Imagine trying to find a friend’s house without knowing their address. That’s what your devices face without proper network name resolution.
If you want your computers, phones, and other gadgets to talk to each other smoothly, setting up network name resolution is key. This simple step can save you from endless frustration and speed up your online tasks. Ready to make your network smarter and faster?
Keep reading, and you’ll learn exactly how to set it up with ease.
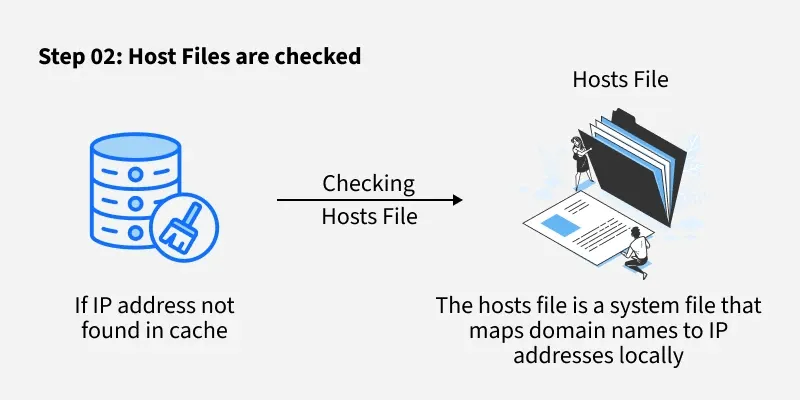
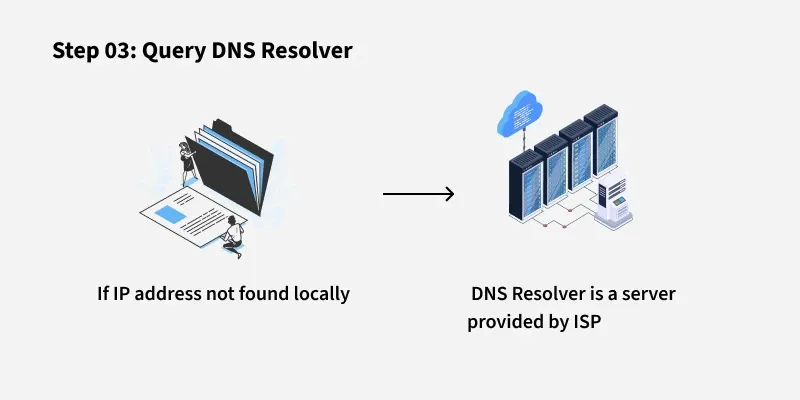
Credit: www.geeksforgeeks.org
Choosing The Right Naming System
Network name resolution helps computers find each other on a network. Choosing the right system makes this process easy and fast.
There are different naming systems to pick from. Each works best in certain situations.
Dns Vs. Hosts File
DNS is a server-based system that translates names to IP addresses. It works well for large networks and the internet.
The hosts file is a simple text file on each computer. It maps names to IP addresses locally without a server.
- DNS updates automatically for many devices
- Hosts file requires manual changes on each device
- DNS is better for big or changing networks
- Hosts file suits small, stable networks
When To Use Mdns
mDNS stands for multicast DNS. It helps devices find each other without a central server.
Use mDNS in small or home networks. It works well for printers, smart devices, and local sharing.
- Works without a DNS server
- Good for zero-configuration networks
- Devices advertise their names automatically
- Not ideal for large or complex networks
Selecting Naming Conventions
Good naming rules make it easy to find devices. Use clear and consistent names.
Include location, device type, or function in names. Avoid spaces and special characters.
- Use short, simple words
- Keep names unique on the network
- Use hyphens or underscores to separate words
- Stick to a pattern for all devices
Credit: medium.com
Configuring Dns Servers
DNS servers help computers find websites and services on a network. Setting them up correctly ensures smooth name resolution.
This guide explains how to configure DNS servers for your network name resolution.
Primary And Secondary Servers
The primary DNS server holds the main copy of zone data. It answers most DNS queries directly.
The secondary DNS server keeps a backup copy. It helps if the primary server is down.
- Primary server stores original zone files
- Secondary server copies data from primary
- Secondary improves reliability and load balancing
- Both servers work together to serve DNS requests
Forwarders And Root Hints
Forwarders send DNS queries to another server when they cannot resolve a name. This reduces your server’s workload.
Root hints help your DNS server find root servers on the internet. They are used if no forwarders are set.
- Use forwarders to improve query speed
- Root hints allow querying outside your network
- Forwarders reduce internet traffic from your server
- Root hints are essential for new DNS servers
Setting Up Zones And Records
Zones divide the DNS namespace. Each zone holds DNS records for a part of your network.
Records map names to IP addresses and other data. They tell DNS servers how to respond to queries.
- Zones organize your DNS data logically
- A records link hostnames to IPv4 addresses
- AAAA records link hostnames to IPv6 addresses
- CNAME records create aliases for hostnames
- MX records define mail servers for domains
Optimizing Network Settings
Network name resolution helps devices find each other by name. Optimizing these settings keeps your network fast and reliable.
