Have you ever wondered how your devices get an IP address automatically when you connect to a network? The answer lies in something called a DHCP lease.
Understanding what a network DHCP lease is can help you grasp how your internet connection works and why sometimes your devices might lose connectivity. You’ll discover exactly what a DHCP lease is, why it matters for your devices, and how it affects your network experience.
Keep reading, and you’ll gain simple yet powerful knowledge to take control of your network like a pro.

Credit: www.vsolcn.com
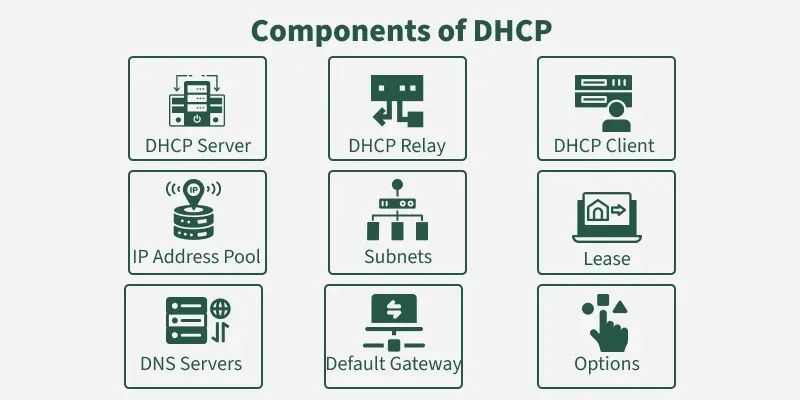
Dhcp Lease Basics
DHCP lease is a key part of how networks give devices IP addresses. It controls how long a device keeps an IP address.
This helps devices connect to the internet without conflicts or errors. Understanding DHCP leases is useful for managing networks.
What Dhcp Lease Means
A DHCP lease is a temporary IP address given to a device. The lease has a set time limit before it expires.
When the lease ends, the device must get a new IP address or renew the old one. This prevents IP conflicts on the network.
- Lease time is set by the network administrator
- Devices must renew leases to keep their IP addresses
- Expired leases free up IP addresses for other devices
How Dhcp Assigns Ip Addresses
DHCP assigns IP addresses automatically when a device joins the network. It uses a process called DHCP handshake.
The device asks for an IP address, and the DHCP server offers one. The device accepts the offer and gets the IP address.
- Device sends a request to the DHCP server
- Server offers an available IP address
- Device accepts the IP address offer
- Server confirms and starts the lease timer

Credit: shilpathota.medium.com
Lease Duration And Renewal
Network DHCP lease controls how long a device can use an IP address. It sets a time limit for the assigned address.
The lease must be renewed before it expires. This keeps the device connected to the network smoothly.
Typical Lease Times
Lease times vary depending on the network setup. Common lease durations range from a few minutes to several days.
Short leases suit busy networks with many devices. Longer leases work well for stable connections.
- Home networks often use lease times of 24 hours
- Public Wi-Fi may have leases as short as 30 minutes
- Corporate networks can set leases for several days
Process Of Lease Renewal
The device asks to renew its IP lease halfway through the lease time. This is called the renewal time.
If the renewal request is accepted, the lease time resets. The device keeps using the same IP address.
- Device sends a renewal request to the DHCP server
- Server approves and extends the lease duration
- Device continues using its assigned IP address
Impact Of Lease Expiry
If the lease expires without renewal, the device must get a new IP address. This can cause brief network loss.
Expired leases free up IP addresses for other devices. This helps manage limited IP resources efficiently.
- Device loses current IP address after lease expiry
- It requests a new IP address from the DHCP server
- Network connection may drop during this process
Dhcp Lease Types
DHCP lease is a temporary IP address given to a device on a network. It helps devices communicate easily without manual setup.
There are different types of DHCP leases. Each type controls how IP addresses are assigned and managed.
Dynamic Leases
Dynamic leases assign IP addresses from a pool for a limited time. The address can change after the lease expires.
This type works well for devices that connect and disconnect often. It saves IP addresses by reusing them.
- IP addresses are temporary
- Addresses come from a shared pool
- Leases have expiration times
- Devices must renew leases to keep IP
Static Leases
Static leases assign a fixed IP address to a device. The address does not change over time.
This type is used for devices needing a constant address. Examples include printers and servers.
- IP addresses stay the same
- Assigned based on device MAC address
- Useful for network devices that need stability
Automatic Leases
Automatic leases assign an IP address permanently from the pool. The device keeps the same address every time.
This type is a mix between dynamic and static leases. It gives a fixed address but uses the pool for allocation.
- IP assigned once from the pool
- Device keeps the address indefinitely
- Simplifies management without manual setup
Managing Ip Addresses With Dhcp
DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. It helps assign IP addresses automatically to devices on a network.
The DHCP lease is the time a device can use an IP address. It manages how devices connect smoothly.
Ip Pool Configuration
The IP pool is a range of addresses DHCP can give to devices. It must be set carefully to cover all devices.
Network admins set the start and end IP address in the pool. This controls which addresses are available.
- Choose a range that fits your network size
- Exclude addresses used by fixed devices
- Keep the pool within your subnet
Avoiding Ip Conflicts
IP conflicts happen if two devices share the same address. This causes connection problems on the network.
DHCP prevents conflicts by tracking leases and giving unique IPs. It also removes addresses from the pool when in use.
- Set DHCP to check if an IP is in use before assigning
- Reserve static IPs outside the DHCP pool
- Monitor network for devices with fixed IPs
Tracking Lease Assignments
Tracking leases helps know which IP is given to which device. It shows lease time and device details.
