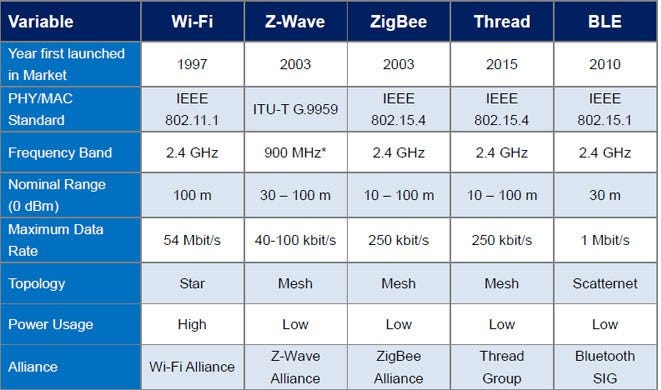
Are you trying to decide between Zigbee and Wi-Fi for your smart home or IoT projects? Choosing the right wireless technology can feel confusing, especially when both promise strong connections and convenience.
But what if understanding their key differences could save you time, money, and frustration? You’ll discover how Zigbee and Wi-Fi stack up in terms of speed, range, power use, and security. By the end, you’ll know exactly which one fits your needs best—and make a confident choice for your devices.
Keep reading to unlock the facts that matter most to you.

Credit: www.mokosmart.com
Zigbee Basics
Zigbee is a wireless communication standard. It is used for short-range connections between devices.
Zigbee is popular in smart homes and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. It is energy efficient and simple to use.
How Zigbee Works
Zigbee connects devices in a mesh network. Each device can send and receive data to others nearby.
This mesh system helps signals travel farther. It also makes the network more reliable.
- Devices communicate using low power radio waves.
- Each device acts as a repeater to extend range.
- Networks can have many devices working together.
Key Features
Zigbee uses low power, which helps devices run longer on batteries. It works well for small data packets.
Zigbee supports many devices in one network. It has strong security to keep data safe.
- Low energy use for longer battery life
- Supports up to 65,000 devices in a network
- Strong encryption for secure communication
- Fast connection setup and low latency
Common Use Cases
Zigbee is often used in smart lighting systems. It controls lights wirelessly and can create schedules.
Zigbee is also common in home security devices and smart thermostats. It helps these devices communicate efficiently.
- Smart home lighting control
- Security sensors and alarms
- Smart thermostats and climate control
- Remote control of appliances
Wi-fi Essentials
Wi-Fi is a wireless technology that connects devices to the internet. It uses radio waves to send data.
Many homes and businesses use Wi-Fi for fast internet access. It supports many devices at once.
Wi-fi Technology Explained
Wi-Fi works by sending data through radio signals. Devices connect to a router or access point.
It uses different frequency bands, mainly 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. These bands carry data at different speeds.
- 2.4 GHz band covers longer distances but is slower
- 5 GHz band is faster but covers shorter distances
- Wi-Fi uses standards like 802.11n, 802.11ac, and 802.11ax
Core Features
Wi-Fi allows multiple devices to connect to a single network. It supports high data speeds for internet use.
Security options like WPA2 and WPA3 keep networks safe. Wi-Fi also supports roaming between access points.
- High data transfer rates up to several gigabits per second
- Supports many devices simultaneously
- Encryption standards for secure connections
- Easy setup and broad device compatibility
Typical Applications
Wi-Fi is common in homes, offices, and public places. It connects smartphones, laptops, and smart home devices.
It is used for streaming videos, online gaming, video calls, and internet browsing. Wi-Fi supports high bandwidth needs.
- Home internet access for multiple devices
- Office networks for computers and printers
- Public Wi-Fi hotspots in cafes and airports
- Smart TVs, security cameras, and smart speakers
Range And Coverage
Range and coverage are important when choosing between Zigbee and Wi-Fi. They affect how far devices can connect and work together.
Understanding their differences helps place devices properly for the best performance.
Zigbee Range Capabilities
Zigbee usually works well within 10 to 100 meters indoors. Its range depends on obstacles like walls and furniture.
Zigbee uses a mesh network. This means devices can pass signals to each other to extend coverage.
