Are you confused about the difference between a network switch and a router? You’re not alone.
Many people use these terms interchangeably, but knowing how each device works can make a big difference in setting up your home or office network. Understanding these differences will help you choose the right equipment, improve your internet speed, and keep your devices connected smoothly.
Keep reading, and by the end of this article, you’ll clearly see how a switch and a router fit into your network—and which one you really need.
Basic Functions
Network switches and routers are key devices in computer networks. They help connect devices and share data.
Each device has a different job to do. Understanding their roles helps build better networks.
Role Of A Network Switch
A network switch connects devices within the same network. It creates a local network for computers, printers, and other devices.
Switches send data only to the device that needs it. This reduces traffic and speeds up communication.
- Connects devices in a local area network (LAN)
- Forwards data based on device addresses
- Improves network speed by managing data flow
- Does not connect different networks
Role Of A Router
A router links different networks together. It connects your home or office network to the internet.
Routers decide where to send data across networks. They use IP addresses to find the best path.
- Connects multiple networks, like LAN to the internet
- Routes data to the correct destination using IP addresses
- Can provide security features like firewalls
- Manages traffic between networks
Credit: www.router-switch.com
Data Handling
Network switches and routers handle data differently in a network. Both devices send data, but they do it in unique ways. Understanding how they process data helps you use them properly.
Switches mainly work inside local networks. Routers connect different networks and manage data between them.
Packet Forwarding In Switches
Switches receive data packets and forward them to the correct device on the same network. They use MAC addresses to find the right destination.
Switches learn where devices are by checking the source addresses in packets. They build a table to remember which device connects to each port.
- Switch checks the packet’s destination MAC address
- Looks up the address in its table
- Sends the packet only to the correct port
- Reduces unnecessary data traffic
Routing In Routers
Routers handle data packets between different networks. They use IP addresses to decide where to send data next.
Routers check their routing tables to find the best path. They can connect a home network to the internet or link several networks together.
- Router reads the packet’s destination IP address
- Finds the best route using its routing table
- Forwards the packet toward the destination network
- Can block or allow traffic based on rules
Network Layers
Network devices work at different layers of the OSI model. These layers help organize how data moves across networks. Switches and routers operate on separate layers.
Understanding which layer each device works on helps explain their functions. This guide focuses on switches at Layer 2 and routers at Layer 3.
Switches And Layer 2
Switches mainly work at Layer 2, the Data Link layer. They use MAC addresses to send data within a local network.
Layer 2 switches create a network by connecting devices like computers and printers. They forward data only to the correct device.
- Use MAC addresses for data forwarding
- Operate within a single local area network (LAN)
- Help reduce network traffic by sending data to specific devices
- Do not handle IP addresses or routing between networks
Routers And Layer 3
Routers work at Layer 3, the Network layer. They use IP addresses to direct data between different networks.
Layer 3 routers connect multiple networks, like your home network to the internet. They decide the best path for data to travel.
- Use IP addresses to route data
- Connect different networks together
- Manage traffic between local and wide area networks
- Support network address translation and firewall features
Connection Types
Network switches and routers connect devices but work differently. Each device supports different connection types.
Understanding these connection types helps choose the right device for your needs.
Local Network Connections
Switches connect devices within the same local network. They use Ethernet cables to link computers, printers, and other devices.
Switches create a network where devices communicate directly and fast.
- Use RJ45 Ethernet ports
- Connect devices in the same building
- Manage traffic between local devices
- Support wired connections only
Internet Connectivity
Routers connect your local network to the internet. They manage data going in and out of your home or office.
Routers support different connection types to link to the internet service provider.
- Use WAN ports to connect to the internet
- Support wired and wireless connections
- Assign IP addresses to devices
- Manage data between local network and internet
Performance And Speed
Network switches and routers both help devices talk to each other. They do this in different ways that affect speed and performance.
Understanding how each device handles data helps choose the right one for your network needs.
Switch Throughput
Switch throughput means how much data the switch can move at once. Switches work at a fast pace because they send data directly to devices.
They use hardware to quickly forward data. This helps reduce delays and keeps the network running smoothly.
- Switches handle data at the frame level
- They forward data based on MAC addresses
- Switch throughput is usually very high
- Good for local network traffic
Router Processing
Routers process data by checking IP addresses. They decide the best path for data to travel across networks.
This processing takes more time than switches. Routers use software and hardware to handle complex tasks.
- Routers work at the network layer
- They manage data between different networks
- Processing can slow down speed slightly
- Important for internet and wide-area networks
Security Features
Network switches and routers both help connect devices. They have different security features to protect data.
Understanding their security can help you keep your network safe from threats and attacks.
Switch Security Options
Switches control data flow inside a local network. They have security features to prevent unauthorized access.
