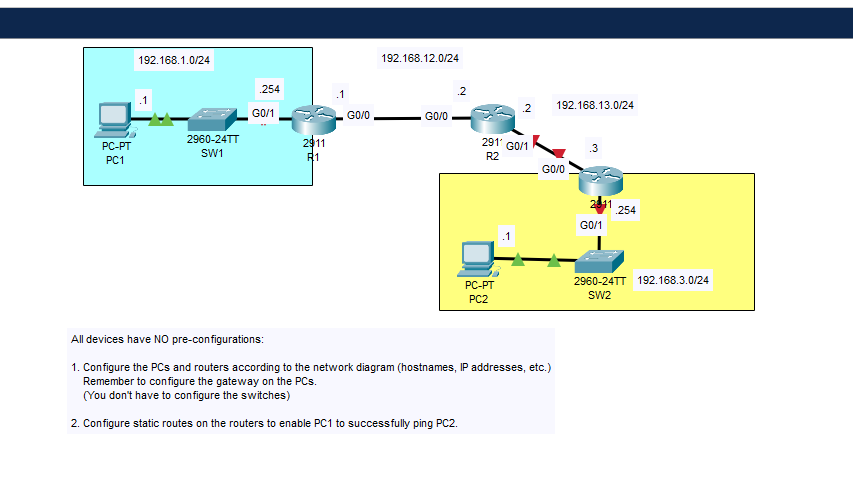
Are you struggling to control how your network directs traffic? Setting static routes on your router can be the simple solution you need.
By defining fixed paths for data to travel, you gain more control, improve network efficiency, and avoid unwanted delays. You’ll learn exactly how to set up static routes step-by-step, so your network runs smoother and faster. Keep reading—you’ll soon discover how this small change can make a big difference in your network’s performance.

Credit: manuals.plus
Basics Of Static Routing
Static routing is a simple way to tell a router where to send data. You set fixed paths manually.
This method helps control traffic in small or stable networks. It uses less processing power than dynamic routing.
What Is A Static Route
A static route is a specific path set by a network administrator. It tells the router exactly where to send packets.
This route does not change unless the admin updates it. It works by defining the destination and the next hop address.
Static Vs Dynamic Routing
Static routing uses fixed paths set by a person. Dynamic routing finds paths automatically using protocols.
Static routes are simple and use less CPU. Dynamic routes adjust to network changes but need more resources.
- Static routing: manual setup, stable paths
- Dynamic routing: automatic updates, flexible paths
- Static is good for small or simple networks
- Dynamic suits large or changing networks
When To Use Static Routes
Use static routes when your network is small and does not change often. They keep routing simple.
They work well for default routes and backup paths. Static routes also help secure network paths.
- Small networks with few routers
- Routes to specific devices or networks
- Backup routes for failover
- When you want full control over routing
Preparing Your Router
Setting static routes helps control how your network traffic moves. Before adding routes, you must prepare your router.
This preparation makes sure the router accepts new settings and works correctly.
Accessing Router Settings
You need to enter your router’s settings page to change routes. Usually, this is done through a web browser.
Type your router’s IP address in the browser’s address bar. This opens the login page.
- Find the router’s IP address (often 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1)
- Use the correct username and password to log in
- Look for sections like “Routing” or “Advanced Settings”
Identifying Network Interfaces
Network interfaces connect your router to other devices. You must know which interface to use for each route.
Interfaces often have names or labels like “eth0” or “WAN.”
- Look for interface names in the router’s settings
- Check which interface connects to your local network
- Note the interface that links to the internet or other networks
Gathering Necessary Information
Before setting static routes, collect all needed information. This helps avoid errors.
You will need the destination network, subnet mask, and gateway address.
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
| Destination Network | The IP range you want to reach |
| Subnet Mask | Defines the size of the network |
| Gateway | The IP address to send traffic through |
Configuring Static Routes
Static routes tell a router where to send network traffic. They are fixed paths set by the user.
Configuring static routes helps control traffic flow and improves network management.
Command Line Configuration
Using the command line interface (CLI) is a common way to set static routes. It gives direct control over the router.
You enter commands that specify the destination network and the next hop or exit interface.
- Access the router’s CLI via console or SSH
- Enter global configuration mode
- Use the command:
ip route [destination] [mask] [next-hop] - Save the configuration to keep changes after reboot
Using Router Gui
Many routers have a graphical user interface (GUI) for easier configuration. It uses menus and forms.
You can add static routes by filling in the destination and gateway details in the route settings page.
- Log in to the router’s web interface
- Navigate to routing or static route section
- Click to add a new static route
- Enter destination network, subnet mask, and next hop
- Save and apply the changes
Verifying Route Entries
After setting static routes, verify they are active and correct. This avoids routing errors.
Use commands or GUI tools to check the routing table and confirm entries.
- On CLI, use
show ip routeto view routes - Look for your static route in the routing table
- Check the next hop and interface for accuracy
- In the GUI, find the routing table or status page
- Confirm the static routes appear and are enabled