- Typical indoor range: 10-20 meters per device
- Outdoor range can reach up to 100 meters
- Mesh network extends overall coverage
Wi-fi Coverage Limits
Wi-Fi usually covers 30 to 50 meters indoors. Walls and floors reduce its signal strength.
Wi-Fi uses a star network. Devices connect directly to the router or access point.
- Indoor range: about 30-50 meters
- Outdoor range can reach 100 meters or more
- Signal weakens with obstacles and distance
Impact On Device Placement
Zigbee devices can be placed farther apart if they form a mesh. This helps cover larger areas.
Wi-Fi devices need to be closer to the router. Signal boosters can help in bigger spaces.
- Zigbee mesh allows flexible device placement
- Wi-Fi needs devices near the router
- Obstacles reduce both Zigbee and Wi-Fi range
Power Consumption
Power consumption is important for smart devices. It affects battery life and energy costs.
Zigbee and Wi-Fi use power differently. Understanding this helps choose the right technology.
Zigbee Energy Efficiency
Zigbee uses very little power. It is made for small devices that need long battery life.
Zigbee devices sleep most of the time. They only wake up to send or receive data.
- Low power use extends battery life
- Good for sensors and small gadgets
- Works well in large networks with many devices
Wi-fi Power Usage
Wi-Fi uses more power than Zigbee. It keeps devices connected and ready all the time.
This high power use suits devices that need fast data and constant internet access.
- Consumes more battery in mobile devices
- Best for streaming and large data transfers
- Needs stronger power sources or frequent charging
Battery Life Considerations
Battery life depends on how much power a device uses. Zigbee usually lasts longer on batteries.
Wi-Fi devices need bigger batteries or regular charging. This limits their use in small gadgets.
- Zigbee suits devices needing months or years of battery life
- Wi-Fi suits devices with easy access to power
- Choose based on how often you can charge or replace batteries
Network Scalability
Network scalability is how well a network grows as more devices join. It is important for smart homes and businesses.
Zigbee and Wi-Fi handle device numbers and expansion differently. This affects which one fits your needs.
Zigbee Device Capacity
Zigbee supports many devices in one network. It uses a mesh network to connect devices efficiently.
A Zigbee network can hold up to 65,000 devices. This makes it good for large smart systems.
- Devices connect through other devices in the mesh
- Each device helps extend the network range
- Network grows without losing performance
Wi-fi Network Limits
Wi-Fi networks usually support fewer devices than Zigbee. Most home routers handle 20 to 50 devices.
Wi-Fi uses a star network, where all devices connect to one router. This can limit scalability.
- Too many devices can slow down Wi-Fi speed
- Router hardware limits maximum device count
- Network range depends on router strength
Managing Large Networks
Zigbee networks manage large groups by routing messages through many devices. This keeps communication smooth.
Wi-Fi networks need strong routers or multiple access points to handle many devices. This can add cost and complexity.
- Zigbee’s mesh design improves reliability as more devices join
- Wi-Fi requires extra hardware for bigger networks
- Both need careful setup to avoid interference and slowdowns
Security Features
Security is very important for smart home devices. It helps keep your data safe and private.
Zigbee and Wi-Fi use different ways to protect your devices. Let’s look at their security features.
Zigbee Security Protocols
Zigbee uses strong security rules to protect device communication. It focuses on low power and short range.
Zigbee has built-in encryption and authentication. This stops unwanted devices from joining the network.
- Uses AES-128 encryption for data protection
- Requires device authentication before joining
- Supports network key updates for safety
- Offers message integrity checks
Wi-fi Security Standards
Wi-Fi uses several security standards to keep connections safe. These include WPA, WPA2, and WPA3.
WPA3 is the newest standard. It has better encryption and protects against password guessing.
- WPA2 uses AES encryption for strong security
- WPA3 adds protection for weak passwords
- Supports secure key exchange methods
- Helps prevent eavesdropping on data
Protecting Smart Devices
To keep smart devices safe, use strong passwords and update software often. This reduces hacking risks.
Use network security features and limit device access. Monitor devices to catch unusual behavior early.