This data helps find network issues and plan for more devices. Admins can see when leases expire and renew them.
| Device Name | IP Address | Lease Start | Lease End |
|---|---|---|---|
| Office-PC | 192.168.1.10 | 2024-06-01 08:00 | 2024-06-01 20:00 |
| Printer | 192.168.1.15 | 2024-06-01 09:00 | 2024-06-01 21:00 |
| Smartphone | 192.168.1.20 | 2024-06-01 07:30 | 2024-06-01 19:30 |
Troubleshooting Dhcp Lease Issues
DHCP lease problems can cause network devices to lose connection. Understanding lease issues helps keep networks running smoothly.
This guide covers common DHCP lease problems, tools for monitoring leases, and steps to fix conflicts.
Common Lease Problems
DHCP lease issues happen when devices cannot get or keep an IP address. This causes loss of internet or local network access.
Some frequent problems include expired leases, duplicate IP addresses, and devices stuck with old leases.
- Expired DHCP leases prevent devices from renewing IP addresses.
- Duplicate IP addresses cause network conflicts and errors.
- Leases stuck on a device block new devices from joining.
- Incorrect lease time settings can cause frequent disconnections.
Tools For Dhcp Monitoring
Monitoring DHCP leases helps spot problems early. Several tools show active leases and device details.
Network admins use these tools to check lease status and troubleshoot issues faster.
- DHCP Server Logs: Track lease assignments and errors.
- IP Address Management (IPAM) Software: Visualizes lease distribution and conflicts.
- Command Line Tools: Use commands like
ipconfigordhcpdumpto view leases. - Network Monitoring Systems: Alert admins to lease problems in real-time.
Steps To Resolve Lease Conflicts
Lease conflicts occur when two devices share the same IP address. Fixing conflicts restores network access.
Follow these steps to clear conflicts and prevent them from returning.
- Identify the conflicting IP address from DHCP logs or error messages.
- Release the IP address on one device using network settings or command line.
- Clear the DHCP lease from the server or reset the DHCP service.
- Restart the affected devices to request new IP addresses.
- Adjust DHCP lease time to reduce overlap and conflicts.
- Reserve IP addresses for important devices to avoid duplicates.
Security Considerations
Network DHCP leases assign IP addresses to devices automatically. This process helps devices connect to the network easily.
Security is important because unauthorized access can happen through DHCP leases. Protecting these leases keeps the network safe.
Risks Of Unauthorized Leases
Unauthorized devices can get IP addresses if DHCP is not secure. These devices may cause network problems or steal data.
Attackers can use fake DHCP leases to intercept traffic or launch attacks. This puts user data and network resources at risk.
- Network disruptions from unknown devices
- Data interception and spying
- Spread of malware or viruses
- Loss of control over network resources
Securing Dhcp Servers
Keeping DHCP servers secure stops unauthorized devices from joining the network. Use strong settings and controls.
Regularly check DHCP logs to find strange activity. Limit which devices can get leases by using filters or authentication.
- Use MAC address filtering to allow known devices only
- Set lease times to expire quickly for better control
- Enable DHCP snooping on network switches
- Keep DHCP server software updated with patches
- Monitor logs for unusual lease assignments
Credit: helpdeskgeek.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is A Dhcp Lease In Networking?
A DHCP lease is a temporary IP address assignment by a DHCP server. It allows devices to connect to a network without manual IP configuration. The lease has a time limit, after which the device must renew it to maintain network access.
How Does Dhcp Lease Time Affect Network Devices?
DHCP lease time determines how long a device keeps its IP address. Short leases free up IPs quickly for new devices. Long leases reduce network traffic but limit IP availability. Proper lease time balances network stability and efficiency.
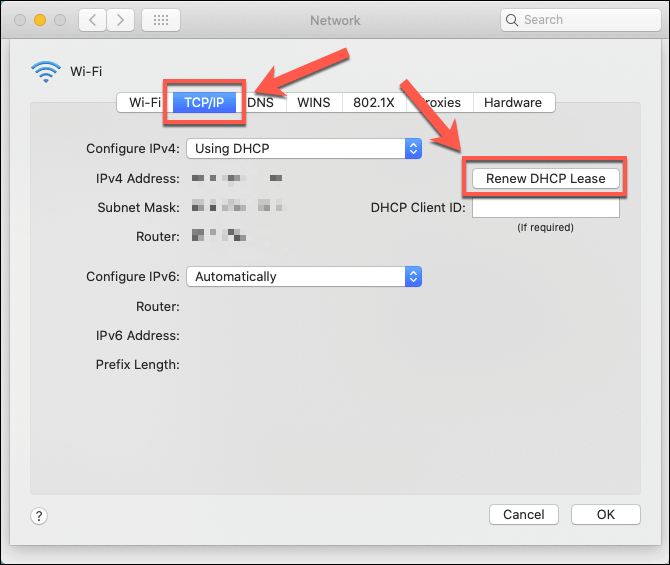
Can A Dhcp Lease Be Manually Renewed?
Yes, DHCP leases can be manually renewed by devices. This process requests a fresh IP assignment from the DHCP server. Renewing helps maintain uninterrupted network access and can resolve connectivity issues without restarting the device.
What Happens When A Dhcp Lease Expires?
When a DHCP lease expires, the device must request a new IP address. If not renewed, the device loses network access. The DHCP server can assign the same or a new IP based on availability and network policies.
Conclusion
Understanding DHCP leases helps manage network resources effectively. It simplifies IP address distribution. This reduces manual errors. DHCP lease ensures devices stay connected. It maintains network efficiency. Network administrators gain control over IP usage. This prevents conflicts and enhances security.
Regular monitoring of DHCP leases is important. It supports smooth network operations. Users enjoy seamless connectivity. Businesses benefit from optimized network performance. Remember, efficient DHCP management is crucial. It impacts overall network health. Keep your network running smoothly.
17 min read