Are you struggling to decide between Wired Ethernet and Powerline for your home network? Choosing the right connection can make a huge difference in your internet speed, reliability, and overall experience.
You want a setup that feels fast, stable, and hassle-free—but how do you know which option fits your needs best? This article breaks down the key differences so you can make a smart choice that keeps your devices running smoothly without frustration.
Keep reading to find out which connection type will power your internet the way you want it.
Wired Ethernet Basics
Wired Ethernet is a common way to connect devices to the internet or a network. It uses cables to send data between devices.
This method is known for fast and stable internet connections. Many homes and offices use wired Ethernet for their networks.
How Ethernet Works
Ethernet sends data using cables called twisted pair or fiber optic cables. Devices connect to a router or switch through these cables.
Data travels in small packets. Ethernet controls how these packets move to avoid collisions and errors.
Common Ethernet Standards
Ethernet has different standards that define speed and cable type. These standards help devices work well together.
- 10BASE-T: 10 Mbps speed using twisted pair cables
- 100BASE-TX: 100 Mbps speed, often called Fast Ethernet
- 1000BASE-T: 1 Gbps speed, known as Gigabit Ethernet
- 10GBASE-T: 10 Gbps speed for high-demand networks
Typical Use Cases
Wired Ethernet works well where fast and steady internet is needed. It is common in homes, offices, and data centers.
- Connecting desktop computers to the internet
- Linking office printers and servers
- Streaming high-quality video without lag
- Gaming setups that need low delay
- Data centers that handle large amounts of data
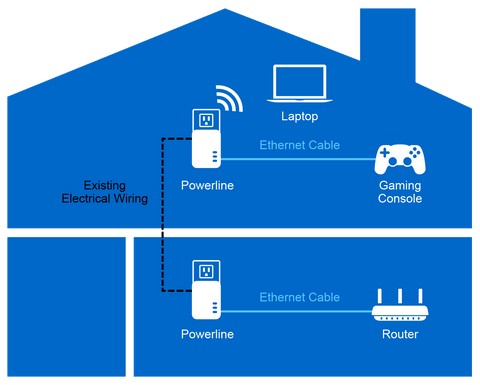
Powerline Networking Essentials
Powerline networking uses your home’s electrical wiring to send internet signals. It helps connect devices without new cables.
This method works well where Wi-Fi is weak or running Ethernet cables is hard. It is simple and uses existing outlets.
Powerline Technology Explained
Powerline adapters plug into electrical outlets. They send data through your home’s wiring to create a network.
The adapters usually come in pairs or sets. One connects to your router, the others connect to your devices.
- Uses your home’s electrical wiring for internet signals
- Adapters plug into standard power outlets
- Creates a network without new cables
- Works best on the same electrical circuit
Popular Powerline Adapters
Many brands offer powerline adapters with different speeds and features. Some have extra Ethernet ports.
Look for adapters with good speed ratings and easy setup. Some models also support Wi-Fi access points.
- Adapters with speeds from 500 Mbps to 2000 Mbps
- Models with one or more Ethernet ports
- Adapters that include Wi-Fi hotspots
- Plug-and-play design for easy setup
When To Choose Powerline
Choose powerline when Wi-Fi signals are weak in some rooms. It helps bring internet without running cables.
Powerline works well in older homes or places with thick walls. It is also good if you want stable wired connections.
- When Wi-Fi coverage is poor in parts of your home
- If running Ethernet cables is difficult or expensive
- For stable wired connections to devices like TVs or game consoles
- In homes with thick walls or large spaces
Speed Comparison
Choosing between wired Ethernet and powerline adapters affects your internet speed. Both options offer different speeds depending on conditions.
Understanding their speed limits helps you pick the best setup for your needs.
Maximum Throughput Limits
Wired Ethernet cables can support very high speeds. Common cables like Cat5e can handle up to 1 Gbps, while Cat6 and above can reach 10 Gbps.
Powerline adapters use your home’s electrical wiring to send data. Their speeds depend on the adapter model, usually ranging from 200 Mbps to 2 Gbps.
- Ethernet supports up to 10 Gbps with good cables
- Powerline adapters range from 200 Mbps to 2 Gbps
- Powerline max speed depends on adapter generation
Real-world Performance
Ethernet usually delivers speeds close to its maximum limits. It offers stable and fast connections with low delay.
