These simple steps help protect your information every day. Security is a shared job; stay aware and prepared. Small actions can stop big problems before they start. Keep learning and improving your network safety habits. Your efforts build a safer digital space for all.
19 min read