- Set unique, strong passwords for devices
- Keep device software and firmware updated
- Use network encryption and firewalls
- Turn off devices when not in use
- Check device activity regularly
Data Speed And Latency
Data speed and latency are important when choosing wireless technology. They affect how fast devices send and receive information.
Zigbee and Wi-Fi have different strengths in speed and latency. These differences impact their use in smart devices.
Zigbee Data Rates
Zigbee offers data rates up to 250 kbps. This speed suits small data packets in home automation.
Its low data rate helps save power and reduces network congestion. This is good for battery-powered devices.
- Maximum speed: 250 kbps
- Optimized for small data packets
- Low power use
- Good for sensor data and controls
Wi-fi Speed Advantages
Wi-Fi supports much higher speeds, from 54 Mbps to over 1 Gbps. It handles large data and video streams well.
Wi-Fi has lower latency than Zigbee in many cases. This means faster response times for devices.
- Speeds range from 54 Mbps to 1+ Gbps
- Supports high data traffic
- Lower latency for quick responses
- Good for video and internet access
Effect On Smart Applications
Zigbee works well with simple smart devices. It handles commands and sensor data with low power use.
Wi-Fi suits devices needing fast data and video. It supports smart cameras and streaming devices.
| Technology | Best Use | Speed | Latency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zigbee | Simple sensors, controls | Up to 250 kbps | Moderate |
| Wi-Fi | Video, internet devices | 54 Mbps to 1+ Gbps | Low |

Credit: www.link-labs.com
Interference And Reliability
Both Zigbee and Wi-Fi face challenges with interference that affect their reliability. Understanding how each handles interference helps in choosing the right technology.
Interference can cause connection drops and slow data transfer. It is important for devices to maintain stable connections for better performance.
Zigbee Interference Handling
Zigbee works on the 2.4 GHz band but uses a mesh network to reduce interference. It automatically switches channels to avoid noisy frequencies.
This network design helps Zigbee devices keep a strong connection, even in busy wireless environments.
- Uses mesh topology for better coverage
- Automatically changes channels to avoid noise
- Consumes less power, reducing signal issues
Wi-fi Signal Stability
Wi-Fi also uses 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. The 5 GHz band has less interference but shorter range.
Wi-Fi signals can weaken due to walls, other devices, and distance from the router.
- 5 GHz band offers faster speeds but less range
- Signal strength drops with obstacles and distance
- Interference from many devices can cause slowdowns
Ensuring Consistent Connectivity
Both Zigbee and Wi-Fi need good setup to stay reliable. Placing devices carefully reduces interference.
Regular updates and using quality equipment help keep connections stable and strong.
- Place devices away from metal and walls
- Update firmware to fix bugs and improve performance
- Use repeaters or extenders if needed
Setup And Compatibility
Zigbee and Wi-Fi are common wireless options for smart devices. Each has different setup steps and works with various gadgets.
Understanding their setup and compatibility helps you pick the right system for your needs.
Installing Zigbee Devices
Zigbee devices need a hub or gateway to connect to your network. The hub talks to all Zigbee devices in your home.
Adding new Zigbee gadgets usually involves pressing a button on the device and the hub. The devices join the network quickly.
- Plug in and set up the Zigbee hub first
- Put devices in pairing mode
- Use the hub app to add devices
- Place devices within range of the hub
Wi-fi Device Integration
Wi-Fi devices connect directly to your home Wi-Fi router. They do not need an extra hub or gateway.
To set up, you use the device app to find your Wi-Fi and enter the password. Devices join the network over your router.
- Ensure your Wi-Fi network is stable
- Use the device app to scan for Wi-Fi
- Enter your Wi-Fi password
- Wait for the device to connect
Cross-platform Support
Zigbee devices often work with multiple brands if they use the same hub or standard. This makes them flexible across platforms.
Wi-Fi devices usually connect to apps or services that support many brands. They rely on internet access to work across platforms.
| Feature | Zigbee | Wi-Fi |
|---|---|---|
| Works with many brands | Yes, via hubs | Yes, via internet apps |
| Needs hub or gateway | Yes | No |
| Device-to-device connection | Yes, mesh network | No |
| Internet required for control | Optional | Yes |
Cost Factors
Choosing between Zigbee and Wi-Fi depends on costs. Both have different price points for devices and equipment.