Credit: avocado89.medium.com
Troubleshooting Static Routes
Static routes help direct traffic in a network. Sometimes, these routes stop working or cause issues. Troubleshooting static routes finds and fixes these problems.
Understanding common errors and testing connections helps keep networks running smoothly. Diagnostic tools also assist in identifying route problems quickly.
Common Configuration Errors
Many static route issues come from simple mistakes in configuration. These errors stop the router from sending data the right way.
- Wrong destination network or subnet mask
- Incorrect next-hop IP address
- Missing or incorrect interface assignment
- Overlapping routes causing conflicts
- Routes not saved after configuration
Double-check each setting carefully. Save your changes and verify the route exists in the routing table.
Testing Route Connectivity
Testing shows if static routes send data properly. Use simple commands to check connectivity and find breaks.
- Ping the next-hop IP to verify it is reachable
- Trace the path to the destination network
- Check the routing table for your static routes
- Verify interface status and IP addresses
If pings fail, check cables and device power. If routes are missing, reconfigure them carefully.
Using Diagnostic Tools
Diagnostic tools give detailed information about routes and connections. These tools help find where data is blocked.
- Use traceroute to see each hop on the path
- Check routing table with show commands
- Use debug commands to watch routing updates
- Review logs for error messages
Run these tools during tests to quickly spot and fix issues with static routes.
Advanced Static Routing Tips
Static routing helps direct traffic in a network using fixed paths. It is simple but needs careful setup for complex networks.
Advanced tips improve how routers handle static routes. These tips help keep networks efficient and secure.
Route Prioritization
Routers use metrics to choose the best path. Lower metric routes get priority over higher ones.
Set metrics carefully when adding static routes. This ensures traffic uses the best available route.
- Assign lower metrics to main routes
- Use higher metrics for backup routes
- Check metric values to avoid conflicts
Handling Multiple Static Routes
Networks often need more than one static route. Manage these routes to avoid loops and confusion.
Use clear network addresses and subnet masks. This keeps routes unique and easy to manage.
- Use specific routes for smaller networks
- Use summary routes to reduce routing entries
- Keep route tables organized and updated
Security Considerations
Static routes can expose your network if not secured. Protect routers and routes from unauthorized changes.
Limit access to router settings. Use strong passwords and encryption for remote management.
- Disable unused router interfaces
- Use access control lists (ACLs) to restrict traffic
- Regularly update router firmware
Maintaining Static Routes
Static routes help direct network traffic through fixed paths. Keeping these routes updated ensures network stability and performance.
Regular maintenance avoids errors and keeps your router running smoothly. It is important to manage static routes carefully.
Updating Routes
Update routes when network changes occur. This keeps data flowing through the correct paths.
Remove old routes that no longer apply. Add new routes for added devices or network segments.
- Check routing tables regularly
- Edit routes to match network updates
- Test routes after changes
Backing Up Configurations
Save router settings before making changes. Backups help restore routes if errors happen.
Store backups on secure devices. Update backups after route updates to keep them current.
- Create backups after every major change
- Use secure storage for backup files
- Test backup files by restoring in a safe environment
Monitoring Network Performance
Watch network traffic and response times. Monitoring helps spot route problems early.
Use tools to track packet loss and delays. Fix routes that cause slow or dropped connections.
- Monitor traffic flow regularly
- Check for unusual delays or drops
- Adjust static routes to improve speed

Credit: www.youtube.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is A Static Route On A Router?
A static route is a manually configured network route. It directs data packets to a specific destination through a predetermined path. Static routes are useful in smaller networks where fewer paths are required. They offer predictable routing behavior without the need for dynamic routing protocols.
Why Use Static Routes In Networking?
Static routes provide control and predictability over data paths. They are ideal for simple, stable networks with limited routes. Using static routes can reduce resource consumption compared to dynamic routing. They allow network administrators to dictate exact paths for data, ensuring efficient and secure routing.
How Do I Configure A Static Route?
To configure a static route, access your router’s interface. Enter the destination network, subnet mask, and next-hop address. Save the configuration to apply changes. Each router model may have different steps, so consult your router’s manual for specific instructions. Always verify the route is functioning correctly after setup.
What Are The Benefits Of Static Routing?
Static routing offers simplicity, minimal resource usage, and enhanced security. It eliminates the need for complex routing protocols. Static routes are easy to configure and maintain. They provide consistent routing paths, which can prevent routing loops. Static routing is suitable for small, stable networks with predictable traffic patterns.
Conclusion
Setting static routes on a router helps direct network traffic clearly. It improves network control and reduces errors. Static routes are easy to set and maintain. They work well in small or simple networks. Understanding how to add and manage routes saves time.
Keep your network organized and efficient with static routes. Practice regularly to gain confidence and avoid mistakes. This skill supports better communication between devices. Try setting routes step-by-step to see results. Small efforts lead to smoother network performance.
16 min read