Are you curious about how different devices connect and communicate in a network? Understanding network topology basics is the key to unlocking this mystery.
Whether you’re setting up your home Wi-Fi or managing a business network, knowing how networks are structured can save you time and headaches. You’ll discover simple explanations and practical insights that make complex ideas easy to grasp. Keep reading, and you’ll soon see how network topologies impact speed, reliability, and security—giving you the power to make smarter decisions for your own network.

Credit: shadowmaster98.medium.com
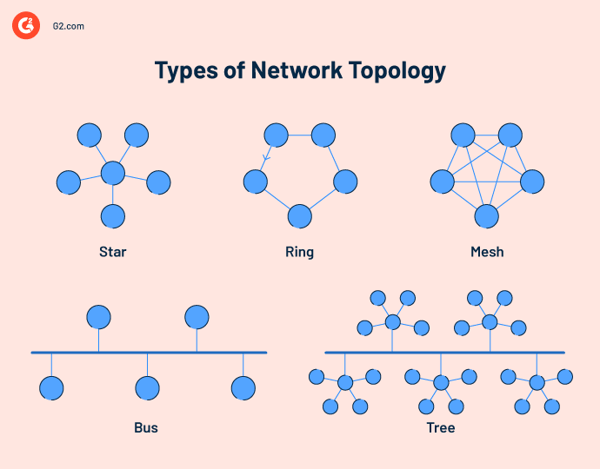
Network Topology Types
Network topology shows how devices connect in a network. It helps organize and manage data flow.
There are several types of network topologies. Each type has its own layout and features.
Bus Topology
Bus topology connects all devices with one main cable. Data travels in both directions along this cable.
It is simple and uses less cable. But if the main cable fails, the whole network stops working.
- Single main cable called a bus
- Devices connect to the bus
- Easy to install and extend
- Failure of bus affects entire network
Star Topology
Star topology connects all devices to a central device, like a switch or hub. Data passes through the center.
This type is easy to manage. If one device fails, others keep working. But if the center fails, the network breaks.
- Central device controls the network
- Devices connect only to the center
- Good for large networks
- Center device failure stops the network
Ring Topology
In ring topology, devices connect in a circle. Data moves in one direction around the ring.
It is easy to install and uses less cable than star. But if one device or connection fails, the whole ring can stop.
- Devices connect to two neighbors
- Data flows in a circle
- Simple cable layout
- One break stops the network
Mesh Topology
Mesh topology connects every device to all others. Data can take many paths to reach the destination.
This makes the network very reliable. If one path fails, data uses another route. It needs lots of cables and is costly.
- Every device connects to all devices
- High reliability and redundancy
- Complex and expensive setup
- Good for critical systems
Tree Topology
Tree topology is a mix of star and bus topologies. Groups of star networks connect to a main bus line.
It is easy to expand and manage. If the main bus fails, all connected branches stop working.
- Combines star groups on a bus
- Easy to add more devices
- Central bus is a single point of failure
- Common in large networks
Hybrid Topology
Hybrid topology combines two or more different topologies. It uses the strengths of each type.
This design fits complex networks. It is flexible but can be hard to design and maintain.
- Mix of two or more topologies
- Flexible and scalable
- Complex to set up and manage
- Used in large, diverse networks
Topology Advantages
Network topology shows how devices connect in a network. It affects how the network works and grows.
Choosing the right topology helps improve network strength and use resources well.
Scalability
Scalability means a network can grow easily. Good topology allows adding new devices without big changes.
This helps businesses expand their networks without extra costs or problems.
Fault Tolerance
Fault tolerance means a network stays working even if one part fails. Some topologies keep data flowing.
This reduces downtime and keeps users connected during device or cable failures.
Cost Efficiency
Cost efficiency means using less money for network setup and maintenance. Some topologies need fewer cables and devices.
This lowers the cost of building and running the network over time.
Performance
Performance means how fast and reliable a network works. Certain topologies reduce delays and data loss.
Good design helps data move quickly and keeps network users happy.
Topology Disadvantages
Network topology shows how devices connect in a network. Each type has its own problems. These problems can affect network performance and cost.
Knowing the disadvantages helps in choosing the right network design. It also prepares you for possible issues.
Complexity
Some network topologies are hard to set up. Complex layouts need careful planning and more parts. This can confuse people new to networking.
Complex networks take longer to connect and test. Mistakes in design can cause big problems later.
Maintenance Challenges
Keeping the network running is harder with some topologies. Troubleshooting issues can take more time. Finding the broken part is not always easy.
Maintenance needs skilled staff. Networks with many devices or connections need more work to fix problems.
Single Point Of Failure
Some topologies have one device or connection that controls the whole network. If this fails, the entire network can stop working.
This risk means the network is less reliable. Extra parts or backup systems are needed to avoid total failure.
Implementation Costs
Some network designs need many cables and devices. This increases the cost of setup. Expensive equipment can make the network costly.
Costs also rise with the need for special tools or expert installation. Budget limits can affect the choice of topology.
Choosing The Right Topology
Choosing the right network topology is key to building a strong network. It affects how devices connect and communicate.
Different topologies work better for different needs. Consider your network’s size, budget, and goals.
Network Size
The size of your network decides which topology fits best. Small networks need simple designs.
Large networks require more complex topologies to handle many devices and traffic.