Powerline adapters often perform slower than their rated speed. Electrical noise and wiring quality reduce actual speed.
- Ethernet gives steady, high-speed connections
- Powerline speed varies by house wiring condition
- Powerline may have occasional drops or delays
Factors Affecting Speed
Ethernet speed depends on cable type and length. Using older cables or long runs can reduce speed.
Powerline speed depends on electrical wiring, interference, and distance between adapters. Devices like microwaves can cause interference.
- Ethernet speed affected by cable quality and length
- Powerline affected by wiring, electrical noise, and distance
- Interference from appliances reduces powerline speed

Credit: www.makeuseof.com
Reliability Factors
Choosing between wired Ethernet and powerline adapters depends on how reliable the connection is. Reliability means the signal stays strong and steady.
We will look at signal stability, interference issues, and connection consistency for both options.
Signal Stability
Wired Ethernet gives a stable signal because it uses cables directly connected to devices. The signal does not drop easily.
Powerline adapters send data through electrical wiring. The signal can weaken if the wiring is old or damaged.
Interference Issues
Ethernet cables are shielded and do not face much interference. This makes the connection clearer and faster.
Powerline signals can face interference from other electrical devices. Appliances like microwaves or vacuum cleaners can cause disruptions.
- Ethernet cables avoid interference by using physical wires
- Powerline depends on electrical wiring quality
- Other devices on the same circuit can create noise
Connection Consistency
Wired Ethernet offers consistent speeds because the connection is direct and dedicated.
Powerline connections may change speed based on the electrical load and wiring layout. Speeds can vary during the day.
- Ethernet connections stay steady over time
- Powerline speeds can drop when many devices use power
- Distance between powerline adapters affects performance
Installation And Setup
Setting up a wired Ethernet or powerline network affects your home internet. Both have different steps and tools.
Choosing the right setup depends on your skills and the space where you want internet access.
Ease Of Setup
Wired Ethernet setup needs running cables from the router to devices. This may take time and effort.
Powerline adapters use your home’s electrical wiring. Plug them in, and the setup is usually quick and simple.
- Wired Ethernet offers stable connections but can be hard to install.
- Powerline adapters are easier to install but can be affected by wiring quality.
Cable And Adapter Requirements
Wired Ethernet needs Ethernet cables (Cat5e, Cat6, or higher) and possibly wall jacks. You also need tools for cable management.
Powerline setups require at least two powerline adapters. They plug into power outlets and connect to your router and device with short Ethernet cables.
- Ethernet cables come in different categories for speed and distance.
- Powerline adapters must be compatible and support your internet speed.
- Adapters should be plugged directly into wall sockets, not power strips.
Troubleshooting Tips
Check all cable connections for wired Ethernet. Loose cables cause no or poor connection.
For powerline, test adapters in different outlets. Electrical noise can affect signal strength.
- Restart your router and devices to reset connections.
- Use shorter cables to avoid signal loss in Ethernet setups.
- Avoid plugging powerline adapters into surge protectors or extension cords.
- Update adapter firmware if available.

Credit: www.truecable.com
Cost Considerations
Choosing between wired Ethernet and powerline depends on costs. Knowing the expenses helps you decide which fits your budget.
This guide looks at the main costs of each option. It covers initial payment, upkeep, and overall value.
Initial Investment
Wired Ethernet needs cables and sometimes extra tools. You may also pay for professional installation.
Powerline adapters cost money but are easy to set up. You only need to plug them into outlets.
- Ethernet cables vary in price by length and quality
- Powerline adapter kits include two devices
- Installation costs for Ethernet can increase total expenses
- Powerline has no installation fees
Long-term Maintenance
Ethernet cables usually last a long time with little care. You might need to replace damaged cables.
Powerline adapters rely on your home’s electrical system. Electrical problems can affect performance and may need fixes.
- Ethernet cables need occasional checking for wear
- Powerline adapters may need replacement if technology changes
- Electrical wiring issues can increase powerline maintenance costs
Value For Money
Ethernet offers stable and fast connections. It often gives better performance for the price.
Powerline adapters provide convenience. They are good if running cables is hard or expensive.
| Option | Strength | Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Wired Ethernet | Reliable speed | Higher setup effort |
| Powerline | Easy setup | Variable speed depending on wiring |
Best Use Scenarios
Wired Ethernet and Powerline are two ways to connect devices to the internet. Each has its own strengths. Choosing the right one depends on your space and needs.