Understanding the cost factors helps you pick the best option for your needs.
Zigbee Device Pricing
Zigbee devices usually cost less than Wi-Fi devices. They are designed for simple communication and low power use.
Many Zigbee sensors and switches are affordable, making them good for large smart home systems.
- Zigbee bulbs often cost less than Wi-Fi bulbs
- Basic Zigbee sensors have low prices
- Devices use less power, lowering running costs
Wi-fi Equipment Costs
Wi-Fi devices can be more expensive due to their advanced features. They also need stronger routers and access points.
The cost for Wi-Fi equipment can rise quickly if you want wide coverage or many devices connected.
- Wi-Fi bulbs and cameras are often pricier
- Strong Wi-Fi routers can cost more upfront
- Extra access points add to total expenses
Long-term Investment
Zigbee saves money over time with lower power use and simpler devices. It suits users who want many connected items.
Wi-Fi may cost more but offers faster speeds and easier setup. It fits users needing high data use and fast control.
- Zigbee lowers electricity bills
- Wi-Fi needs more frequent upgrades
- Both need maintenance and device replacement
Choosing The Right Protocol
Zigbee and Wi-Fi are two common wireless protocols. Both help devices connect and communicate in smart homes and offices.
Choosing the right one depends on your needs like range, power use, and device type.
When To Pick Zigbee
Zigbee works well for many small devices that need low power. It forms a mesh network where devices help each other send data.
Choose Zigbee if you want to connect many devices spread across your home or office. It saves battery life and handles many devices easily.
- Use for smart lights, sensors, and switches
- Good for devices with limited battery
- Works well in large areas with many devices
- Mesh network improves signal range and reliability
When To Opt For Wi-fi
Wi-Fi is best for devices that need high speed and lots of data. It is common in smartphones, cameras, and computers.
Pick Wi-Fi if you want faster internet connection or if your devices already use Wi-Fi. It connects directly to your home router.
- Good for streaming devices and cameras
- Supports high data transfer rates
- Works well with existing home internet
- Needs more power than Zigbee
Hybrid Network Possibilities
You can use both Zigbee and Wi-Fi together. This allows devices to use the best protocol for their needs.
Smart hubs often link Zigbee devices to Wi-Fi. This way, you get good coverage and fast internet on the same network.
- Zigbee for low power, many sensors
- Wi-Fi for cameras and streaming
- Smart hubs connect both networks
- Improves overall device performance

Credit: www.reddit.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Main Difference Between Zigbee And Wi-fi?
Zigbee is designed for low-power, short-range communication, ideal for IoT devices. Wi-Fi offers higher data rates and broader coverage, suitable for internet access and media streaming. Zigbee is more energy-efficient, while Wi-Fi supports more bandwidth-intensive applications.
Is Zigbee More Secure Than Wi-fi?
Zigbee includes built-in security features like encryption and authentication to protect IoT networks. Wi-Fi also provides strong security measures, including WPA3 encryption. However, Zigbee is often considered more secure for IoT due to its focused design, while Wi-Fi security depends on correct configuration.
Can Zigbee And Wi-fi Coexist?
Yes, Zigbee and Wi-Fi can coexist without interference. Zigbee operates on the 2. 4 GHz band but uses a different protocol. Proper channel management and network planning help minimize potential interference, allowing both technologies to function efficiently in the same environment.
Which Is Better For Smart Home Devices?
Zigbee is often preferred for smart home devices due to its low power consumption and reliable mesh networking. It extends battery life and provides robust connectivity. Wi-Fi is suitable for high-data applications but may drain batteries faster in IoT devices compared to Zigbee.
Conclusion
Zigbee and Wi-Fi each serve different needs in smart homes. Zigbee uses less power and connects many devices easily. Wi-Fi offers faster speed and wider coverage. Choosing depends on your device type and home size. Think about battery life and signal strength too.
Both have strengths that help smart living. Decide what fits your setup best. Simple and clear choices make smart homes work well.
26 min read