- Small networks often use star or bus topologies
- Medium networks may use ring or mesh topologies
- Large networks benefit from hybrid or hierarchical topologies
Budget Considerations
Your budget limits the type of topology you can choose. Some topologies cost more to install.
Consider the cost of cables, devices, and maintenance before picking a topology.
- Bus topology is low cost but less reliable
- Star topology costs more but is easier to manage
- Mesh topology is expensive but offers high reliability
Purpose And Requirements
Think about what the network needs to do. Some topologies fit certain tasks better.
Choose a topology that supports your network’s speed, security, and data flow needs.
- Star topology is good for easy management and security
- Ring topology supports fast data transfer
- Mesh topology offers strong fault tolerance
Future Growth
Plan for future growth. Your network should handle more devices and data later.
Pick a topology that can expand without costly changes or downtime.
- Star topology allows easy addition of new devices
- Bus topology is harder to expand
- Hybrid topology supports scalable growth
Physical Vs Logical Topology
Network topology shows how devices connect in a network. It helps understand network setup and data flow.
Physical and logical topology are two ways to look at networks. They explain different network features.
Physical Layout
Physical topology means the real arrangement of cables and devices. It shows where devices sit in the network.
Common physical topologies include star, bus, ring, and mesh. Each has a unique wiring setup.
- Star: devices connect to a central hub
- Bus: all devices share one cable
- Ring: devices connect in a circle
- Mesh: devices connect to many others
Data Flow Patterns
Logical topology shows how data moves through the network. It focuses on the path data takes.
Data flow can follow different patterns like broadcast, unicast, or multicast. This affects network speed and control.
- Broadcast: data goes to all devices
- Unicast: data goes to one device
- Multicast: data goes to a group
Impact On Network Design
Physical and logical topologies shape network performance and reliability. Designers choose them to fit needs.
Good design balances cost, speed, and fault tolerance. Some layouts are easier to fix or expand than others.
- Star is easy to manage but needs more cables
- Bus is cheap but can slow with many devices
- Ring sends data quickly but a break stops flow
- Mesh is strong but costly and complex

Credit: 8grams.medium.com
Common Network Devices
Network devices connect computers and other devices in a network. They help data move from one place to another.
Each device has a special role to make the network work well. Knowing these devices helps understand network basics.
Switches
Switches connect devices in a local network. They send data only to the device it is meant for.
Switches reduce network traffic by managing data paths. They work at the data link layer of the network.
- Connect multiple devices in a network
- Send data directly to the right device
- Improve network speed and efficiency
Routers
Routers connect different networks, like your home to the internet. They decide the best path for data.
They work at the network layer and can also provide security and manage traffic.
- Connect multiple networks together
- Route data between networks
- Provide security features like firewalls
Hubs
Hubs connect several devices in a network. They send data to all devices, not just one.
Hubs work at the physical layer and are less efficient than switches because they do not filter data.
- Connect devices in a network
- Broadcast data to all connected devices
- Simple and cheap but less secure
Bridges
Bridges connect two or more network segments. They help divide a large network into smaller parts.
Bridges filter data and reduce traffic by sending data only to the needed segment.
- Connect different parts of a network
- Filter data to reduce traffic
- Work at the data link layer
Topology Trends And Innovations
Network topology is how devices connect and communicate. New trends change how networks work.
Innovations improve network speed, security, and flexibility. Let’s explore some key trends.
Wireless Topologies
Wireless topologies use radio waves to link devices. They remove the need for cables.
New wireless topologies support more devices with better speed. Mesh networks are popular now.
- Mesh networks connect devices directly to many nodes
- Star topology is common in Wi-Fi setups
- Ad hoc networks allow devices to connect without a router
Software-defined Networking
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) separates control from hardware. It lets admins manage networks from one place.
SDN improves network flexibility and reduces costs. It helps quickly adapt to changes in demand.
- Central control simplifies network management
- Easy to add or remove devices
- Improves security with quick updates
Cloud-based Networks
Cloud networks use internet servers to run network services. This reduces the need for physical hardware.
Cloud networks offer scalability. They grow or shrink based on user needs without extra equipment.
- Easy access from anywhere
- Cost-effective for small and large businesses
- Supports remote work and mobile devices
Credit: networkingwithjenish.hashnode.dev
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Network Topology In Simple Terms?
Network topology is the layout pattern of interconnected devices in a network. It defines how devices communicate and share data efficiently.
Which Are The Common Types Of Network Topology?
Common types include bus, star, ring, mesh, and hybrid topologies. Each has unique benefits and use cases for different networks.
How Does Network Topology Affect Performance?
Topology influences data flow, speed, and fault tolerance. A well-chosen topology improves reliability and reduces network congestion.
What Is The Best Network Topology For Small Businesses?
Star topology is ideal for small businesses. It offers easy management, scalability, and fault isolation for reliable connections.
Conclusion
Understanding network topology is crucial for setting up efficient networks. Each type—star, ring, bus, and mesh—offers unique benefits. They cater to different needs and environments. Choosing the right topology impacts performance. It also influences network maintenance. Always consider scalability and cost-effectiveness.
Whether managing a small business or a large organization, topology knowledge is essential. It aids in making informed decisions. Simplified network management begins with the basics. Keep exploring and learning. Your network’s success depends on it.
19 min read