Proper setup reduces delays and avoids conflicts in connecting devices. This guide covers key steps to improve name resolution.
Configuring Dhcp For Name Resolution
DHCP assigns IP addresses and can update name records automatically. This makes it easier for devices to locate each other.
Enable dynamic DNS updates in DHCP settings. This ensures host names and IP addresses stay synchronized.
- Set DHCP to update DNS records for clients
- Use secure updates to prevent wrong entries
- Choose appropriate lease times to balance updates
Managing Ttl Values
TTL (Time to Live) controls how long name records stay valid. Shorter TTL means faster updates but more queries.
Set TTL based on how often devices change IP addresses. Use longer TTL for stable networks to reduce traffic.
- Low TTL for mobile or dynamic devices
- High TTL for servers and fixed devices
- Balance TTL to improve performance and accuracy
Handling Caching And Replication
Caching stores name records to speed up lookups. Replication copies records between servers to keep data consistent.
Clear caches regularly to avoid stale data. Set replication intervals to update all servers quickly but avoid overload.
- Use cache expiration to keep data fresh
- Schedule replication during low network use
- Monitor cache hit rates and replication success
Troubleshooting Name Resolution Issues
Name resolution is key for network communication. It translates domain names into IP addresses.
When name resolution fails, network tasks stop working. Troubleshooting helps find and fix these issues.
Common Dns Errors
DNS errors stop devices from finding web addresses. These errors can be simple or complex.
- DNS server not responding
- Domain name not found
- Timeout waiting for DNS reply
- Incorrect DNS settings
- DNS cache corruption
Check these errors first to understand the problem. Fixing them restores normal network use.
Using Diagnostic Tools
Diagnostic tools help find where name resolution fails. They show details about DNS queries.
- Ping tests network reachability of IP addresses.
- Nslookup checks DNS records for domain names.
- Tracert traces the path to a network host.
- IPConfig shows current DNS server settings.
- Wireshark captures network packets for deep analysis.
Use these tools to detect DNS problems quickly. They guide you to the source of errors.
Resolving Conflicts And Loops
Conflicts and loops disrupt name resolution. They cause repeated requests and slow networks.
- Check for duplicate DNS entries in your server.
- Avoid circular DNS forwarding between servers.
- Clear DNS caches to remove stale data.
- Ensure only one DHCP server assigns DNS settings.
- Update firmware and software to fix bugs.
Fixing these issues stops loops and conflicts. This improves network speed and reliability.
Security Considerations
Network name resolution is critical for connecting devices. Protecting it keeps your network safe.
Security helps stop attackers from redirecting traffic or stealing data.
Preventing Dns Spoofing
DNS spoofing tricks users by sending false address information. This can lead to fake websites.
Use trusted DNS servers and secure network settings to reduce spoofing risks.
- Use encrypted connections like DNS over HTTPS
- Keep DNS software updated
- Limit who can query your DNS servers
- Check DNS responses for unusual changes
Implementing Dnssec
DNSSEC adds digital signatures to DNS data. This proves the data is real and not changed.
It stops attackers from sending fake DNS answers. Many DNS providers support DNSSEC today.
- Enable DNSSEC on your domain
- Verify DNSSEC signatures in your resolvers
- Regularly check DNSSEC status and keys
Access Controls And Monitoring
Control who can access your DNS servers. Limit access to trusted users and devices.
Monitor DNS logs to find unusual queries or attacks. Early detection helps prevent damage.
- Use firewalls to restrict DNS server access
- Set strong authentication for DNS management
- Log DNS queries and review them regularly
- Alert on suspicious DNS activities
Credit: medium.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Network Name Resolution?
Network name resolution is the process of converting human-friendly domain names into IP addresses. This is essential for computers to locate and communicate with each other on the internet. It typically involves DNS servers that map domain names to their respective IP addresses, enabling seamless connectivity and interaction.
Why Is Dns Important In Name Resolution?
DNS is crucial because it translates domain names into IP addresses. This translation allows users to access websites without memorizing numerical IP addresses. By converting easy-to-remember domain names into machine-readable IP addresses, DNS facilitates efficient internet navigation and connectivity, enhancing user experience and network communication.
How Does Dns Caching Improve Performance?
DNS caching temporarily stores DNS query results, reducing the need to repeatedly query DNS servers. This speeds up the loading time of frequently visited websites and decreases network congestion. By minimizing DNS lookups, caching enhances browsing speed and efficiency, providing a smoother and faster internet experience.
Can I Manually Configure Dns Settings?
Yes, you can manually configure DNS settings on your devices. This involves entering preferred DNS server addresses in the network settings. Custom DNS configurations can improve security, enhance privacy, and potentially increase browsing speed. Many users opt for public DNS providers like Google DNS or Cloudflare for these benefits.
Conclusion
Setting up network name resolution helps devices find each other fast. It keeps your network running smoothly and saves time. Clear names mean less confusion and fewer errors. Use simple, reliable methods for the best results. Check your settings often to avoid problems.
A good setup supports all users and devices well. Small steps now prevent big issues later. Trust the process and enjoy a stable network.
15 min read