These features help stop hackers from entering through the switch ports or intercepting data.
- Port Security limits devices on each switch port.
- MAC Address Filtering blocks unknown devices.
- VLANs separate network traffic for safety.
- Storm Control stops traffic floods that can crash networks.
- Access Control Lists (ACLs) restrict data flow by rules.
Router Security Capabilities
Routers connect different networks, like your home to the internet. They have strong security tools.
Routers block unwanted traffic and protect your network from outside attacks.
- Firewalls block harmful data from entering the network.
- VPN support allows secure remote connections.
- Network Address Translation (NAT) hides internal IP addresses.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) spot and stop attacks.
- Access Control Lists (ACLs) filter traffic based on rules.
Use Cases
Network switches and routers are key devices in building a network. They help connect devices but serve different roles. Understanding when to use each device improves network performance and management.
Choosing the right device depends on your network needs. Both switches and routers have unique use cases that fit different scenarios.
When To Use A Switch
Use a network switch to connect multiple devices within the same local network. Switches create a network where devices can share files and printers easily.
Switches work best in places like offices or homes where many devices need to talk to each other quickly. They help reduce network traffic by sending data only to the right device.
- Connect computers in the same room or building
- Share files and printers among devices
- Expand the number of available network ports
- Improve communication speed inside a local network
When To Use A Router
Routers connect different networks, such as your home network to the internet. They direct data between devices and external networks.
Use a router when you need to share an internet connection. Routers also provide security features like firewalls to protect your network.
- Connect your home or office network to the internet
- Manage traffic between different networks
- Provide Wi-Fi access to wireless devices
- Protect your network with security settings
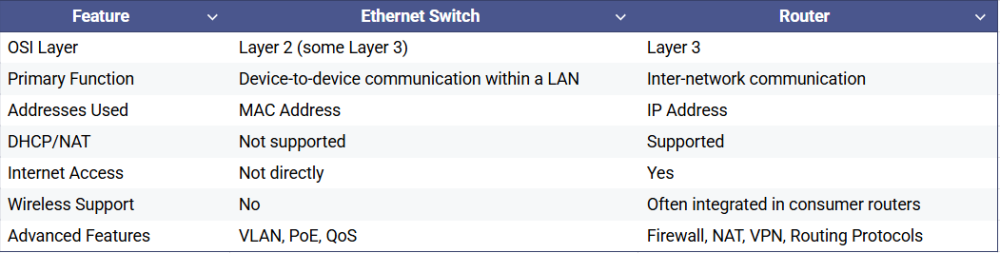
Credit: www.router-switch.com
Cost Differences
Network switches and routers both help connect devices in a network. Their prices vary a lot based on features and uses.
Understanding cost differences helps you pick the right device for your needs and budget.
Initial Purchase Price
Switches usually cost less than routers. Simple switches are cheaper because they only connect devices.
Routers have more features like routing traffic between networks. This makes them more expensive.
- Basic switch: $20 to $100
- Basic router: $50 to $200
- Advanced router: $200 and up
Maintenance And Upgrades
Switches require less maintenance than routers. They have fewer settings to manage.
Routers need regular firmware updates and security checks. This can add to the overall cost.
- Switches: Low maintenance cost
- Routers: Moderate to high maintenance cost
Scalability And Long-term Costs
Switches can scale easily by adding more units. This keeps costs low for growing networks.
Routers handle complex tasks but may need costly upgrades as network demands grow.
- Switches: Affordable scaling
- Routers: Higher upgrade costs
Credit: medium.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Main Difference Between A Switch And A Router?
A switch connects devices within a local network, while a router connects multiple networks. Switches manage data flow internally; routers manage data traffic between different networks, such as the internet and a home network.
Can A Router Replace A Network Switch?
No, routers and switches serve different purposes. Routers direct traffic between networks; switches connect devices within the same network. For efficient network performance, both are often used together.
How Does A Switch Improve Network Performance?
Switches reduce network congestion by sending data only to the intended device. This targeted communication increases speed and efficiency within the local network, improving overall performance.
Do Routers Provide Security Features That Switches Don’t?
Yes, routers offer security features like firewalls and NAT, protecting the network from external threats. Switches typically do not have these security functions and focus on data transmission within the network.
Conclusion
Routers and switches serve unique roles in a network setup. Routers connect different networks. They manage traffic efficiently. Switches, on the other hand, link devices within a single network. They facilitate smooth communication. Choose based on your specific networking needs.
Smaller networks may need only switches. Larger setups often require routers. Understanding these differences ensures better network performance. The right choice optimizes data flow. It also enhances connectivity. Evaluate your network size and complexity. Make informed decisions for reliable and efficient networking solutions.
17 min read