Knowing the best use for each can help you get a faster and more stable connection. Let’s look at where Ethernet and Powerline work best.
Ideal Environments For Ethernet
Ethernet works best in places with easy access to cable runs. It needs a direct wire connection from the router to the device.
This setup is great for offices, homes with new wiring, or rooms close to the router. It gives the fastest and most stable internet.
- Offices with structured cable systems
- Homes with walls that allow cable installation
- Rooms near the router or network switch
- Places needing low lag for gaming or streaming
Optimal Conditions For Powerline
Powerline uses your home’s electrical wiring to send internet signals. It works well when running Ethernet cables is hard.
Powerline adapters perform best in homes with simple wiring and fewer electrical devices that cause interference.
- Homes where cables are difficult to install
- Buildings with consistent electrical wiring
- Rooms far from the router without cable access
- Users needing easy setup without drilling walls
Hybrid Network Solutions
A hybrid network uses both Ethernet and Powerline. It fits homes or offices with mixed wiring and room layouts.
This approach gives flexibility. Use Ethernet for devices needing speed. Use Powerline where cables can’t reach easily.
- Large homes with many rooms
- Offices with some cable access and some wireless needs
- Places wanting a balance of speed and convenience
- Users who want a backup connection option

Credit: www.makeuseof.com
Future Trends
Wired Ethernet and Powerline networks both have unique strengths. Their future depends on new technology and user needs.
Understanding future trends helps choose the right network for home or office use.
Advancements In Ethernet Tech
Ethernet technology keeps improving with faster speeds and better reliability. New standards like 2.5G and 10G Ethernet are becoming more common.
These speeds support high-demand uses like gaming, streaming, and large data transfers.
- Higher data rates up to 100 Gbps
- Improved cable designs for less interference
- Better energy efficiency with low-power modes
- Integration with smart home systems
Innovations In Powerline
Powerline networking uses electrical wiring to send data. New standards like G.hn improve speed and stability.
These updates reduce interference and increase range, making Powerline better for larger homes and offices.
- Speeds reaching up to 2 Gbps
- Enhanced noise filtering for clear signals
- Better support for multiple devices
- Improved security features
Emerging Alternatives
New network options are appearing alongside Ethernet and Powerline. These include mesh Wi-Fi and fiber optic cables.
Each option fits different needs, such as wireless convenience or ultra-fast data transfer.
- Mesh Wi-Fi offers wide wireless coverage
- Fiber optics provide very high speeds over long distances
- MoCA uses coaxial cables for stable connections
- 5G home internet adds wireless mobility
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Wired Ethernet?
Wired Ethernet is a network connection using physical cables. It provides fast and stable internet. It’s often preferred for tasks requiring high-speed data transfer and low latency. Wired Ethernet is commonly used in gaming and professional environments. It’s reliable but requires physical cabling between devices and routers.
How Does Powerline Networking Work?
Powerline networking uses your home’s electrical wiring for internet connectivity. It enables data transmission through power outlets. This solution is convenient for areas with limited Wi-Fi coverage. Powerline adapters are plugged into outlets, connecting them to the network. It’s ideal for extending internet access without additional cabling.
Is Wired Ethernet Faster Than Powerline?
Yes, Wired Ethernet generally offers faster speeds than Powerline. Ethernet connections provide consistent and high-speed data transfer. Powerline speeds can vary due to electrical interference and wiring quality. For bandwidth-intensive activities like gaming or streaming, Ethernet is usually the better choice.
It ensures optimal performance and reliability.
Can Powerline Replace Wi-fi?
Powerline can complement Wi-Fi but not replace it entirely. It’s useful for extending network coverage in areas with weak Wi-Fi. Powerline provides a stable connection through electrical wiring. However, Wi-Fi offers more flexibility for mobile devices. Both technologies can work together to enhance home networking.
Conclusion
Choosing between wired Ethernet and powerline depends on your needs. Wired Ethernet offers fast and stable connections. Powerline is easier to set up and uses existing wiring. Both have limits in speed and range. Think about your space and device locations.
For gaming or streaming, wired Ethernet works best. For casual browsing, powerline can be enough. Weigh speed, convenience, and cost before deciding. Your home setup guides the right choice. Simple steps lead to better internet at home.
21 min read